Update: This article was last updated on 8th January 2026 to reflect the accuracy and up-to-date information on the page.
Robots, from industrial machines to personal assistants, have seamlessly integrated into our daily lives. But what truly powers these marvels? Delving into the key components of robot system—the essential robotics components that underpin every robot is key to unraveling their functionality. In this piece, we’ll dissect the eight fundamental components present in nearly every robot, shedding light on their collective role in task execution.
In addition, an excellent resource that talks about the benefits of robots and automation is one that highlights the former’s significant importance in enhancing efficiency and productivity. Advanced robot parts are making these technologies change the face of various industries. Due to their efficiency and precision, these technologies can work faster, hence revolutionizing these industries. The need for humans in hazardous jobs has been minimized through these technologies, enhancing workplace safety, while making processes more streamlined and innovative. Ultimately, these improvements translate to lower prices and better products for the consumer.
Let’s talk about the eight key components of robot in this blog. Also, it will definitely help you to build your own robot.
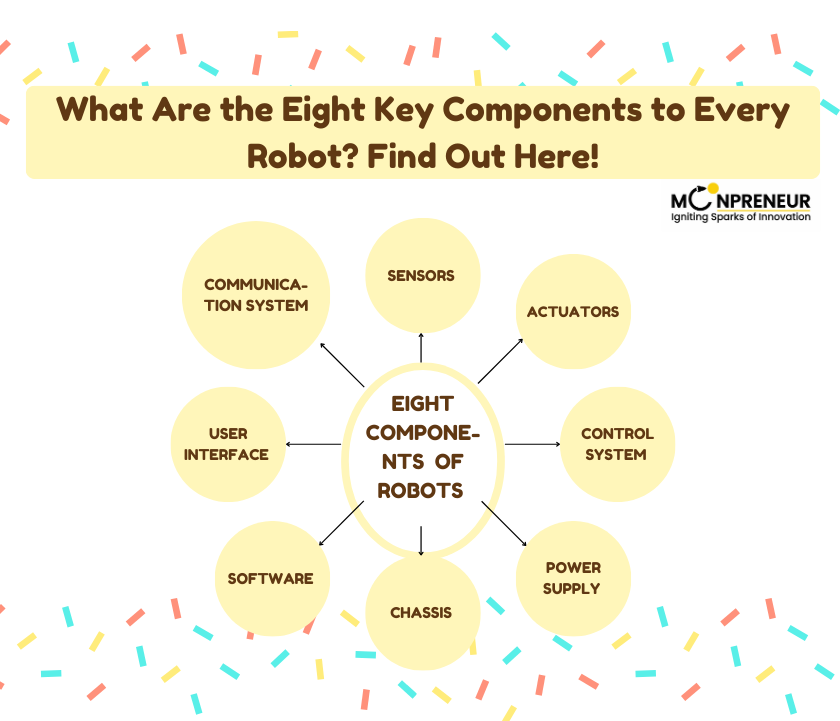
Eight Components of Robots Explained

1. Sensors
Some of the key components of robot include sensors, which act as the robot’s eyes and ears. They help a robot to adapt to its environment by collecting data about the distance, temperature, light levels, and obstacles around it. Cameras, infrared sensors, ultrasonic sensors, and tactile sensors are some of the most common types of sensors. Through interpretation of the information collected by these sensors, robots can make informed decisions and respond to changes in their environment, thus making them highly adaptable.
2. Actuators
The actuators are some of the key components of robot, and the actuators in a robot can be termed as the muscles of a robot, as they provide motion to the robot. They are responsible for changing electrical energy into mechanical motion to enable the robot to walk, lift, or move objects. Based on the robot’s design and function, electric motors, and hydraulic, and pneumatic devices are used.
You may love reading: RoboRevolution – The Rise of Robotics in Modern Industries


3. Control System
The control system of different robotics parts acts as the brain of the robot, which guarantees a reliable decision-making process. It processes information from the sensors and sends commands to the actuators. This includes hardware and software that enables the robot to analyze data, make decisions, and execute tasks. Microcontrollers and embedded systems are some of the common components of a robot’s control system, allowing for real-time processing and controls.
Check on this PDF:
4. Power Supply
A power source is needed for the functioning of any robot, and this power supply, which forms one of the crucial robotics components, provides the necessary energy for operating the sensors, actuators, and control system. Depending on the robot’s application, its power sources could be batteries, solar panels, or direct electrical connections. The choice of the power supply is very crucial since it determines the range, efficiency, and operational time of the robot. This is one of the important key components of robot.

