Industrial robots have revolutionized manufacturing processes across various industries, streamlining production, increasing efficiency, and ensuring precision. However, the efficiency of these robots has been significantly driven by the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
This blog explores the transformative impact of AI on industrial robots, expressing how it enhances their capabilities to meet the demands of modern industrial settings.
Introduction to Industrial Robots

Industrial robots, also known as robotic arms or mechanical arms, are programmable machines designed to perform tasks traditionally carried out by human workers in manufacturing facilities.
These robots are equipped with mechanical arms, sensors, and controllers, enabling them to execute repetitive tasks with high precision and efficiency. The role of industrial robots in automation is paramount, as they contribute to increased productivity, cost savings, and improved quality control in production processes.
The Evolution of Industrial Robotics
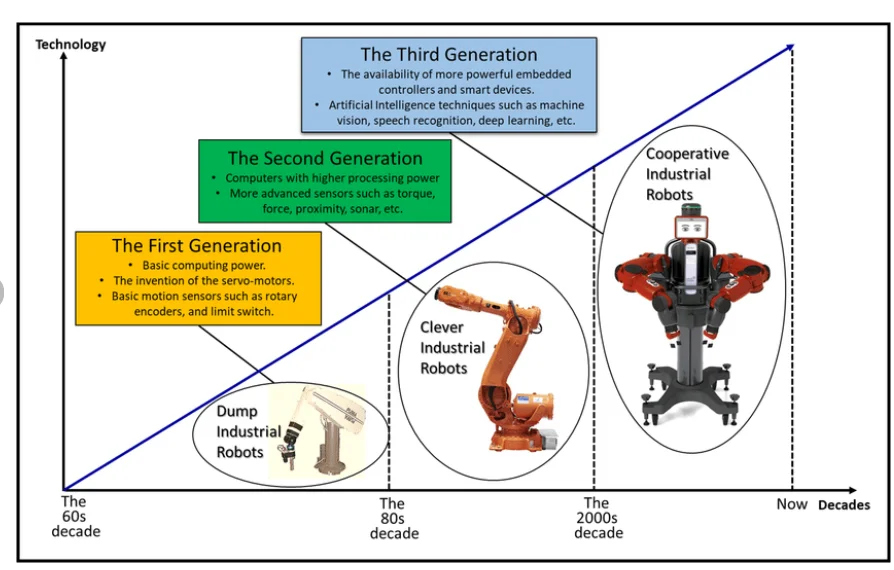
Since their inception in the 1950s, industrial robots have undergone significant advancements in design, functionality, and performance. Early industrial robots were primarily used for tasks such as welding, painting, and assembly in automotive plants.
Automation has been essential for manufacturing competitiveness on a global scale during the last few decades. During this time, industrial robot adoption has increased rapidly. Just 200 industrial robots were operating in the US in 1970. The figure shot up to 4,000 by 1980 and then to 1.6 million by 2015. Over 3 million industrial robots are reportedly in use worldwide at the moment.
Robotics attracted more attention and excitement in the middle of the 1980s. Engineers started pushing the boundaries to promote industrial development and increase manufacturing competitiveness, seeing robots as the “machines of the future.” The basis of the modern industrial robot was established at this time as sophisticated sensors and basic machine vision systems started to be incorporated.
Now, the software has been the main driver of industrial robots progress since the early 2000s. Robots are increasingly capable of learning, improving, and making decisions on their own without human direction or guidance all thanks to emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML).
Introduction of AI in Industrial Robotics

The goal of artificial intelligence (AI) in robotics is to improve automation by fostering an intelligent environment. Intelligent programming, reinforcement learning, and computer vision techniques are used to educate robots to perform tasks in dynamic environments and make decisions similar to those of a person.
How AI is improving robotics
The use of industrial robots in manufacturing is not new. As a matter of fact, they have been present for decades, serving in roles including material handling, welding, and painting. Large, heavy devices with a single task-per-task capability were the earliest robots. Robotic automation technology developments have made industrial robots more intelligent, safe, small, and adaptable today. One of the main factors influencing the development of the more advanced class of industrial robots is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with robotics. Compared to earlier models, modern robots can carry out a wider range of activities, more intricate operations, and a higher production volume.
As a result of artificial intelligence, robot functionality, versatility, and precision have improved since advanced software, vision systems, and sensors have been developed. Industrial robots are becoming a crucial resource for enterprises as artificial intelligence (AI) makes them more intelligent and autonomous. Leading robot producers KUKA and FANUC understand the benefits of incorporating AI into their robotic systems.
