Update: This article was last updated on 9th January 2026 to reflect the accuracy and up-to-date information on the page.
In robotics, sensors are like the robot’s senses. They help the robot figure out what’s going on around it, similar to how our sensory organs work for us. Just like our eyes, ears, and skin help us understand the world, robot sensors help the robot do its job well.
What is a Robot Sensor?

A robot sensor is a device that detects and measures physical or environmental conditions, providing crucial data for a robot to understand and interact with its surroundings. As mentioned earlier, it functions akin to human sensory organs, offering information on parameters such as position, size, orientation, velocity, distance, temperature, weight, and force. They use a process called energy conversion, or transduction that enables them to perform tasks efficiently and respond dynamically to changes in their environment.
Different robots need different types of sensors to stay in control and adapt to what’s happening in their surroundings.
So How Does A Robot Sensor Work?
Robot sensors identify changes in the surrounding environment and convert them into electrical signals that can be processed by a robot’s computer.
By employing various types of sensors, robots can effectively observe and perceive their surroundings, facilitating the execution of diverse and intricate tasks.
The operation of a robot sensor depends on the principle of transduction, which essentially involves the conversion of energy.
How it works?
Robot sensors measure the conditions and environmental factors by detecting changes in physical or environmental parameters such as position, distance, temperature, light intensity, and more. Once these changes are detected, the sensors translate them into electronic signals, which are then transmitted to the robot’s controller or computer system.
These electronic signals serve as valuable inputs for the robot’s decision-making processes, allowing it to adjust its actions accordingly. For instance, if a proximity sensor detects an obstacle in the robot’s path, it can send a signal to the robot’s controller, prompting it to change direction or stop to avoid a collision.
In essence, without these sensors, robots would lack the ability to adapt to changes in their environment and execute tasks with precision.
Mentioned below are a few of the most prevalent types of sensors used in robots:
| Sensor Name | Function |
|---|---|
| Proximity Sensors | Employ magnetic fields to detect objects close to the robot, calculating distance from objects not in direct physical contact. |
| Touch Sensors | Detect changes in velocity, position, acceleration, torque, or force at robot joints and end-effectors. |
| Light Sensors | Detect light and produce a voltage difference. |
| Temperature Sensors | Track changes in surrounding temperature using a change in voltage difference approach. |
| Gyroscopes | Measure robot's orientation and angular velocity by detecting changes in rotation. |
| Contact Sensors | Contact sensors detect physical interactions between robots and their environment. |
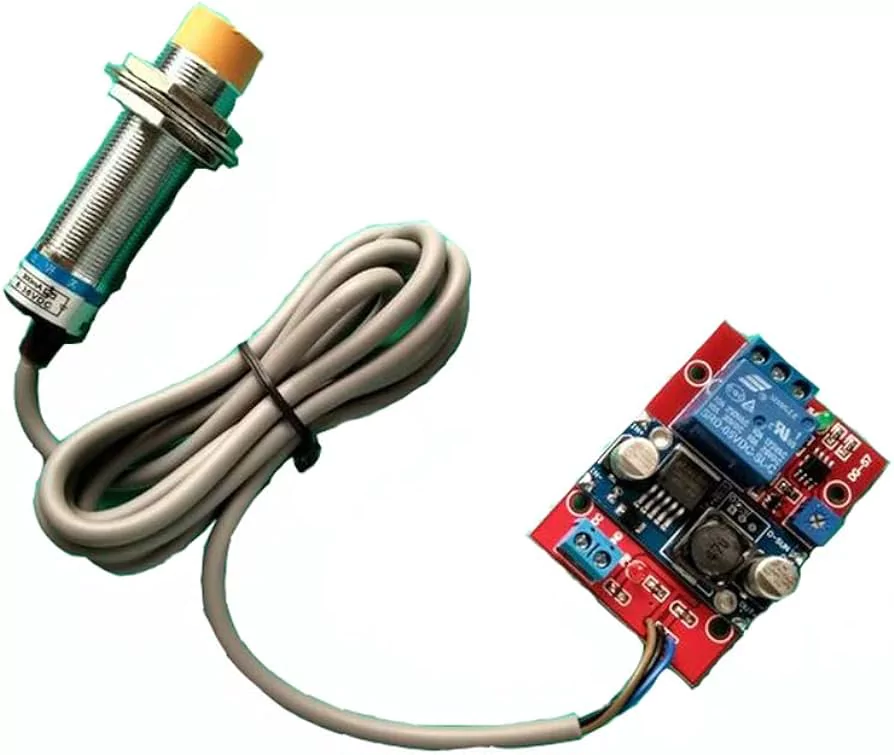

(i) Proximity sensors
Robot proximity sensors employ magnetic fields to detect objects that are close to them and to calculate their distance from objects with which they’re not in direct physical contact. These sensors come in two varieties: photoresistors and ultrasonic sensors.