5. Chassis
The chassis is the most important part of a robot, as it provides the support and housing structure for its various components. Its design determines the shape, size, and stability of the robot. Chassis designs can range from wheeled or tracked bases for mobile robots to articulated frames for robotic arms. A good chassis design will ensure that the robot navigates its environment and performs tasks effectively.
You may love reading:
- Aibo Robot Dog – The Future of AI and Robotics
- Building and Programming Robots with AI in 2023
- Top 10 Robotics Games For Kids
- Loona Robot – An Intelligent PETBOT
- How Robotics Certification Can Help You in College Admission?
- Robots in Disaster Response: Innovations in Crisis Management
- The Future of Swarm Robotics
6. Software
A robot’s sensor, actuators, and its control systems work on software; it is that part of a robot that deals with the data processing, motion control, and complex tasks are executed by this part. Such algorithms are made on programming languages Python, C++, and ROS: Robot Operating System. The quality of software development is critical in achieving efficient and reliable robot performance. With AI in the building and programming of robots, it combines machine learning and neural networks to enhance a robot’s ability to learn from its environment. This fusion leads to more autonomy and adaptability, which enables robots to efficiently execute complex tasks in dynamic environments.

7. User Interface
Human-robot interaction is essentially bridged through the user interface. It gives users the option to control, monitor, and receive feedback about the performance of the robot. UIs could be as simple as buttons and switches or touch screen displays that can be accompanied by voice commands. A good interface is what makes it accessible and simple enough for operators to communicate with the robot and be able to access features..
8. Communication System
The communication system is the means through which the robot can communicate with other robots or devices. It can be achieved through wired connections, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or other wireless protocols. Effective communication allows robots to work collaboratively, share data, and perform tasks more efficiently in a connected environment. The advent of humanoid robots is revolutionizing communication. These robots, mimicking human gestures and expressions, make interactions more natural and engaging. Consider Sophia and Pepper, advanced AI-enabled robots that can well understand and respond to human emotions, thereby leading to a future where humans can interact seamlessly with robots.

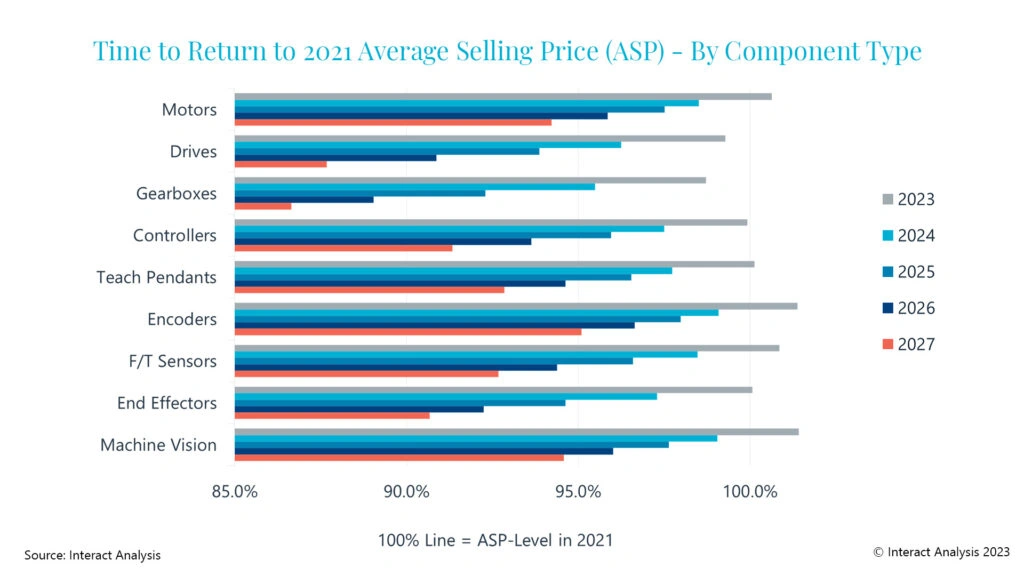
A recent report by Interact Analysis stated that global demand for basic components in industrial robots hit a $12.1 billion threshold in 2022, indicating a 14.7 percent year-on-year growth. In this regard, the report concluded that the bulk of the production was mainly seen in collaborative and SCARA robots. The component market is said to slow down as the robot market matures and stabilizes in the coming years. The market for industrial robot components, however is likely to increase by 8.8 percent annually during the 2022 to 2027 period.
Key Components of Robots
| Components | Function |
|---|---|
| Sensors | Detects environmental changes and provides data to the control system. |
| Actuators | Convert energy into movement, enabling physical actions like lifting or rotating. |
| Control System | Acts as the robot's brain, processing sensor data and sending commands to actuators. |
| Power Supply | Provides the energy needed to power the robot’s functions, such as batteries or solar power. |
| Chassis | The physical structure that houses the robot’s components and ensures stability. |
| Software | Runs the algorithms that guide the robot’s behavior, ensuring task execution. |
| User Interface | Allows humans to interact with the robot, controlling or monitoring its functions. |
| Communication System | Enables the robot to communicate with other systems or devices, facilitating data exchange. |
| Mechanical Parts | Enable movement, gripping, turning, and lifting through motors, pistons, and gears. |
| Manipulator | Acts as the robot's flexible arm with joints and links for various tasks. |
| End Effectors | Tools at the manipulator’s end for interacting with the environment, like gripping or welding. |
| Locomotion Device | Motors that allow movement, using wheeled or tracked systems. |
| Feedback Devices | Monitor performance and ensure accurate task completion. |
Other Components
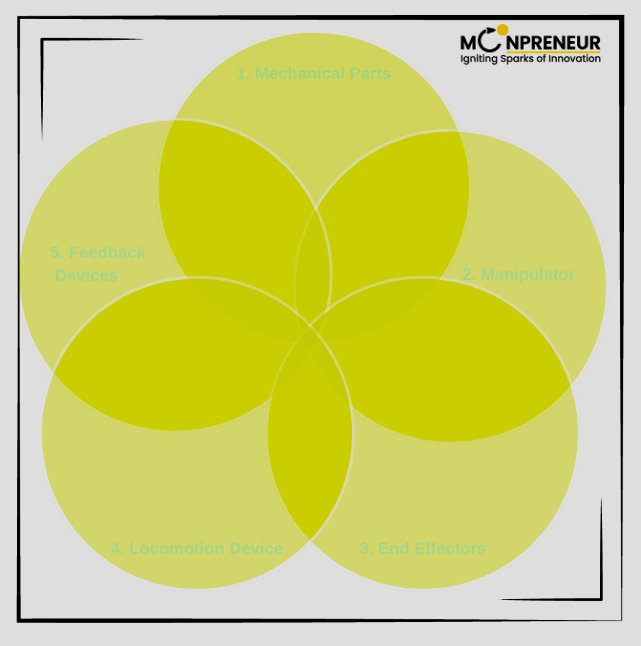

