In a rapidly evolving world, more than traditional skills and knowledge is needed to guarantee success. The concept of ’21st-century skills’ has emerged, encompassing a set of abilities and knowledge essential for today’s globalized and tech-driven society.

Image Source: Wikipedia
This article not only breaks down these skills into essential categories and explores their growing importance, but also offers practical and actionable insights into how they can be nurtured, empowering you to make a difference in education.
In 1981, the US Secretary of Education created the National Commission on Excellence in Education to examine the quality of education in the United States. The commission issued its report A Nation at Risk: The Imperative for Educational Reform in 1983. A key finding was that ‘educational reform should focus on the goal of creating a Learning Society’, a vision that holds the potential to transform our educational landscape and inspire hope for a brighter future.
Why 21st Century Skills Are Important for Future Careers?
The need for 21st-century skills is reshaping education and employment as technology accelerates and global connections deepen. According to the World Economic Forum, 21st-century skills—such as digital literacy, critical thinking, creativity, and adaptability—have become essential to the workforce and are transforming job requirements across industries. With many companies reporting a shortage of candidates proficient in these areas, the development of these skills presents a promising future for students and professionals alike.
1. Adapting to a Changing Job Market
The impact of AI and automation on the workforce is profound. Research from McKinsey estimates that by 2030, up to 375 million workers—or 14% of the global workforce—may need to switch occupational categories due to automation and AI integration. This shift underscores the importance of skills such as adaptability and critical thinking, which allow individuals to respond effectively to industry changes and new career demands.
“The World Economic Forum predicts that by 2025, over 50% of all employees will need reskilling to meet the demands of new technologies. LinkedIn’s research also identifies problem-solving, analytical thinking, and digital literacy as three of the top ten skills needed in today’s economy.”
2. Strengthens Academic and Career Pathways
For students, 21st-century skills provide a strong foundation for lifelong learning and career readiness. A study by The Partnership for 21st Century Skills (P21) found that students who engage in programs that develop critical thinking, collaboration, and creativity achieve higher academic results. These skills not only prepare them for college but also improve their adaptability to diverse career paths.
As the workplace becomes more diverse and interconnected, emotional intelligence and cultural awareness become equally critical. According to Harvard Business Review, teams with high cultural awareness and interpersonal communication skills outperform homogeneous teams in creativity and problem-solving by up to 35%.
“Companies like Tesla and IBM understand the importance of continuous training in problem-solving and adaptability to keep their workforce relevant in tech-heavy environments. Programs like IBM’s P-TECH initiative, available in over 24 countries, prepare students with skills and credentials that are directly applicable to the workforce, emphasizing the value of lifelong learning in staying competitive.”
3. Building an Inclusive, Innovative Workforce
21st-century skills enhance individual employability and contribute to a more agile, inclusive, and innovative workforce. Organizations benefit from employees who can handle rapid changes, collaborate across cultures, and think creatively, making these skills crucial for navigating today’s dynamic professional landscape.
By cultivating these skills, individuals are better prepared to manage changes, collaborate effectively, and confidently tackle new challenges, setting them up for success in an unpredictable world.
“Companies like Google place significant value on 21st-century skills. Google’s hiring practices focus on ‘soft’ skills like leadership and communication, often prioritizing these over purely technical abilities. These ‘soft’ skills are considered crucial because they enable employees to work effectively in teams, communicate their ideas clearly, and lead others, all of which are essential in today’s collaborative and fast-paced work environments.”
