
Update: This article was last updated on 12th January 2026 to reflect the accuracy and up-to-date information on the page.
Micro:bit and Arduino are popular among kids for their do-it-yourself (DIY) electronics projects. Both micro:bit and Arduino provide users with a versatile and accessible way to experiment with coding and hardware, making them valuable tools for beginners and seasoned enthusiasts.
These two microcontrollers are ideal for little ones who enjoy fun gadgets, experiments, and games!

An study conducted by Discovery Research showed that 90% of students said the BBC micro:bit showed them anyone could code, while 86% of students said the BBC micro:bit made Computer Science more interesting for them.
 Source: Learning Development
Source: Learning Development
Let’s learn about these two platforms’ similarities, differences, strengths, and limitations and decide which is better for your kids.
1. Overview of micro:bit and Arduino:
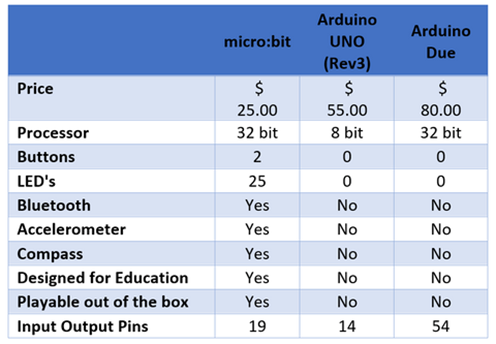
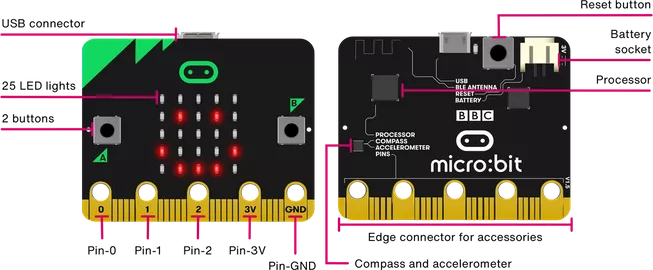
The micro:bit features a 5X5 LED grid, push buttons, a Micro-USB port, a magnetometer, and an accelerometer, with Bluetooth functionality. It offers more processing power and memory than Arduino, making it beginner-friendly for coding experiments, especially in education. Compatible with Python and JavaScript, it has a web-based interface, eliminating the need for downloads.
Source: microbit
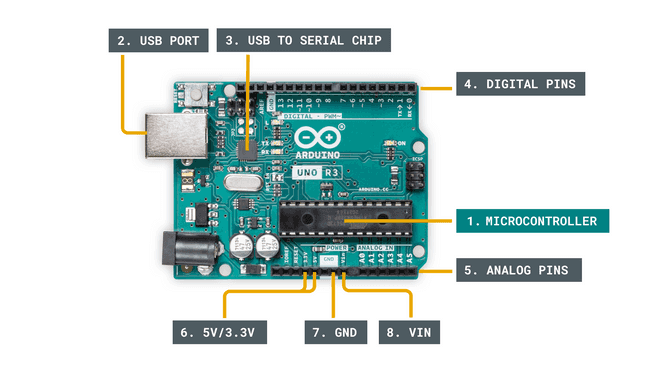
Arduino, on the other hand, has numerous input/output pins, offering vast connectivity possibilities with other electronic components. Its GPIO pins support both 3V and 5V logic levels, distinguishing it from the micro:bit. To program the Arduino, the Arduino IDE must be downloaded, and it employs C and C++ languages. With an emphasis on GPIO pins and a somewhat more intricate coding process, Arduino suits those delving into advanced electronics projects.
2. Ease of Use:
Both micro:bit and Arduino are suitable for beginners as they offer user-friendly environments.
For Micro:bit, simplicity is one of the critical strengths. It provides a block-based programming interface that allows users to drag and drop code blocks, making it easy for young learners to get started. Additionally, micro:bit supports various programming languages, including Python and JavaScript, offering a smooth transition to text-based coding.
Arduino’s programming environment is also beginner-friendly. It primarily utilizes a text-based language, similar to C++, called the Arduino programming language. This may present a steeper learning curve for novices. However, Arduino’s vast community support, extensive documentation, and numerous example projects make it easier to find solutions and learn from others’ experiences.
