
Update: This article was last updated on 30th September 2024 to reflect the accuracy and up-to-date information on the page.

Trends in higher education are rapidly transforming as global shifts in technology, culture, and society reshape the landscape. Universities and colleges are increasingly challenged to adapt to these changes while upholding their mission of providing quality education.
Digital transformation, such as the adoption of online learning platforms, virtual classrooms, and AI-driven educational tools, diversity initiatives, and evolving student needs are at the forefront, pushing institutions to innovate and remain relevant in the 21st century while preparing learners for a competitive and dynamic workforce.
Moonpreneur
Trends in higher education highlight the vital role that universities and colleges play in fostering educational excellence and workforce readiness by promoting diversity and inclusivity. While many institutions claimed a commitment to diversity, significant progress began in the 1980s, when students of color made up 17.33% of undergraduates. By 1996, that number increased to 29.6%, and by 2016, it rose to 45.2%, reflecting growing efforts to break barriers and provide equal opportunities for all students. The benefits of this diversity are evident in the enriched learning environment, increased cultural understanding, and the preparation of students for a globalized workforce.
Universities and colleges are at the forefront of several key trends that are shaping the future of higher education. They are impacting how institutions operate, how students learn, and how knowledge is shared, empowering them to lead the way in these transformative times.
Below are some of the most significant trends in higher education today:

Suggested Reading: Hillsborough County School District: Excellence in Education
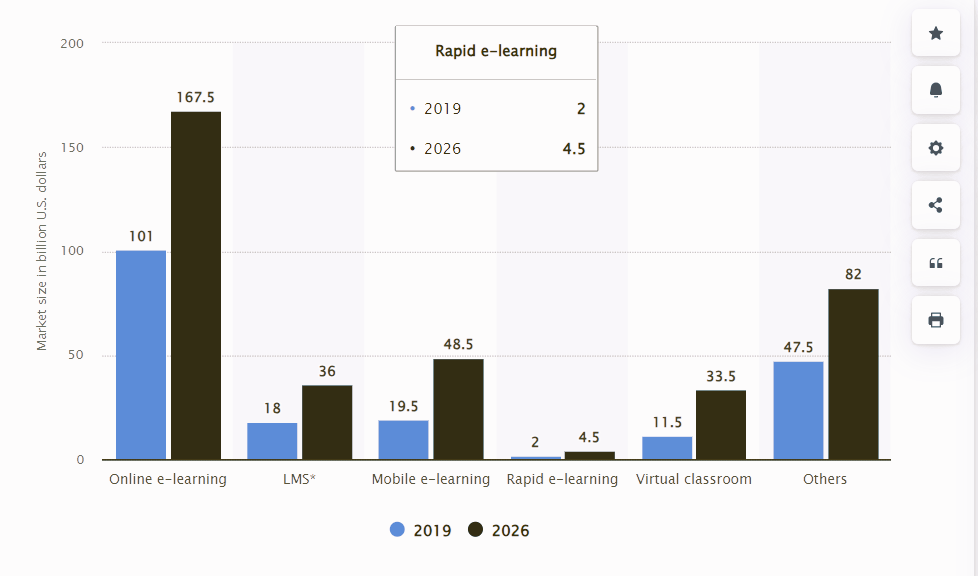
The rapid digitization of learning, one of the most prominent trends in higher education, has been significantly accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic. This global crisis has pushed institutions to swiftly develop or expand their digital infrastructure, leading to the popularity of hybrid and fully online programs. These programs offer flexibility to students who may not be able to attend traditional on-campus classes, making education more accessible in these challenging times.
Higher education trends are increasingly showcasing the rise of Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs), which are gaining traction and providing affordable and accessible learning opportunities worldwide. Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy have partnered with universities to offer accredited courses that cater to the needs of a diverse, global student body. The increased use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is revolutionizing the learning experience, enabling personalized education. This technological advancement offers an optimistic view of the future of learning, where students receive tailored learning paths and real-time feedback. Today, 55% of college students are Gen Z, a generation comfortable with technology. According to Pew Research, 95% of Gen Z students have smartphones, and 97% use at least one major online platform.

In response to a rapidly changing job market, there is a growing demand for micro-credentials—short, focused programs that allow learners to develop specific skills. These practical certifications, often referred to as “stackable credentials,” allow students and professionals to build a portfolio of competencies without committing to a full degree program, preparing them for the evolving job market.
Recommended Reading: 14 Education Stats for 2025 You Need To Know
This trend aligns with the increasing importance of lifelong learning, where individuals continue to upskill and reskill throughout their careers. Universities are responding by offering flexible, modular courses that can be combined to form comprehensive qualifications. This shift is particularly beneficial for working professionals who need to adapt to new technologies and industries, fostering a sense of adaptability and openness to change.

Technology trends in education play a vital role in a student’s life, as they are the future leaders who will tackle today’s global challenges—such as climate change and healthcare innovation. These challenges demand solutions that integrate multiple fields of expertise, making interdisciplinary studies more prominent in higher education.
Institutions are dismantling traditional academic silos to foster collaboration across diverse disciplines, merging areas like engineering with ethics and computer science with sociology. This interdisciplinary approach reshapes curricula, equipping students with the skills needed for real-world problem-solving. Additionally, universities are launching specialized programs that bridge fields, including bioinformatics, data science, and environmental studies, to combine knowledge from various domains effectively.

