
Update: This article was last updated on 28th February 2024 to reflect the accuracy and up-to-date information on the page.
STEM and STEAM are not exactly very new ideas when you think about them. But of late, more and more people have started focusing on the importance of both. The concepts are considered unique and significant for comprehending and incorporating a diverse range of learning modalities.
Educators see these two concepts as something vital for catering to real-world issues. In the U.S. alone, more than 10 million people are working in the STEM field, representing the country’s 6.6% of the workforce. This fact alone testifies to the significance of STEM and STEAM in the career graph of any individual.
Leveraging STEAM enables teachers to adopt project-based learning. It transcends the five disciplines (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics) and paves the way for a welcoming learning experience.
Compared to conventional learning models, educators utilizing the STEAM framework merge diverse disciplines. They harness the collaboration between modeling procedures and mathematical and scientific concepts.
Before diving into which learning concept is better, you should know the difference between STEM and STEAM.
What is STEM?
STEM education, which includes math, science, technology, and engineering, gives professionals a variety of skills they need to succeed in the modern global market. This extensive curriculum includes subspecialties in statistics, biology, psychology, economics, agriculture, and aeronautics in addition to traditional topics. Because STEM disciplines are dynamic, employers want not only subject-specific expertise but also flexibility to meet changing needs.
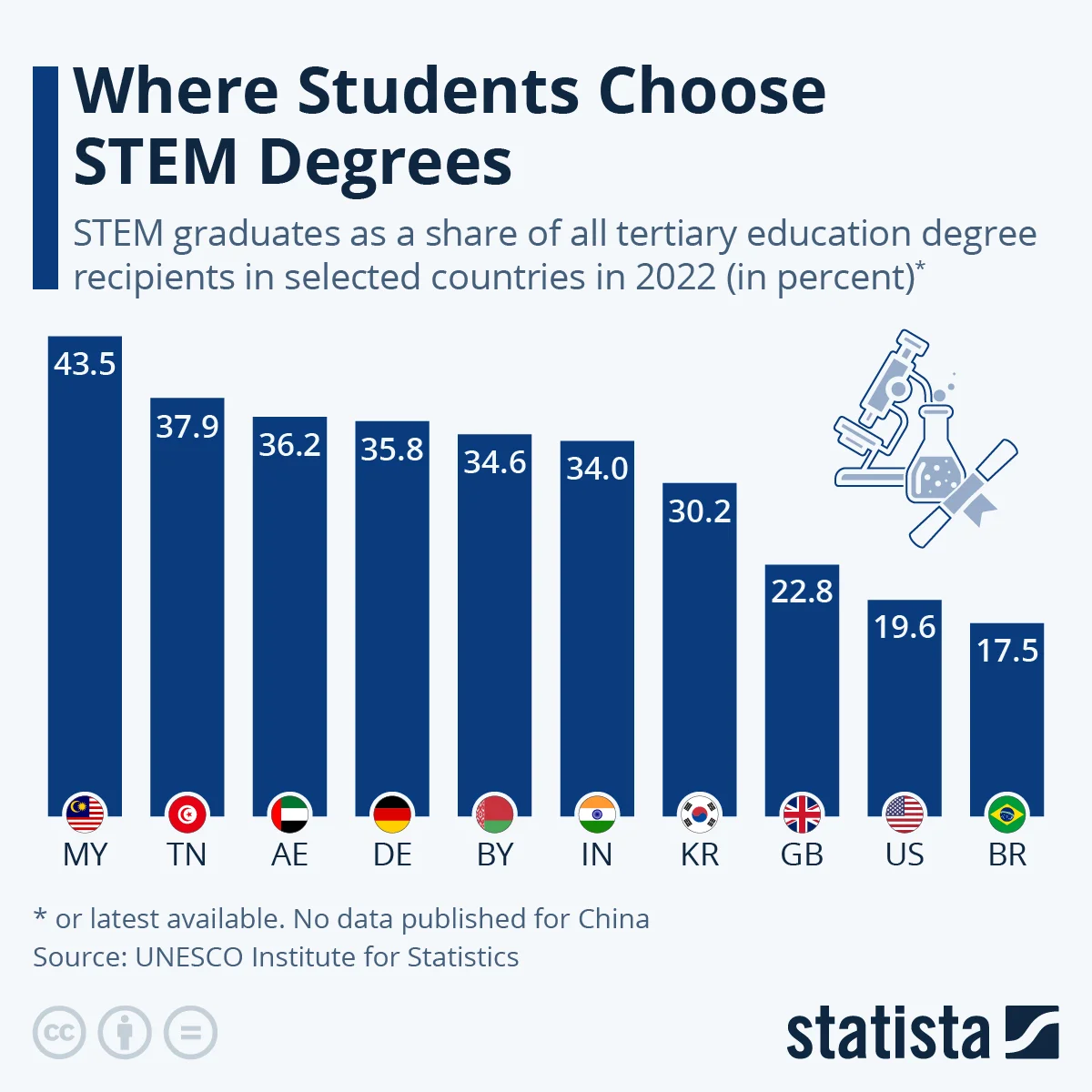
STEM graduates are in high demand worldwide but are not enough to meet needs. Countries are trying to increase the number of students in STEM to support growing industries like technology and healthcare. Malaysia and Tunisia have the highest percentages of STEM graduates, with about 40% to 43.5%. India also has a high number of STEM students, thanks to its large population. However, data for China is unclear, with different sources reporting varying numbers of graduates. Other countries like the United Arab Emirates, Germany, Belarus, and South Korea also have many STEM graduates. In contrast, Western Europe and the Americas have lower percentages of STEM graduates, showing how STEM education’s popularity varies around the world.
The constantly changing environment of STEM professions creates distinct obstacles despite the obvious benefits.