1. Mechanical Parts
The mechanical parts are the fundamental components of a robot that provide the movement and interaction with the environment. The subcategories under this category are as follows:
- Motors: This provides power to various movements.
- Pistons: Converts fluid pressure into linear motion.
- Grippers: It helps in the gripping and manipulation of objects.
- Wheels: They enable the movement across surfaces.
- Gears: Change the direction and speed of motion and facilitate power transfer effectively.
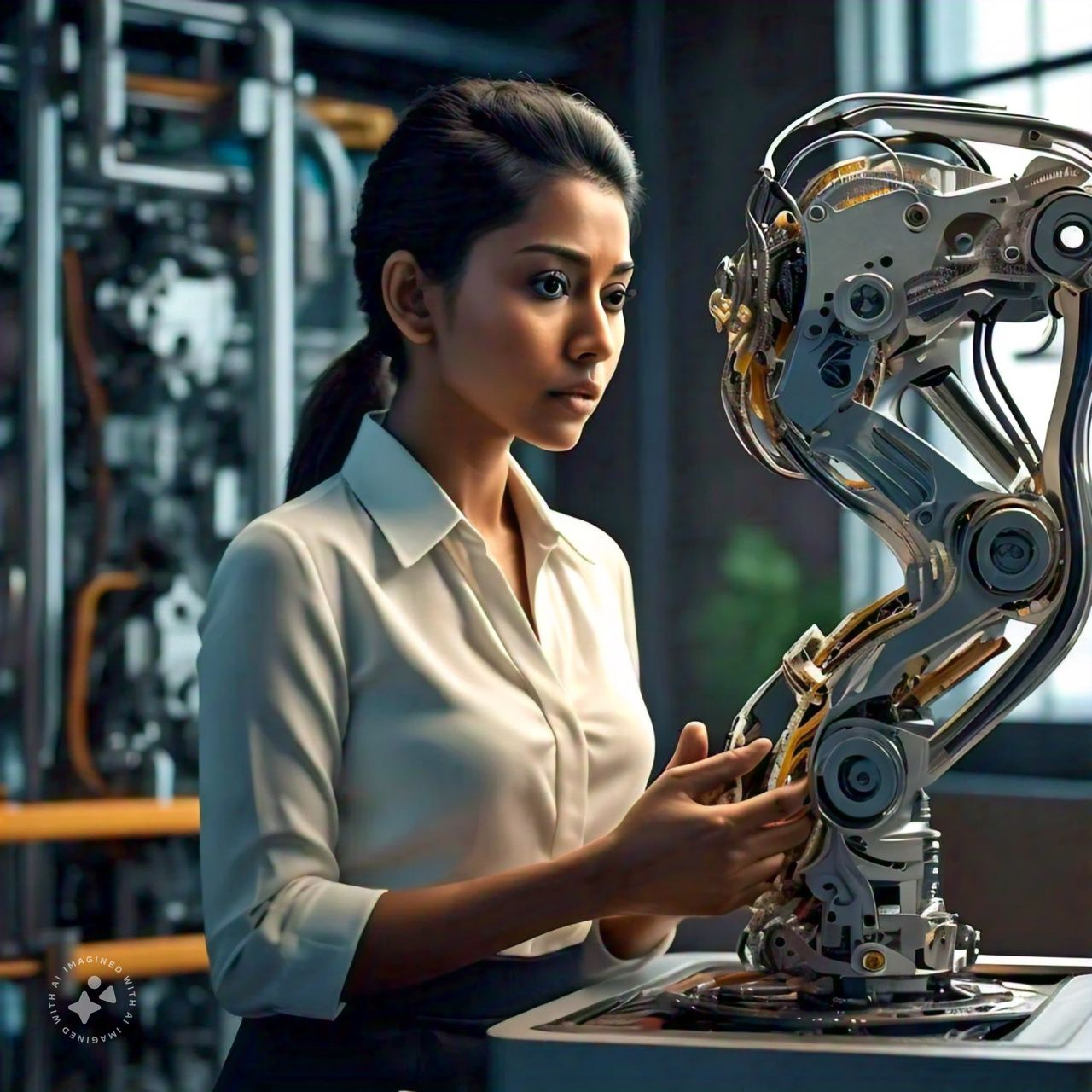