AI technology has been integrated by KUKA into their range of collaborative robots. Because of its sophisticated sensors that shield people from potentially harmful interactions, its AI-based cobots can safely operate alongside people.
Robots can now identify specific parts even in cases where the part placement varies or where there is a mixture of parts in a bin thanks to AI-driven vision systems. When an industrial robot is shown an image of a certain part, it can learn which parts to detect or move. These pictures are stored by artificial intelligence software, which the robot can access during operation.
Predictive maintenance software is another type of artificial intelligence being researched in robotics. Robots using predictive maintenance software can self-monitor their condition or performance problems. Then, when a service is required, or a problem has to be fixed, robots can notify users. By keeping maintenance on schedule, predictive maintenance software helps to minimize expensive downtime brought on by robot malfunctions. Additionally, it prolongs the robot’s operational life by assisting users in resolving any problems before they become more serious repairs.
By assisting industrial robots in becoming more sophisticated and self-sufficient devices, artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the robotics sector. Robots are becoming more precise, efficient, and capable of operating at higher speeds, which enables producers to make goods of superior quality more quickly.
Maximizing Industrial Efficiency with AI Integration
In the fast-paced world of manufacturing, precision and efficiency are paramount. Thanks to the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI), industrial robots are now able to reach new levels of productivity, ushering in a new era of streamlined operations. Let’s delve into how AI is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape by enhancing precision, adaptability, safety, cost-effectiveness, and workforce dynamics.
1. Enhanced Precision and Efficiency
AI-driven developments have accelerated industrial robots to previously unheard-of levels of accuracy and productivity. Robots can fine-tune their actions for optimal results by analyzing complex data sets in real-time by utilizing machine learning techniques. This reduces the need for continual human supervision while improving quality control and lowering mistake rates throughout the manufacturing process.
2. Adaptive and Flexible Operations
AI-enabled industrial robots stand out for their exceptional ability to adjust to changing operating requirements. These robots are not limited to pre-programmed duties like their conventional counterparts. Rather, they quickly adjust to new difficulties on the industrial floor, streamline processes, and draw lessons from past mistakes. This adaptability gives producers the ability to react swiftly to changes in the market, resulting in increased operational resilience and agility.
3. Improved Safety Measures
In any industrial setting, safety comes first, and artificial intelligence (AI) is a major factor in improving workplace safety. Robots can anticipate possible dangers and take proactive measures to remedy them before they worsen, thanks to predictive maintenance algorithms and AI-powered sensors. By taking a proactive stance, the likelihood of accidents is reduced and a safer working environment is created for human workers, which lowers downtime and increases overall productivity.
4. Cost Reduction and Return on Investment
Integrating AI into industrial robotics isn’t just about efficiency—it’s also about the bottom line. By optimizing resource utilization, minimizing downtime, and improving overall efficiency, AI-driven robots deliver substantial cost savings for businesses. These savings translate into a significant return on investment, supporting the financial viability of automation initiatives and enhancing the competitive edge of companies in the global market.
5. Impact on Job Roles and Human Labor
Contrary to popular belief, the rise of AI in manufacturing isn’t about replacing human workers—it’s about empowering them. By augmenting human capabilities, AI-enabled robots enable workers to focus on tasks that require creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills. This symbiotic relationship between humans and machines creates new job opportunities and fosters a culture of continuous learning and development in the workforce.
6. Future Trends and Innovations
The future of industrial robotics is brimming with possibilities, driven by ongoing innovations in AI and other emerging technologies. From autonomous decision-making to collaborative interactions, the next generation of robots is poised to revolutionize the manufacturing landscape. Predictive analytics, augmented reality, and Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity are just a few of the trends shaping the future of industrial automation, promising even greater efficiency, agility, and innovation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of AI into industrial robotics represents a game-changer for the manufacturing industry, unlocking new levels of efficiency, safety, and innovation. By harnessing the power of AI, businesses can optimize their operations, drive cost savings, and empower their workforce to thrive in the digital age of automation. As we embrace the future of manufacturing, it’s essential to prioritize ethical considerations, collaboration, and responsible use of AI to ensure a brighter, more sustainable future for all stakeholders involved.
Want to make your child future-ready with Robotics? Moonpreneur offers a tailor-made program. Reserve a spot in our free 60-minute workshop today and introduce them to the amazing world of robotics and innovations!