According to the National Bureau of Economic Research, the employment environment is always changing due to the rapid improvements in technology. Therefore, it is important to prioritize not just subject-specific knowledge but also the development of flexibility and well-roundedness, which are essential for adapting to changing conditions.
A workforce with the skills to drive innovation and address the challenges of the future labor market is fostered by STEM education, which is strategically matched with the changing demands of the global labor market.
What is STEAM?
A response to the growing focus on soft skills across industries, STEAM education seamlessly incorporates the arts into the STEM framework. According to The Conversation, creative abilities and an understanding of the arts, such as literature, history, and design, are crucial for encouraging STEM workers to solve problems creatively and innovatively.
The STEAM-focused curriculum broadens the scope of education by including the humanities, language arts, dance, theater, music, visual arts, design, and new media. In line with senior executives’ inclinations, this inclusive strategy not only addresses current workforce trends but also reflects their preference—57 percent of them place a higher value on soft skills than on hard abilities, as per a 2018 LinkedIn research. Furthermore, a 2019 LinkedIn research highlights the importance of creativity, persuasion, and teamwork by naming these as the top three abilities that employers look for in potential hires.
To develop a complete mind: Study the science of art; Study the art of science. Learn how to see. Realize that everything connects to everything else.
- Leonardo Da Vinci
In reality, several schools use the STEAM learning strategy to smoothly include the arts in STEM instruction. This all-encompassing approach guarantees that besides the core STEM courses, students receive training in the humanities, language arts, dance, theater, music, design, and new media. The deliberate blending of various fields is intended to improve students’ employability by offering a comprehensive skill set that strikes a balance between the technical expertise of STEM and the fundamental soft skills required by the contemporary workforce.
STEM vs. STEAM: How are they different?
The differences between STEM and STEAM are seen in how they handle scientific ideas. With an emphasis on hard scientific, technical, engineering, or mathematical abilities, STEM seeks to advance knowledge or provide novel ideas. On the other hand, STEAM, as mentioned by The Conversation, embraces a more comprehensive viewpoint by promoting the use of both hard and soft talents in problem-solving.