(ii) Touch sensors
The robotics industry uses a touch sensor, also known as a contact sensor. These are mostly used for detecting a change in velocity, position, acceleration, torque, or force at the joints of the manipulator and end-effecter. These sensors need physical contact to work the robot properly and act accordingly. Touch sensors are used in several switches, including tactile bumper switches, button switches, and limit switches.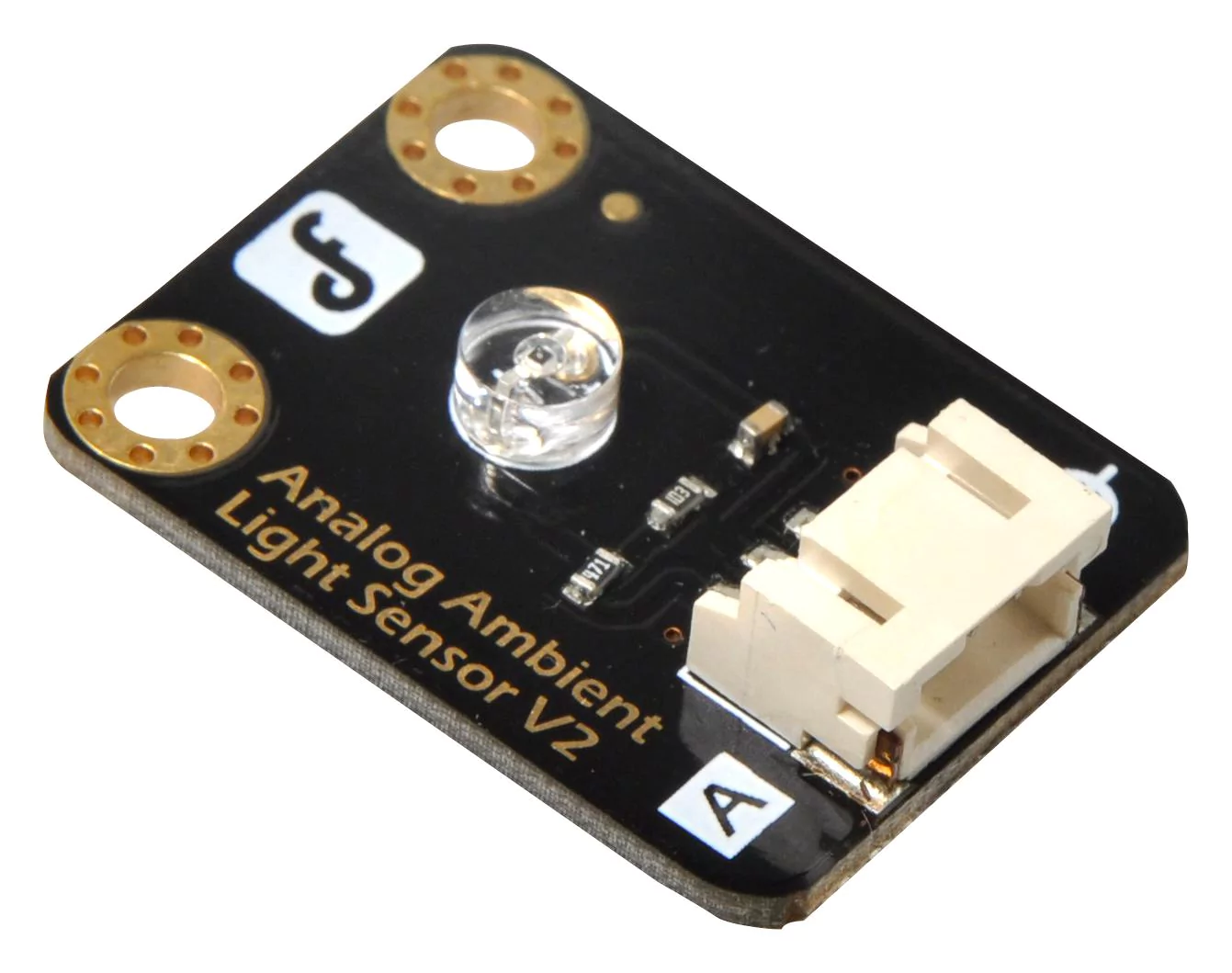
(iii) Light sensors
The light sensor detects light and produces a voltage difference. Robots employ two different types of light sensors: photovoltaic cells and photoresistors. Solar robot manufacturing uses photovoltaic cells, which work on converting the sun’s radiation energy to electrical energy. Photoresistors, on the other hand, are employed to alter their resistance by changing light intensities. When light is more on it, then resistance will be less. These light sensors are not expensive, so used widely in robots.