Core Categories of 21st Century Skills
21st-century skills are broadly categorized into three main groups: Learning and Innovation Skills, Literacy Skills, and Life and Career Skills. Each of these categories covers a range of specific competencies that are increasingly valued across education and the workforce.
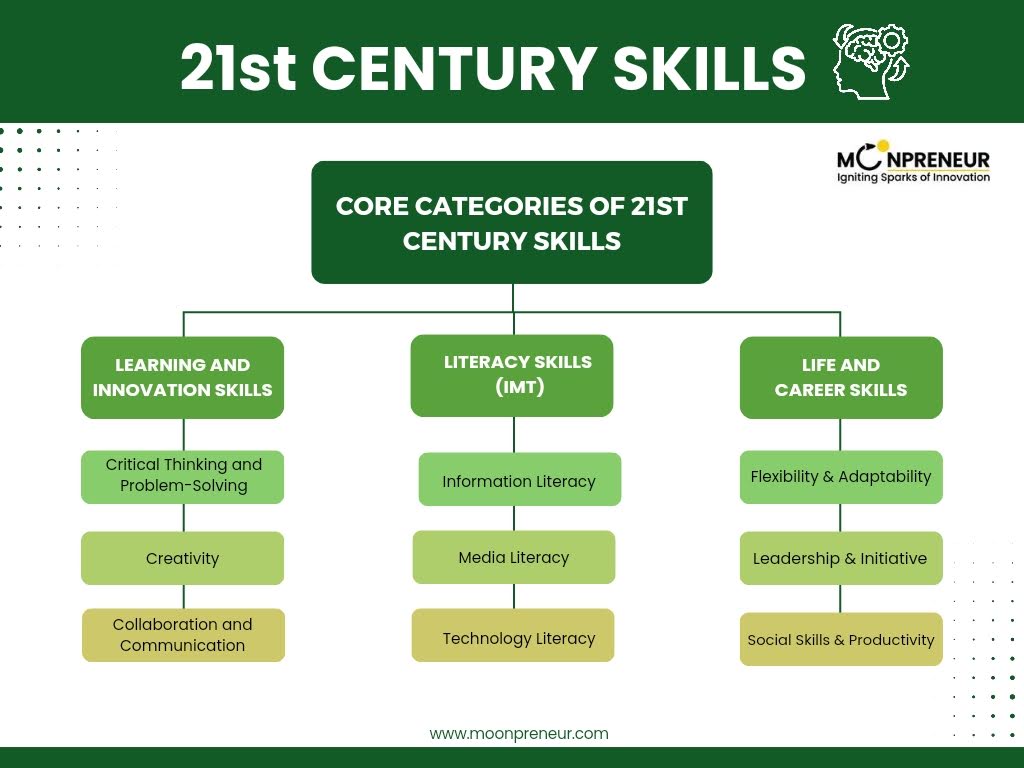
1. Learning and Innovation Skills
These skills (4C’s) focus on cognitive development and are crucial for innovative thinking and effective communication in a complex world. They include:
- Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Individuals proficient in critical thinking can analyze situations from multiple angles, evaluate evidence, and make informed decisions. This skill is not just theoretical, but highly practical, enabling individuals to identify, address, and solve complex problems—an asset in any industry, especially in tech and business. - Creativity
Creativity involves thinking beyond conventional solutions to generate new ideas and approaches. In today’s innovation-driven economy, creativity is not just a skill, but a driving force, as shown by the World Economic Forum ranking it among the top skills demanded by employers in various fields, including technology and media. - Collaboration and Communication
These skills are not just important, but essential for effective teamwork and clear idea expression. Collaboration involves not just working, but thriving with diverse teams, while communication is not just the ability, but the art of conveying ideas, data, and insights effectively—both vital in today’s globally interconnected environments.
2. Literacy Skills (IMT Skills)
Literacy skills are often abbreviated as IMT (Information, Media, and Technology); these skills enable individuals to navigate and utilize today’s digital and media landscapes effectively:
- Information Literacy
Information literacy, the power to find, evaluate, and use information effectively, is a key that unlocks doors in research, business, and education. It empowers individuals to discern reliable information from vast digital sources, instilling confidence and capability. - Media Literacy
Media literacy, a tool that equips individuals to understand and critically evaluate media content, is more important than ever in the age of social media and digital platforms. It helps recognize biases, understand underlying messages, and interact responsibly with media, fostering a sense of discernment and awareness. - Technology Literacy
Technology literacy, the proficiency in using digital tools and technologies to accomplish tasks, solve problems, and create content, is not just a skill, but a competitive edge. It is highly valued, especially in fields that rely on data analysis, automation, and digital content creation. LinkedIn reports indicate that technology literacy has become a key requirement for most modern jobs, making the audience feel more prepared and competitive.
3. Life and Career Skills
Life and career skills focus on personal and professional abilities that foster adaptability, productivity, and leadership, which are critical for thriving in diverse work environments:
- Flexibility and Adaptability
Flexibility, the ability to adapt to changing roles, technologies, or project goals, is a cornerstone skill in dynamic work environments. It’s not just a nice-to-have but a crucial skill that can make or break your career. Adaptability, especially in the context of remote and hybrid work, is equally important. It enables employees to remain productive and positive amid change, providing a sense of reassurance and preparedness. - Leadership and Initiative
Leadership involves guiding teams and projects, while initiative emphasizes taking proactive steps to solve problems or improve processes. These skills not only reflect an individual’s capacity to motivate others and drive innovation but also empower them to make a significant impact in their workplace. - Social Skills and Productivity
Emotional intelligence, teamwork, and time management are key components of social skills. Mastering these skills not only fosters a productive and harmonious work environment but also brings a sense of accomplishment, making employees more effective and improving overall team performance.
Additional 21st Century Skills Essential for Students and Workers
1. Cultural and Global Awareness

