
Robots can accomplish anything from mopping and cleaning to harvesting and warehouse management. Can you guess who’s behind them? It’s the robotics engineers.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Robotics Engineer
| Task | Roles and Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| 1. Research and Development |
|
| 2. Design and Prototyping |
|
| 3. Construction and Configuration |
|
| 4. Testing and Debugging |
|
| 5. Installation and Operation |
|
| 6. Calibration and Maintenance |
|
| 7. Safety and Modification |
|
Who are Robotics Engineers?
Simply put, robotics engineers are the wizards who design, build, and maintain robots. They’re the brainpower behind the machines that help us in countless ways. These engineers blend science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) to bring robots to life.

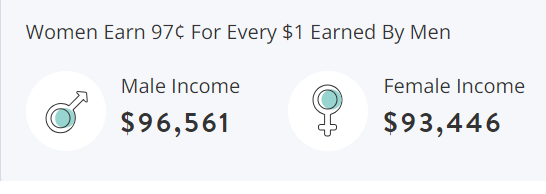
Source: zippia.com
Types of Engineers in the Field of Robotics
| Mechanical Engineering |
| Electrical Engineering |
| Electronics Engineering |
| Computer Science and Software Engineering |
| Control Systems Engineering |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) Engineering |
| Materials Engineering |
| Biomechanical Engineering |
| Aerospace Engineering |
| Industrial Engineering |
The Everyday Robots
Let’s take a moment to appreciate the robots we interact with on a regular basis:
1. Self-Driving Car
Imagine a car that drives itself! It’s not science fiction; it’s a reality thanks to robotics engineers. They create algorithms and systems that allow cars to perceive their environment and make decisions just like a human driver. Example: Tesla
2. Smartphones and Virtual Assistants

Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa – these friendly voices are powered by robotics and artificial intelligence. Engineers work tirelessly to improve their ability to understand and respond to our questions and commands.
3. Medical Robots
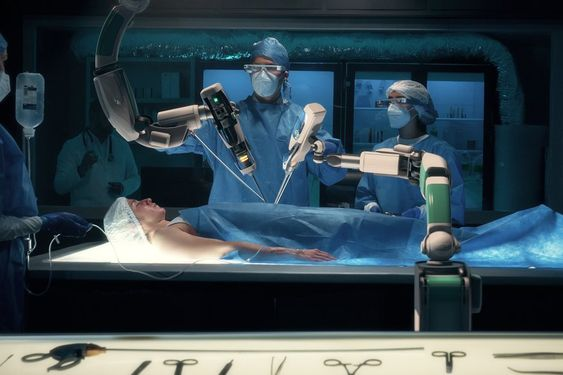
Robotic surgeons and assistants are revolutionizing the field of medicine. They help surgeons perform complex procedures with precision, reducing risks and improving patient outcomes.
4. Manufacturing Robots:
From assembling cars to packaging goods, robots have transformed the manufacturing industry. Robotics engineers create machines that work tirelessly, accurately, and efficiently, ultimately saving time and resources.
The Skills of a Robotics Engineer
To become a robotics engineer, one needs a mix of skills:
1. Programming: Knowing how to code is like speaking the language of robots. Engineers use languages like Python, C++, and Java to instruct robots on what to do.
2. Mathematics: Math is the backbone of robotics. Engineers use math to solve problems, analyze data, and design algorithms.
3. Mechanical and Electrical Engineering: Understanding how machines and circuits work is crucial. This knowledge helps engineers design the physical components of a robot.
4. Problem-Solving: Engineers are like puzzle solvers. They need to figure out how to make robots perform specific tasks efficiently and reliably.
The Future of Robotics
As technology advances, so does the role of robotics engineers. We can expect even more incredible robots to become a part of our lives. From household helpers to advanced medical devices, the possibilities are limitless.
Conclusion
Next time you encounter a robot, remember the hardworking engineers who made it possible. Robotics engineers are the unsung heroes of our modern world, shaping the future one robot at a time. Their dedication and innovation are the driving force behind the robots that make our lives easier, safer, and more enjoyable. So, here’s to the robots and the engineers who bring them to life!
Moonpreneur is on a mission to disrupt traditional education and future-proof the next generation with holistic learning solutions. Its Innovator Program is building tomorrow’s workforce by training students in AI/ML, Robotics, Coding, IoT, and Apps, enabling entrepreneurship through experiential learning.















What is the daily life of a robotic engineer?
Day-to-day duties of Robotics Engineer include building, configuring, and testing robots. Designing software systems to control their robotic systems, such as those robots used for manufacturing.