
Update: This article was last updated on 9th January 2026, to reflect the accuracy and up-to-date information on the page.
STEM and STEAM aren’t necessarily really brand new concepts if you think about it. However, lately, more and more individuals have been paying greater attention to both being important. STEM vs STEAM are held as distinctive and worthwhile for understanding and integrating diverse varieties of learning modes.
Teachers view these two ideas as something essential for addressing actual issues in the world. In the United States alone, over 10 million individuals are employed in the field of STEM, accounting for the nation’s 6.6% of labor force. This stat alone is a testament to how important STEM and STEAM are in the professional line graph of any given person.
Recommended reading: STEAM is the Way to Go
Utilizing STEAM allows instructors to embrace project-based instruction. It goes beyond the five disciplines, creating an opening to a friendly learning process.
In contrast to the traditional learning structures, educators using the STEAM vs STEM model combine various disciplines. They utilize the synergy of modeling procedures and mathematical and scientific concepts.
Before we get to which learning principle is superior, you need to understand the difference between STEM or STEAM. Knowing STEM vs STEAM education is important for choosing the right learning strategy. Is STEAM superior to STEM? This has been a matter of debate in the education field. Learning about STEAM and STEM enables students to acquire problem-solving skills by incorporating creativity and innovation.
What is STEM and STEAM? Both these methods of education focus on distinct methodologies, but both are integral to education in today’s world.
Recommended reading: 6 Ace STEAM Jobs in the Future
What is STEM?
STEM education, which encompasses mathematics, science, technology, and engineering, equips professionals with a range of skills that enable them to excel in the contemporary global economy and also raises an important question— how do you introduce kids to stem-as the broad curriculum incorporates subspecialties in statistics, biology, psychology, economics, agriculture, and aeronautics as well as mainstream subjects. Since STEM fields are ever-evolving, employers require not only discipline-specific knowledge but also adaptability to respond to emerging demands.
In recent years, the debate of STEM vs STEAM has gained attention, emphasizing the importance of integrating arts into the traditional STEM fields. The shift from STEM to STEAM—where ‘A’ stands for Arts—aims to foster creativity alongside technical expertise. This raises questions like is STEAM better than STEM or whether STEM and STEAM can coexist to provide a balanced education.
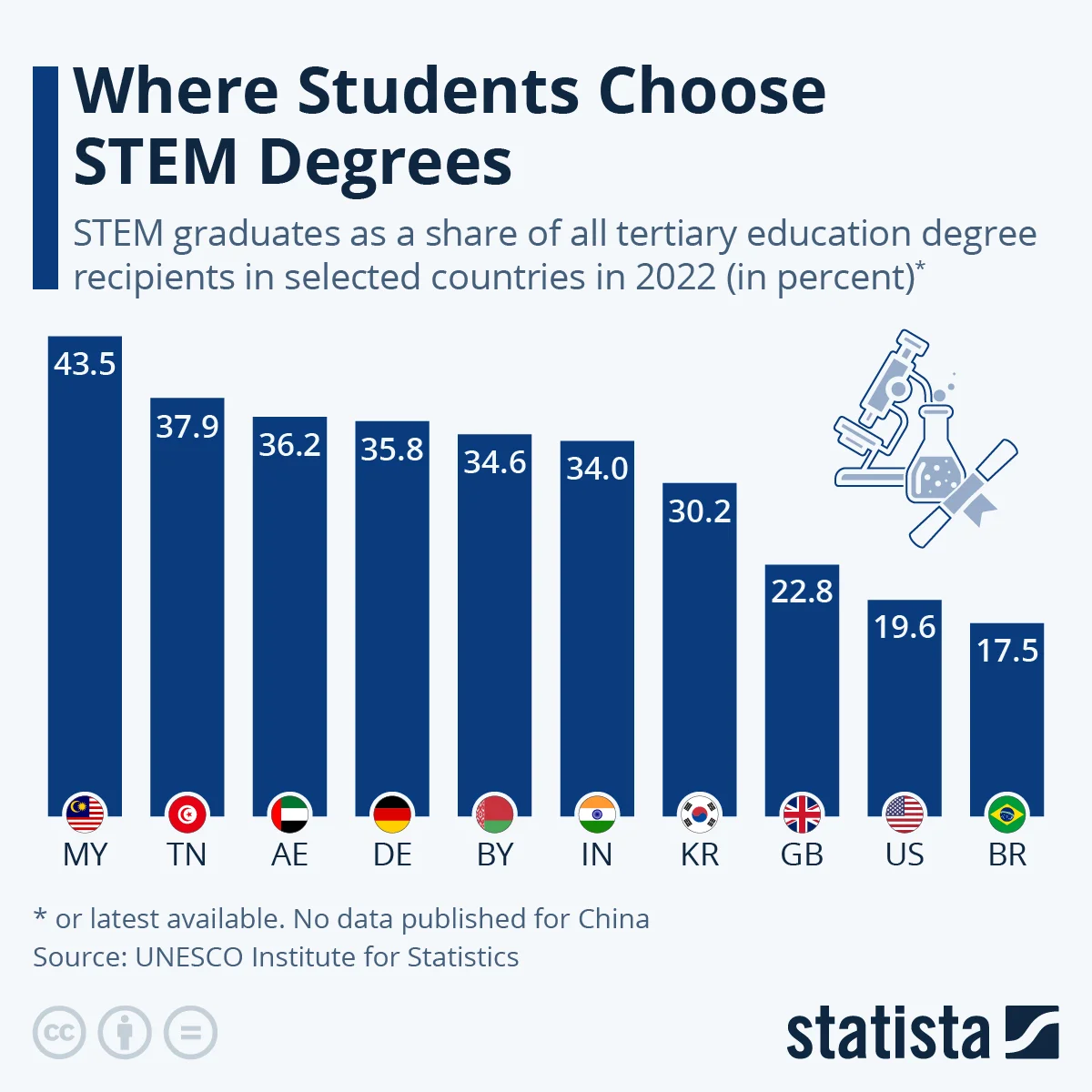
STEM graduates are highly sought after across the globe but are still insufficient to match demands. Nations are attempting to widen the number of students studying STEM to serve expanding sectors such as technology and medicine. Malaysia and Tunisia have the highest rates of STEM graduates, at approximately 40% to 43.5%. India also has a high proportion of STEM students due to its huge population. But statistics for China are ambiguous, and various sources provide different graduation numbers. There are a lot of STEM graduates in the United Arab Emirates, Germany, Belarus, and South Korea, too. Western Europe and the Americas have smaller percentages of STEM graduates, demonstrating the popularity of STEM education differs globally.
The ever-evolving nature of STEM careers provides unique challenges despite the clear advantage.