(iv) Temperature sensors:
To effectively track changes in the surrounding temperature, a temperature sensor is employed inside Robots. This sensor primarily uses the change in voltage difference approach to calculate the equivalent temperature value of the surrounding air and respond to a change in the temperature.
(v) Gyroscopes:
These sensors measure the robot’s orientation and angular velocity. They work by detecting changes in the rotation of the robot. Gyroscope is also used to measure the revolution rate around a specific axis. This sensor is highly useful if you want your robot to maintain orientation independent of the earth’s gravity.

(vi) Contact Sensors:
These sensors enable robots to interact safely and effectively with objects, surfaces, and even humans. They come in various forms, including tactile sensors, force-sensitive resistors (FSRs), and capacitive sensors, each tailored for specific applications. Contact sensors play a significant role in industrial automation by detecting the end of a robot’s range of motion or contact with workpieces, enhancing operational safety and efficiency. Additionally, in human-robot interaction scenarios, contact sensors ensure safe collaboration by detecting and responding to contact with humans.Applications Of Robot Sensors Across Sectors
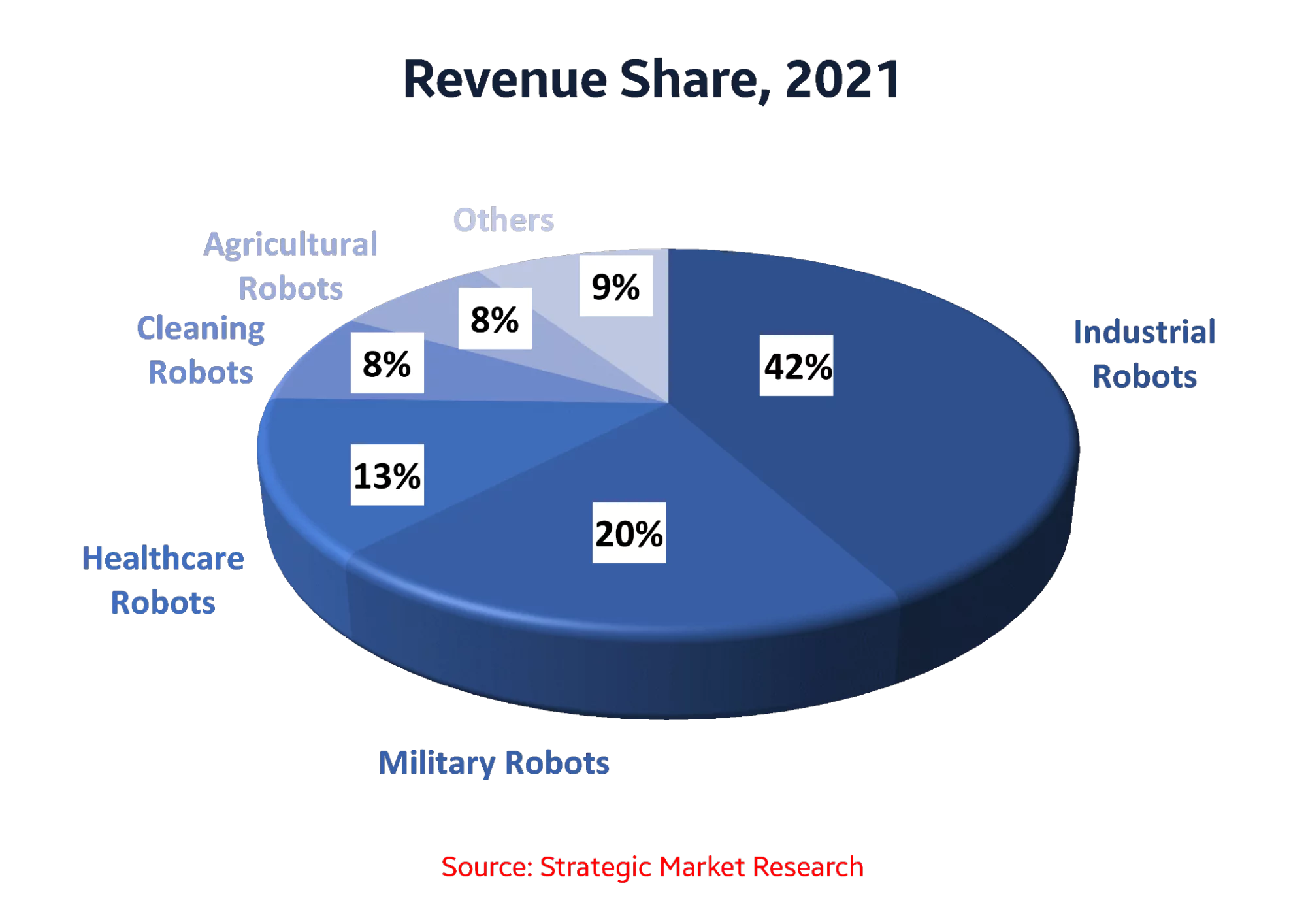
The growth of the Robotics industry across various sectors has resulted in the wide usage of these Robot sensors, such as
Manufacturing
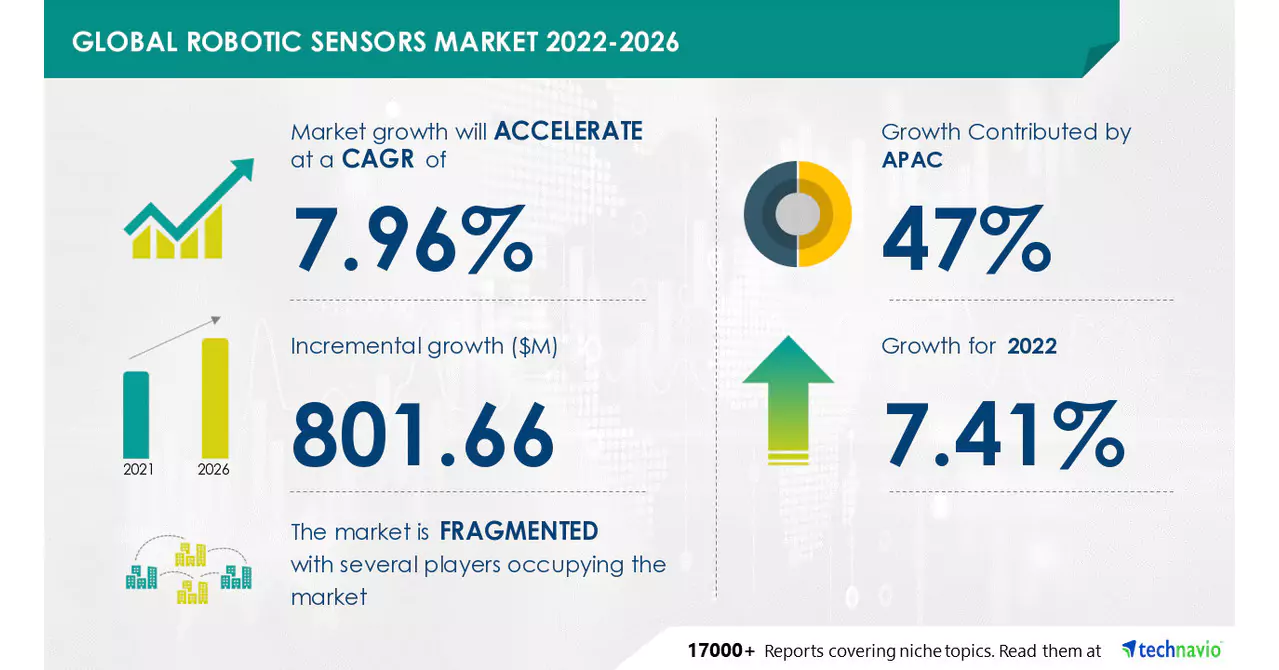
In the United States, Robots are widely used in manufacturing industries, and sensors are used to detect the position of objects on the production line and to ensure that the robots are performing their tasks accurately. The majority of the automation in the US has taken place in the manufacturing industry, which accounts for approximately 82.3% of all industrial robot installations across the country’s industries in 2018.