As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, cultural awareness is essential for effective collaboration and communication across diverse teams. Understanding and appreciating different perspectives encourages inclusivity, strengthens teamwork, and drives innovative ideas. Harvard Business Review reports that diverse, culturally aware teams consistently outperform others in both creativity and problem-solving.
Key Aspects:
- Cultural Sensitivity: Acknowledges and respects diversity by celebrating cultural holidays, providing language training, and promoting inclusive policies.
- Global Citizenship: Involves understanding global issues and committing to ethical, sustainable practices in diverse work environments.
- Intercultural Communication: Goes beyond language to foster connection and engagement, enhancing collaboration and team cohesion in multinational settings.
2. Technology and Data Literacy

Proficiency with technology and data is now a cornerstone for success in almost every industry. Technology literacy empowers individuals to effectively use digital tools, while data literacy enables them to interpret and apply data-driven insights. The World Economic Forum has identified data and AI skills as some of the most valuable for future jobs, particularly in sectors like finance,marketing, and AI in healthcare.
Key Aspects:
- Basic Coding and Digital Skills: It provides a foundation for understanding automation and digital tools.
- Data Interpretation: Data Interpretation equips individuals to make informed decisions based on data.
- Cybersecurity Awareness: Cybersecurity Awareness plays a key role in safeguarding personal and organizational data, which is becoming increasingly important.
“A 2023 report from the OECD highlighted that 63% of employers value adaptability and problem-solving over traditional skills, making them not just useful, but essential for both students and experienced professionals. This emphasis on these skills makes the audience feel valued and important in the job market.”
Practical Ways to Develop 21st Century Skills in Education
Education systems worldwide are adapting to incorporate these essential skills. Educators and policymakers play a crucial role in this adaptation, implementing methods that are gaining popularity. Here are some of these methods:
- Project-Based Learning: The method of project-based learning inspires students to work on real-life projects, effectively fostering skills such as collaboration and problem-solving.
- Interdisciplinary Programs: These innovative programs that combine subjects (like STEM education with arts) are designed to ignite creative thinking.
- Virtual Learning Models: Digital and hybrid platforms provide students with resources to develop digital literacy.
“A study by the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) shows that schools implementing project-based learning report a 50% improvement in student engagement.”
P21 Framework for 21st Century Skills Development
To structure 21st-century skills development, several frameworks have been created, with the P21 Framework being one of the most influential. Established by the Partnership for 21st Century Learning (P21), this framework is implemented in schools through a curriculum that emphasizes:
- Student-Centered Learning: SCL fosters inquiry and project-based learning environments where students actively engage with content.
- Technology Integration: Embedding digital tools in learning to cultivate digital literacy.
- Real-World Applications: Connecting theoretical knowledge to practical, real-world scenarios helps students see the relevance and impact of what they’re learning.
“The OECD’s Learning Compass 2030 emphasizes “transformative competencies” that go beyond basic cognitive skills, incorporating elements like personal and social development, an area often underrepresented in other frameworks.”
Global Examples of Successful Implementation of 21st Century Skills Programs
1. Singapore: Holistic Development through Character and Citizenship Education (CCE)