It is stated by the National Bureau of Economic Research that the employment scenario is constantly shifting because of the fast-paced advances in technology. Hence, not only subject-specific knowledge should be given emphasis but also flexibility and broad-basedness, which are necessary for adjustment to new conditions.
With increasing debate regarding STEM or STEAM, most teachers and policymakers are considering whether STEAM versus STEM education presents a more future-oriented strategy. While STEM STEAM variations emphasize the place of arts in innovation, both streams attempt to provide students with essential problem-solving abilities.
Recommended reading: How has the Industrial Revolution Shaped Education? Why STEM Learning Is the Need of the Hour?
What is STEAM?
A reaction to the increasing emphasis on soft skills in all industries, STEAM education naturally integrates the arts into the STEM model. The Conversation states that creative skills and knowledge of the arts, including literature, history, and design, are essential for inspiring STEM employees to think creatively and solve problems innovatively.
The STEAM vs STEM controversy brings to light how the STEAM-oriented curriculum widens the horizon of learning by incorporating the humanities, language arts, dance, theater, music, visual arts, design, and new media. Consistent with the views of senior executives, this diverse approach not only responds to existing workforce trends but also to their own preference—57 percent of them value soft skills more than hard skills, according to a 2018 LinkedIn study. In addition, a 2019 LinkedIn study points to the need for creativity, persuasion, and teamwork by listing these as the top three skills that employers seek in prospective employees.
As debate over STEM vs STEAM education rages on, most teachers and businesspeople wonder: Is STEAM superior to STEM? Integrating arts in STEAM and STEM education encourages a balanced set of skills that meet workforce needs. Knowing what is STEM and STEAM are enables students and professionals to make educated choices about their academic directions, allowing them to acquire both technical knowledge and critical soft skills.
Recommended reading: The Power of STEM Education in Shaping the Future
To develop a complete mind: Study the science of art; Study the art of science. Learn how to see. Realize that everything connects to everything else.
- Leonardo Da Vinci
In fact, some schools implement the STEAM learning approach to seamlessly integrate the arts into STEM education. This holistic approach ensures that apart from the STEM core courses, students are also trained in the humanities, language arts, dance, theater, music, design, and new media. The intentional integration of different disciplines aims to enhance the employability of students by providing a well-rounded skill set that balances the technical knowledge of STEM with the basic soft skills needed by the modern workforce.
This begs the question: STEM vs STEAM, which method is more effective for today’s education? The STEAM vs STEM debate centers on whether or not adding the arts does improve learning results or if just STEM is adequate. Some instructors believe that either STEM or STEAM should be selected based on students’ professional goals, but others feel that both STEM and STEAM produce a better-rounded education. Knowing what STEM and STEAM is enables parents and teachers to make sound choices regarding curriculum options. Finally, the debate regarding STEM vs STEAM education hinges on one question: Is STEAM superior to STEM when it comes to driving innovation and employability?
