Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics that focuses on specific functions of angles and their application in calculations.
There are six primary trigonometric functions commonly used:
- sine (sin)m
- cosine (cos)
- tangent (tan)
- cotangent (cot)
- secant (sec)
- cosecant (csc)
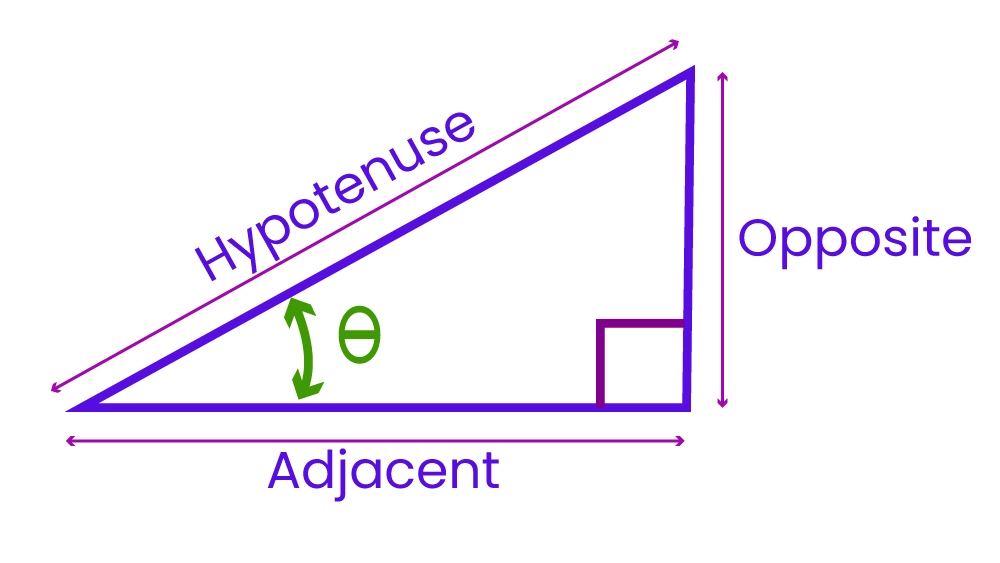
These functions relate to the angles and sides of a right triangle, as shown in the figure. For instance, in a triangle with angle A, the ratio of the length of the side opposite angle A to the length of the hypotenuse is known as the sine of A, or sin A. The other trigonometric functions are defined in a similar manner. These functions are properties of angle A and are independent of the size of the triangle.
Remember, trigonometric functions are essential for determining unknown angles and distances based on known or measured angles in geometric figures. Historically, values for these functions were tabulated from many angles before computers made such tables obsolete.
Recommended reading: Developing a Deeper Understanding of Math Concepts
Meaning of Tangent
The word “tangent” means “to touch,” derived from the Latin word “tangere”.
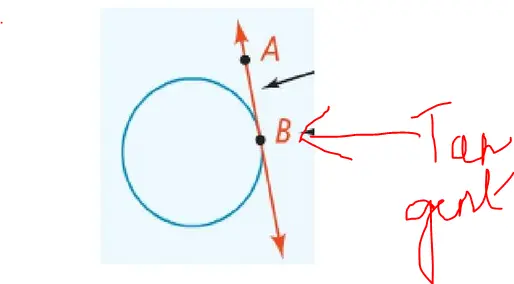
In general terms, a tangent is a line that intersects a circle at exactly one point on its circumference without entering the circle’s interior. A circle can have multiple tangents, each of which is perpendicular to the radius at the point of contact.
Recommended Reading: Top Math Board Games For Kids to Boost Math Skills
Definition of Tangent
Tangent is defined in the context of a right triangle ABC. For an angle A, the tangent function (tan) is given by the ratio of the length of the side opposite angle A to the length of the side adjacent to angle A:
tan A = length of side opposite angle A
————————————–
length of the side adjacent to angle A
In geometry, a tangent is a line that touches a curve at a single point without crossing it. A real-life example of a tangent is the contact point between a bicycle wheel and the road—every point on the circumference of the wheel forms a tangent with the road.
Recommended reading: Surviving the Hardest Math Class in High School: Tips and Tricks
Definition of Tangent (function)
The tangent function, denoted as tan(x), represents the ratio of the side opposite an angle in a right triangle to its adjacent side.
Recommended reading: Is Advanced Calculus The Hardest Math Class In High School? A Student’s Perspective
Tangent (line)
A line that touches a curve at a single point and matches the curve’s slope at that point is called a tangent.
On the left is a tangent to a general curve, and below is a tangent to an ellipse:
Recommended reading: 5 Creative Ways to Make Math Fun for Kids
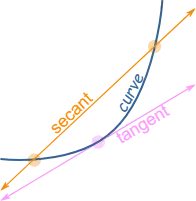
Here is another image of a tangent to a general curve.
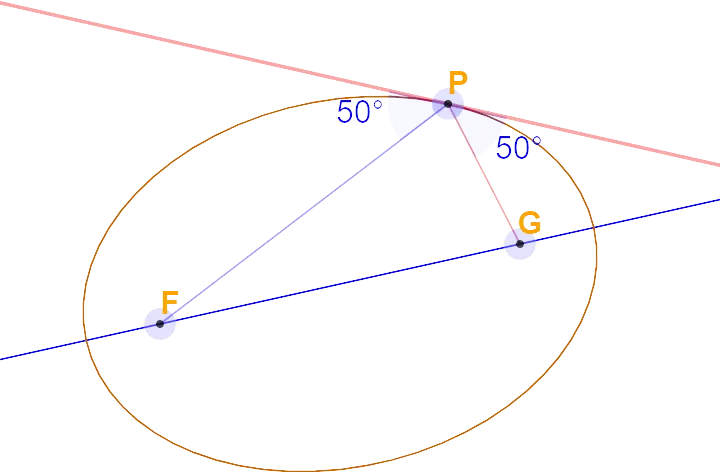
Recommended reading: Guide to High School Math Classes: Which Ones Are Essential?
Conclusion
The concept of tangents is a cornerstone of both geometry and calculus, offering valuable insights and tools for understanding curves and their properties. From simple geometric shapes like circles to complex functions in calculus, tangents provide a way to explore and analyze the world of mathematics. Their applications in various fields underscore their significance, making tangents an essential topic for anyone delving into the depths of mathematical study.
Want to excite your child about math and sharpen their math skills? Moonpreneur’s online math curriculum is unique as it helps children understand math skills through hands-on lessons, assists them in building real-life applications, and excites them to learn maths. You can opt for our Advanced Math or Vedic Math+Mental Math courses. Our Math Quiz for grades 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 6th helps in further exciting and engaging in mathematics with hands-on lessons.