Collaboration is essential to understanding STEM ideas in STEAM education. By incorporating artistic concepts and practices, STEAM practitioners may use resources like fine art imagery and data visualization to improve students’ comprehension of science, math, and technology. STEAM experts may use 3D printers to create new goods or to simplify complicated data sets into readily understood formats like infographics by using this nontraditional approach to problem-solving.
To put it simply, STEM and STEAM are two different approaches to science. While STEM stresses using hard scientific skills to solve issues in the real world, STEAM uses both hard and soft talents to solve difficulties. People collaborate to comprehend STEM concepts within the STEAM framework, using tools such as data visualization to improve math and science comprehension. This kind of imaginative thinking not only encourages creativity but also helps to make difficult facts easier to understand.
Similarities between STEM and STEAM
Both STEM and STEAM value integration, which means they don’t teach each subject separately but focus on holistic education. This approach reflects how to solve real-life problems by considering all the different factors and looking at the problem as a whole.
By combining different skills, one can become a more proficient and capable individual.
Is STEAM better than STEM?
When it comes to the STEM vs STEAM debate, it’s important to recognize that there are opportunities for growth in science, tech, engineering, arts, and math fields.
Choosing between the two fields should be based on your individual skills, career aspirations, and interests. The emergence of STEAM has highlighted the importance of having a broad skill set that encompasses both hard skills and soft skills.
As projects become more complex and technology changes job roles, LinkedIn highlights the importance of soft skills training. Soft skills are essential for success in an era of AI and technology where machines can’t replicate human qualities such as leadership and collaboration.
Many STEM professionals struggle to develop soft skills because of the focus on technology. However, soft skills are essential for personal development. STEAM, on the other hand, brings soft skills into the classroom. It encourages collaboration not just within STEM disciplines, but with the arts and humanities as well. This inclusive strategy recognizes that different skills are mutually dependent, preparing students for a variety of career paths in a constantly changing professional environment.
Opportunities for STEM Careers Are Increasing
The need for STEM workers is at an all-time high in the U.S., with 40% of Americans describing the shortage as a crisis, according to a survey conducted by technology and engineering company Emerson. The survey also found that the demand for STEM-related jobs is growing faster than the available workforce. According to a Deloitte study, the skills gap within manufacturing alone could create 2.4 million new unfilled jobs from 2018 to 2028.
Predictions show that job prospects in the STEM fields are expected to expand significantly for a variety of professions. Information security analysts may anticipate a 28% growth in career possibilities between 2016 and 2026, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). In a similar vein, it is anticipated that employment in other STEM fields, such as statistics and math, will expand significantly by 33% during the same time frame.
Types of careers you can pursue in STEAM
Many careers fall under the STEAM umbrella. Some of the most popular ones are Graphic designers, Software developers, architects, biomedical engineers, animators, data scientists, game designers, musicians, environmental scientists, fashion designers, etc.
Wrapping Up
While you may feel like your child should focus more on STEM than STEAM for multiple reasons, you should encourage your kid to follow their heart and goals. It’s good for kids to learn that they can be creative and analytical at the same time. STEAM helps with this by teaching them to use both sides of their brain to solve problems. By using STEAM to learn, kids will be better prepared for their future careers, no matter what kind of job they want to do.
As jobs become more complicated and technology changes things, learning soft skills is very important. New classes that STEM skills like leadership, communication, and working together will help people do well in a world with A.I. and technology. These skills are things that you cannot trust the machines to do, so humans need to learn them to stay abreast of industry requirements.
Want to make your child future-ready with Robotics? Moonpreneur offers a tailor-made program. Reserve a spot in our free 60-minute workshop today and introduce them to the amazing world of robotics and innovations!















Does the integration of arts in STEAM truly enhance innovation more than the traditional STEM approach?
The integration of arts in STEAM fosters diverse perspectives and creativity, enriching problem-solving and innovation beyond what traditional STEM education alone can achieve.
In terms of long-term career success and adaptability, do STEAM graduates have an edge over STEM graduates?
STEAM graduates often possess versatile skills, blending creativity with technical expertise, offering an edge in adapting to diverse career demands and fostering innovative solutions.