What is the Long Division Method?
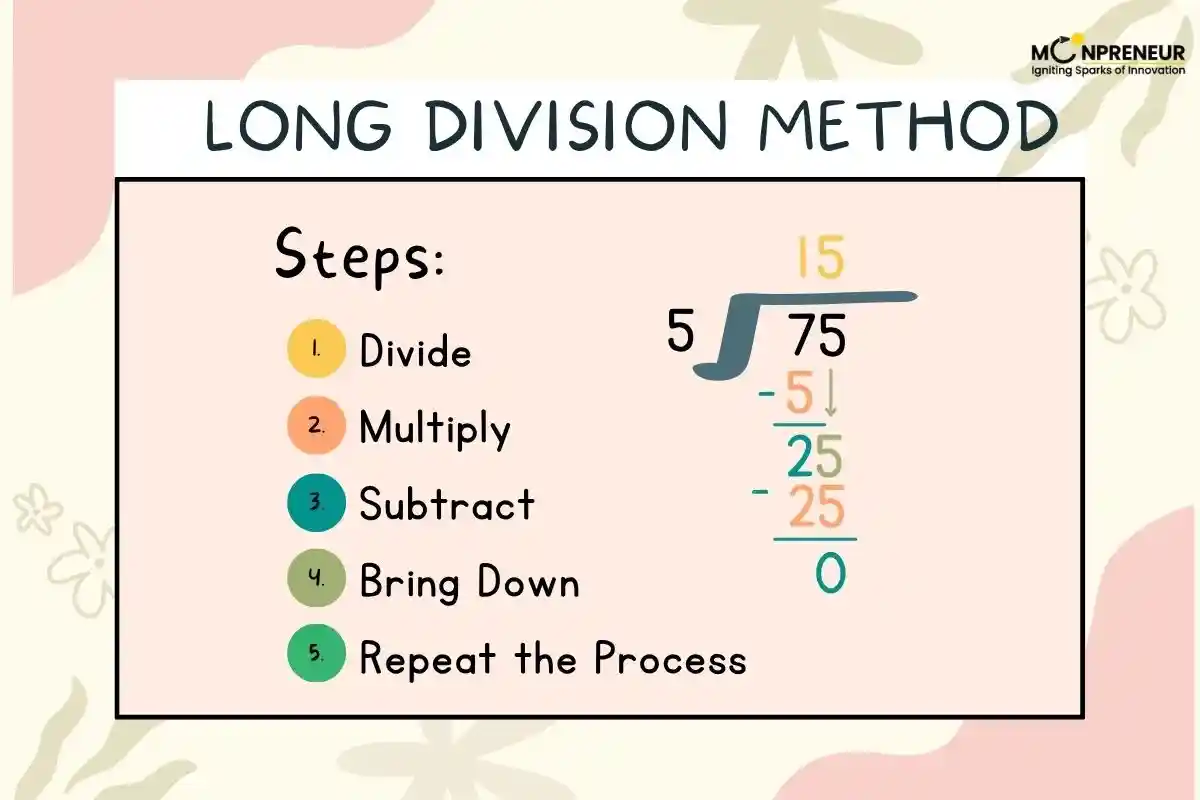
The long division method is a mathematical technique used to divide large numbers into smaller parts. It breaks down the division problem into a series of easier steps. Instead of solving everything at once, you solve one digit at a time. This method is especially helpful when dividing numbers that don’t go evenly.
Why is Long Division Important?
Long division is an important math skill that helps students solve complex division problems. It lays the foundation for advanced math concepts like algebra, fractions, and decimals. Understanding this method also builds confidence in handling large numbers.
Steps of Long Division Method
Here are the 5 main steps in the long division process. You can remember them using the acronym DMSBR (Divide, Multiply, Subtract, Bring down, Repeat).
1. Divide
Check how many times the divisor fits into the leftmost digits of the dividend.
Example: How many times does 4 go into 8? The answer is 2.
2. Multiply
Multiply the divisor by the quotient found in the first step.
4 × 2 = 8
3. Subtract
Subtract the result of multiplication from the selected digits of the dividend.
8 − 8 = 0
4. Bring Down
Bring down the next digit of the dividend and repeat the steps.
If the dividend is 84, bring down the 4.
5. Repeat or Remainder
Continue dividing until all digits are used. If there are no more digits and you can’t divide further, the number left is called the remainder.
First Long Division Example: 84 ÷ 4
1. Let’s divide 84 ÷ 4 using long division:
21 ← Quotient (Answer)
____
4 ⟌ 84 ← Dividend = 84, Divisor = 4
- 8 ← 4 × 2 = 8
----
04 ← Bring down the 4
- 4 ← 4 × 1 = 4
---
0 ← Remainder = 0
So, 84 ÷ 4 = 21 with no remainder.
Final Answer: 84 ÷ 4 = 21
Let me break it down step-by-step:
- Divide: 4 goes into 8 two times. Write 2 on top.
- Multiply: 2 × 4 = 8
- Subtract: 8 − 8 = 0
- Bring Down: Bring down the next digit (4).
- Divide Again: 4 goes into 4 one time. Write 1 on top.
- Multiply: 1 × 4 = 4
- Subtract: 4 − 4 = 0
No remainder is left. So the final answer is 21
Second Long Division Example: 87 ÷ 5
We are dividing 87 by 5:
1 7 ← Quotient (Answer so far)
______
5 ) 8 7
- 5 ← 5 × 1 = 5
----
3 7 ← 8 - 5 = 3; bring down the 7
- 35 ← 5 × 7 = 35
-----
2 ← 37 - 35 = 2 (Remainder)
Final Answer: 87 ÷ 5 = 17 R2
✍️ Step-by-Step Breakdown:
- Divide: 5 goes into 8 once. Write 1 on top.
- Multiply: 1 × 5 = 5
- Subtract: 8 − 5 = 3
- Bring Down: Bring down the next digit (7), making it 37.
- Divide Again: 5 goes into 37 seven times. Write 7 on top.
- Multiply: 7 × 5 = 35
- Subtract: 37 − 35 = 2
So, 2 is the remainder.
Final Answer:
87 ÷ 5 = 17 remainder 2
or
87 ÷ 5 = 17 Reminder:2
Tips to Teach Long Division to Kids
- Use real-life examples like sharing candies or toys.
- Practice with simple numbers first.
- Use visual aids or long division charts.
- Break the problem into small steps.
Common Mistakes in Long Division
- Forgetting to bring down the next digit.
- Incorrect multiplication in steps.
- Misplacing the quotient digits.
- Not checking the remainder.
Practice makes perfect! The more you practice, the easier long division becomes.
Conclusion
The long division method is a powerful tool for solving big division problems in a simple, step-by-step manner. Once mastered, it opens doors to advanced math concepts and real-world applications. Help your child learn and practice long division with fun exercises and real-life examples!
Want to spark your child’s interest in math and boost their skills? Moonpreneur’s online math curriculum stands out because it engages kids with hands-on lessons, helps them apply math in real-life situations, and makes learning math exciting!
You can opt for our Advanced Math or Vedic Math+Mental Math courses. Our Math Quiz for grades 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 6th helps in further exciting and engaging in mathematics with hands-on lessons.
