2. Manipulator
A manipulator behaves like an arm of a robot, because its design comprises different joints and links which facilitate mobility. Main points:
- The arm is equipped with several joints through which the entire arm is directed to the preferred movement; similarly, human arms are fitted with the elbow or knee.
- Links Connect The joints that give the manipulator its form and length. A manipulator can serve a lot of different tasks, including reaching and lifting or rotating, much like a human arm does.
3. End Effectors
These are tools affixed to the end of the manipulator, allowing the robot to directly interact with its environment. Examples include:
- Grippers: Used to pick up or move material.
- Welding Torches: For joining materials together.
- Surgical Instruments: Used in medical applications for precise operations.
These tools are necessary to perform tasks effectively and accurately, thus making robots versatile in various applications.

4. Locomotion Device
A locomotion device is an essential part of a robot that performs the movement of the robot. It consists of motors and mechanisms that enable the robot to navigate its environment. Types include:
- Wheeled Drives: These drives employ wheels for motion and offer a smooth movement along a flat ground, which make them suitable for indoor and level outdoor surfaces.
- Tracked Drives: With this drive system, the robot can move through rugged or rough grounds. It is an important part of the mobility of robots since it makes it possible to position the robots appropriately for certain operations.

5. Feedback Devices
Feedback devices, the vigilant eyes of the robot, monitor its operations and confirm that tasks have been completed as intended. They provide crucial information to the controller, ensuring the robot’s:
- Performance: Ensuring the robot is functioning correctly.
Accuracy: These appliances are the guarantors of accuracy. Such devices check all work being conducted as necessary to be performed correctly. They can help keep running integrity and have robots learn throughout their processes by adjusting their process to improve. This is also an indication that technology has strong powers.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, a robot is more than just parts; the key components of robotics come together to create a machine that can perform complicated tasks. With technology advancing day by day, robotics for kids is becoming more important as it will prepare the next generation to understand and build versatile robots that will play pivotal roles in our future lives.
Moonpreneur offers a tailored robotics program. Book a free 60-minute workshop today and introduce them to the fantastic world of robotics and innovations!

























It reminded me of a robotics competition I participated in where we had to design a maze-solving robot. The most challenging part was fine-tuning the sensors to navigate accurately and integrating them with the control system. It really hit home how crucial it is for all the components like sensors, actuators, and programming, to work seamlessly together. It was a rewarding experience and deepened my appreciation for how complex and interconnected robotics truly is.
I’m curious to know when it comes to integrating sensors with actuators in a robot, what are some of the biggest challenges students face in ensuring they work together seamlessly? Is there a specific technology or approach that’s helping to improve this integration?
Thank you for sharing your curiosity!! Integrating sensors with actuators can be challenging as it requires precise coordination for real-time responses. A major hurdle is minimizing latency between sensor data and actuator actions to avoid delays in movement. Sensor fusion, where data from multiple sensors is combined, helps improve accuracy and decision-making. Additionally, advanced control algorithms ensure smoother coordination. At Moonpreneur, we focus on hands-on projects that give students the chance to experiment with these technologies and see how sensors, actuators, and control systems work together in real-world applications.