Suggested Reading: Beyond the Report Card: Rethinking Assessment in Education
Colleges and universities are at the forefront of the current trends in education, actively fostering diverse, equitable, and inclusive (DEI) learning environments in higher education. Their efforts to attract students from underrepresented groups, diversify their faculty and staff, and ensure that curricula incorporate a range of perspectives are shaping the future of education. This focus on DEI not only enriches the educational experience but also prepares all students for success in an increasingly diverse society.
Institutions are implementing initiatives to reduce systemic barriers and promote social justice, such as scholarships, mentorship programs, and support services for marginalized students. These efforts not only enrich campus culture but also make students feel valued and integral to the educational system, preparing them for success in diverse professional environments.
While many institutions long claimed a commitment to diversity, few fully embraced it early. The 1980s and 1990s were pivotal decades, with colleges beginning to expand opportunities for all students. This led to a significant rise in the percentage of students of color, from 17.33% in 1980 to 29.6% in 1996. By 2016, this figure reached 45.2%, showcasing the significant progress in diversification efforts (American Council on Education, 2019).
This progress is not just a statistic but a reflection of the growing recognition of the importance of creating inclusive and supportive educational environments. These environments are not just beneficial, but essential for the success and well-being of all students.

Higher education is becoming increasingly global, with universities forming international partnerships, encouraging student exchange programs, and promoting collaborative research across borders. This trend allows institutions to tap into a larger pool of resources and knowledge, fostering a more global perspective on education. This global perspective is not just a trend, but a necessity in today’s interconnected world, enlightening us and broadening our minds.
The rise of international branch campuses, where universities open satellite campuses abroad, is also a reflection of this trend. Such efforts aim to reach a broader audience of students and expand educational opportunities in emerging markets. The globalization of higher education is not just a trend, but a system that values and integrates students, helping them develop a deeper understanding of global issues and prepare for careers in an interconnected world.

As the urgency to address climate change grows, many higher education institutions are taking significant steps to reduce their environmental impact. These sustainability initiatives, increasingly common on campuses, are not just about carbon neutrality, waste reduction, and green building practices, but also about fostering a more hopeful and optimistic future for our planet.
Furthermore, sustainability is not just a part of the curriculum, but also a part of student life. With more programs focused on environmental science, renewable energy, and sustainable business practices, universities are empowering students to lead sustainability projects and research. This active involvement is crucial in preparing the next generation to take on the planet’s environmental challenges, thereby shaping a more sustainable future.

Data analytics is becoming a key tool in trends in early childhood education, enabling educators to make informed decisions based on child development, learning progress, and enrollment trends. Predictive analytics, for instance, can identify children who may need additional support and suggest targeted interventions to enhance early learning outcomes and improve long-term educational success.
There is a pressing need for accountability in higher education. Students, governments, and employers are increasingly scrutinizing the value of a degree, looking at factors such as graduation rates, job placement outcomes, and return on investment. Universities are responding by adopting more transparent metrics and focusing on delivering measurable results for their students.

Mental health has become a critical concern for colleges and universities, especially in the wake of the pandemic. The pressures of academic life, compounded by social, economic, and personal challenges, have led to a significant rise in mental health issues among students.
Given the rise in mental health issues among students, it is imperative for institutions to prioritize mental health services. They are responding by expanding these services, increasing access to counseling, and promoting a culture of well-being. Some schools are even going a step further by incorporating mindfulness programs, peer support groups, and stress management workshops to help students maintain mental and emotional balance.
Suggested Reading: Agora Cyber Charter School: A Deep Dive into Online Education in Pennsylvania
A study by the National Center for Education Statistics revealed that of the 20 million students enrolled in higher education institutions in 2019, 19.9 million faced mental health challenges (Imagine America Foundation, 2020). Issues such as depression, eating disorders, anxiety, addiction, and suicide are not isolated cases but prevalent among today’s college students. The American College Health Association (ACHA) reported that 60% of students experienced anxiety, while 40% dealt with depression (ACHA, 2019). These concerns are not just numbers but a pressing reality that students are increasingly finding difficult to ignore.

A nontraditional student is characterized as minimally nontraditional (one characteristic), moderately nontraditional (2 or 3 characteristics), or highly nontraditional (4 or more characteristics). The following are selected findings from the study.
Traditionally, college students were seen as 18- to 24-year-olds who went to school right after high school. However, after the 2008 Great Recession, many adults without higher education lost their jobs, and more people began returning to school to reskill or upskill. Colleges adapted to support these non-traditional students, including full-time workers, parents, and retirees. By 2015, 40% of undergraduates in the U.S. were non-traditional students.
Suggested Reading: Transitioning from Early Childhood Special Education to Kindergarten
Conclusion
The trends in higher education reflect broader shifts in society, technology, and the global economy. As universities and colleges continue to evolve, they are embracing digital transformation, promoting inclusivity, and playing a crucial role in addressing global challenges like sustainability and mental health. These trends not only reshape how education is delivered but also redefine the skills and knowledge students need to succeed in a rapidly changing world. Institutions that adapt to these trends will be better positioned to provide a relevant, impactful education that prepares students for the future, empowering policymakers to make a difference in these global challenges.
Moonpreneur is dedicated to transforming conventional education, preparing the next generation with comprehensive learning experiences. Our Innovator Program equips students with vital skills in AI/ML, Robotics, Coding, Game Development, and App Development, fostering entrepreneurship through hands-on learning. This initiative aims to cultivate the workforce of tomorrow by integrating innovative technologies and practical skills in school curriculums.
Register for a 60-minute free workshop today!























The integration of AR/VR technologies is enhancing experiential learning—from virtual labs to immersive simulations that bring concepts to life.
https://techpragna.com/