Moonpreneur
| Micro:bit and Arduino: Similarities |
|---|
|
3. Hardware Features
Micro:bit’s built-in features, including an LED matrix, buttons, and sensors, make it an all-in-one platform for fast and straightforward projects. The LED matrix allows for primary visual output, and the sensors enable interaction with the physical world without needing extra components.
Arduino boards offer extensive hardware capabilities. They can be connected to various sensors, actuators, and shields, providing immense flexibility for complex projects. Arduino’s modular nature empowers users to select the board that best suits their needs in size, processing power, and connectivity options.
4. Project Complexity
Micro:bit is perfect for beginners as it simplifies coding and electronics. It’s great for simple projects like temperature sensors, basic games, or LED matrix displays. However, its limited processing power and memory may limit more advanced projects.
Arduino, on the other hand, offers versatility and expandability. It’s suitable for projects ranging from simple to highly complex, such as home automation systems, robots, and interactive artwork. With powerful microcontrollers and extensive library support, Arduino enables ambitious undertakings in the DIY electronics realm.
5. Educational Applications
Both micro:bit and Arduino are widely used in educational settings.
Micro:bit’s user-friendly design, educational resources, and accessibility make it an excellent choice for introducing programming and electronics in classrooms. Its suitability for kids and educators is reflected in the availability of teaching materials and online support tailored specifically to its use.
Arduino’s popularity among educators stems from its robust ecosystem and educational resources. Its versatility allows for interdisciplinary projects, integrating science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) concepts. Arduino’s extensive community support and active forums enable educators to find inspiration, share ideas, and collaborate on educational projects.
| Micro:bit | Arduino | |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Micro:bit is a pocket-sized board for teaching coding and electronics. | Arduino is an open-source ecosystem with various board options. |
| Programming | Micro:bit uses a block-based programming interface. | Arduino primarily uses a text-based language called Arduino programming language. |
| Features | Micro:bit has built-in features like an LED matrix and sensors, suitable for simple projects. | Arduino boards offer extensive hardware capabilities for complex projects with multiple sensors, actuators, and shields. |
| Limitations | Micro:bit is limited in processing power and memory. | Arduino offers versatility for highly complex projects. |
| Price | Micro:bit is relatively affordable. | Arduino board prices vary based on models and features. |
6. Cost and Availability
Micro:bit is relatively affordable, making it an accessible option for individuals and educational institutions.
Arduino boards vary in price depending on the model and features. While some entry-level boards are budget-friendly, more advanced options with additional functionalities may be more expensive.
7. Community Support
The Micro:bit community is thriving, supported by dedicated educators, developers, and enthusiasts. The official website offers many resources, tutorials, and project ideas. Online forums and social media groups provide additional support.
Similarly, Arduino boasts a vast and established community. Its website features extensive documentation, tutorials, and a helpful forum, while its open-source ecosystem encourages collaboration, resulting in a vast library of open-source projects and contributed code.
8. Compatibility and Integration
Micro:bit is designed to be compatible with other devices and platforms. It can be easily integrated with smartphones, tablets, computers, and other microcontrollers.
Arduino’s wide range of libraries and modules ensures compatibility with various sensors, actuators, and communication protocols. It can interface with external devices and systems, making it suitable for integration into larger projects or existing setups.
Conclusion
Both micro:bit and Arduino offer unique strengths and benefits for DIY electronics projects. Micro:bit excels in simplicity, accessibility, and educational applications. This makes micro:bit a good choice for beginners and educational settings.
Conversely, Arduino provides versatility, expandability, and a robust community support system, making it ideal for more complex and ambitious projects.
Whether starting or looking for advanced capabilities, both platforms offer exciting opportunities for creativity and learning.
Moonpreneur is on a mission to disrupt traditional education and future-proof the next generation with holistic learning solutions. Its Innovator Program is building tomorrow’s workforce by training students in AI/ML, Robotics, Coding, IoT, and Apps, enabling entrepreneurship through experiential learning.
























With Arduino , there is a driver issue etc often for connecting it through the USB port. Micro bit is a bit better in that case. So for ease of use, micro bit is better IMHO
Which platform offers a more seamless entry point for young learners in terms of programming complexity?
So, what cool tricks can Micro:bit do for IoT and wearables?
Micro:bit shines in IoT and wearables with its built-in sensors like accelerometer and compass. Its Bluetooth connectivity enables seamless interaction with other devices, making it ideal for creating interactive wearables and IoT gadgets.