Entertainment
From 2021 to 2026, the robotics market share in the entertainment sector is projected to grow by $901.83 million, with a CAGR of 15.21% for the market. Robots are used in entertainment, such as theme parks and movies, to provide an immersive experience for visitors. These robots use motion sensors, as they have to be more aware of their surroundings. Vision sensors and touch-sensing systems are another set of vital sensors used in the entertainment industry.
Agriculture
The market for agricultural robots was valued at $4,082.8 million in 2018 and is projected to increase at a CAGR of 19.2% to reach $16,640.4 million by 2026. Robots are used to automate processes like planting, watering, and harvesting crops, and sensors are used in agriculture to measure environmental factors such as temperature and soil moisture.
Transportation
There has been a significant increase in the usage of Robots in the transportation sector. Autonomous vehicles and drones use sensors to navigate their environment and avoid obstacles.
Healthcare
Robots assist with surgery, rehabilitation, and patient care. Sensors monitor vital signs, detect changes in the patient’s condition, and provide feedback to the robot’s computer. According to data, more than 1 million robotic devices were purchased in the healthcare industry from (2015-2021).
Robot sensors are used extensively. People are frequently perplexed as to how robots operate, and this article clarifies everything by outlining the many kinds of robot sensors and how they work.
Want to make your child future-ready with Robotics? Moonpreneur offers a tailor-made program. Reserve a spot in our free 60-minute workshop today and introduce them to the amazing world of robotics and innovations!