Recommended Reading: Important Life Skills Kids Learn from Coding
Singapore’s education system is renowned for its emphasis on both academic and character education. The Character and Citizenship Education (CCE) program integrates traditional academics with values such as resilience, respect, and responsibility, which are crucial for teamwork and leadership. Through CCE, students engage in activities designed to build social and emotional competencies, preparing them to thrive in diverse and collaborative environments. This holistic approach has consistently placed Singaporean students at the top of global rankings in adaptability and problem-solving skills .
Outcome: Singaporean students consistently rank high in global assessments, demonstrating not only academic excellence but also strong social and emotional skills. This success story from Singapore’s education system is a testament to the power of a holistic approach and can serve as an inspiration for educators, policymakers, and researchers worldwide.
2. Finland: Emphasis on Personalized and Phenomenon-Based Learning
Finland’s education model is not only progressive but also highly adaptable. It focuses on phenomenon-based learning, a unique approach that encourages students to explore real-world issues from multiple disciplinary perspectives. This fosters critical thinking, collaboration, and creativity and prepares students for success in a fast-changing world. The adaptability of this model is a reason for hope and optimism in the field of education.
Outcome: Finland’s students consistently perform well in critical thinking and problem-solving, as seen in the global PISA (Programme for International Student Assessment) rankings, which are conducted by the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development) and are widely regarded as a benchmark for educational performance worldwide.
3. Australia: The New Basics Project

Recommended Reading: Project-Based Learning: A Popular way of Learning
Australia’s New Basics Project is a groundbreaking initiative that incorporates project-based learning and digital literacy. By engaging students in hands-on projects that tackle real-world problems, the program builds competencies like problem-solving, adaptability, and teamwork. For instance, students might participate in cross-disciplinary projects like designing sustainable urban environments, creating innovative solutions to global health challenges, or developing strategies for managing natural disasters. These projects apply knowledge from subjects like science, math, and social studies to practical scenarios, helping students understand the relevance of academic skills in real-life contexts.
Outcome: Students report higher engagement and retention rates, and teachers observe improved collaboration and critical thinking skills.
4. United States: IBM’s P-TECH (Pathways in Technology Early College High Schools)

Do You Know?
IBM’s P-TECH program is a unique educational model that integrates high school and community college curricula with industry-specific training. What sets P-TECH apart is its focus on providing students with both a high school diploma and an associate degree, along with practical, employable skills in fields like technology and engineering. This comprehensive approach, combined with the program’s partnerships with industry, creates pathways to employment, equipping students with both technical and life skills.
Outcome: The success of P-TECH is evident in its graduates, with 86% either securing jobs or pursuing further education in STEM fields. This showcases the program’s effectiveness in aligning education with workforce needs and instills confidence in the potential of education-industry partnerships to create pathways to employment.
How Parents and Educators Can Support 21st Century Skill Development

These focused strategies create a supportive framework for developing essential 21st-century skills, benefiting children, and strengthening community connections. By working together, stakeholders can foster an environment that prepares children for future challenges, ensuring that everyone feels included and part of the process.
Conclusion: The Future of 21st Century Skills
21st-century skills represent a bridge between education and the future workforce, preparing students and professionals alike to thrive in an evolving world. By fostering adaptability, digital literacy, and creativity, these skills are shaping a generation that is prepared to meet the challenges and opportunities of tomorrow.
Mastering these skills can open doors to fulfilling careers and empower individuals to make meaningful contributions to society. Embracing a holistic approach to learning and development, these skills are not just tools for success—they are essential assets for navigating the complexities of the modern world.
Moonpreneur is on a mission to disrupt traditional education and future-proof the next generation with holistic learning solutions. Its Innovator Program is building tomorrow’s workforce by training students in AI/ML, Robotics, Coding, IoT, and Apps, enabling entrepreneurship through experiential learning.

























When my son started his journey in game development, I realized how vital 21st-century skills like critical thinking and adaptability are. The way he applies problem-solving to coding and teamwork in projects shows how these skills are shaping him for future challenges. It’s incredible how these skills blend naturally with passions like his.
The case studies given in the blog highlight the growing significance of 21st-century skills like critical thinking and adaptability in children’s development. It’s fascinating how these skills, when taught early, help students excel in various areas. I’d love to know more about how these skills are being practically integrated into everyday learning, especially in traditional classrooms.
Integrating 21st-century skills into the classroom doesn’t have to be complicated! Simple strategies like project-based learning, collaborative tasks, and using technology in creative ways can help develop 21st-century skills . At Moonpreneur, we believe in empowering kids with the skills that will shape their future. Our hands-on, project-based learning approach naturally incorporates 21st-century skills like critical thinking, teamwork, and adaptability. It’s all about making these skills a natural part of everyday learning. The key is consistency and finding opportunities to apply them in real-world contexts. What’s your experience with these skills in education?