Recommended reading: Santa Loves STEM: Christmas Activities For Kids
STEM vs. STEAM: How are they different?
The differences between STEM and STEAM lie in how each approaches scientific concepts. Focused on hard scientific, technical, engineering, or mathematical skills, STEM attempts to contribute to increased understanding or new concepts. STEAM, however, as discussed by The Conversation, takes a more holistic perspective by advocating for the application of both hard and soft skills in solving problems.
Collaboration is key to learning STEM concepts in STEAM education. By integrating concepts of art and artistic practices, STEAM professionals can utilize materials such as fine art images and data visualization to enhance students’ understanding of science, math, and technology. STEAM professionals can utilize 3D printers to develop new products or to break down complex data sets into easy-to-understand forms such as infographics by employing this unconventional method of problem-solving.
In short, STEM and STEAM are two distinct methods of science. STEM emphasizes applying hard scientific abilities to resolve problems in the real world, whereas STEAM applies both hard and soft abilities to resolve challenges. Individuals work together to understand STEM concepts within the context of STEAM, employing tools like data visualization to enhance math and science understanding. This type of creative thinking not only promotes creativity but also facilitates the simplification of hard facts.
Moreover, the debate regarding “STEM vs STEAM education” arises with a question: Is STEAM superior to STEM? While both STEM and STEAM target problem-solving, STEAM brings artistic elements onboard to enrich critical thinking and creativity. “What is STEM and STEAM” can provide information to educators that will assist in determining which route is ideal for their teaching goal. Incorporation of STEAM into STEM makes education better-balanced in acquiring analytical as well as creative expertise.
Similarities between STEM and STEAM
Both STEM and STEAM believe in integration, i.e., they do not teach all the subjects individually but emphasize comprehensive education. This is how real-life problems are solved by keeping in mind all the various factors and viewing the problem as a whole.
By integrating various skills, one can become a more skilled and competent person.
This STEM vs STEAM comparison shows the significance of cross-disciplinary learning. Whether STEM or STEAM, both methods seek to cultivate problem-solving and critical thinking skills. Most educators argue “Is STEAM better than STEM?” since STEAM incorporates the arts, encouraging creativity in addition to technical understanding. Knowing what STEM and STEAM is aids in making educational decisions. The debate on STEM vs STEAM education continues to influence contemporary learning strategies.
Is STEAM better than STEM?
When it comes to the STEM vs STEAM debate, it’s important to recognize that there are opportunities for growth in STEM and STEAM fields, including science, tech, engineering, arts, and math. Choosing between the two—STEM or STEAM—should be based on your individual skills, career aspirations, and interests. The emergence of STEAM and STEM has highlighted the importance of having a broad skill set that encompasses both hard skills and soft skills.
As jobs evolve and technology alters the nature of work, LinkedIn emphasizes the need for soft skills training. Soft skills are critical to success in a world of AI and technology where machines cannot imitate human traits like leadership and teamwork.
Most STEM vs STEAM education professionals find it challenging to hone soft skills due to the emphasis on technology. Nevertheless, personal growth requires soft skills. STEAM vs STEM, however, introduces soft skills to the classroom. It fosters collaboration not only among STEM STEAM disciplines, but with the arts and humanities as well.
This integrated approach acknowledges that various skills are interdependent, equipping students for a wide range of professional roles within an ever-evolving business world. What is STEAM and STEM, and is STEAM superior to STEM? This relies on the mix of technical knowledge and imagination, both of which are essential to modern-day employment.
Opportunities for STEM Careers Are Increasing
The demand for STEM employees is higher than ever in the U.S., with 40% of Americans labeling the shortage a crisis, based on a survey by technology and engineering firm Emerson. The survey also revealed that the need for STEM jobs is increasing at a faster rate than the available talent. Based on a Deloitte report, the manufacturing skills gap alone could generate 2.4 million new unfilled positions between 2018 and 2028.
Forecasts indicate that career opportunities in the STEM fields are likely to increase considerably for many types of careers. Information security analysts can expect a 28% increase in career opportunities from 2016 through 2026, based on data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Similarly, employment within other STEM fields, including statistics and mathematics, is also projected to increase considerably by 33% by the same period.
Types of careers you can pursue in STEAM
Numerous careers come under the STEAM category. Few of the most sought-after ones are Graphic designers, Software developers, architects, biomedical engineers, animators, data scientists, game designers, musicians, environmental scientists, fashion designers, and so on.
Wrapping Up
Although you might feel that your kid should study more on STEM than STEAM for various reasons, you need to try to make your child pursue their heart and objectives. It’s a good thing for children to know that they can be analytical and creative simultaneously. STEAM makes this possible by showing them how to utilize both sides of their brain to find solutions. Using STEAM to learn, children will be well equipped for their future professions regardless of the type of work they wish to pursue.
As things get more complex in jobs and technology alters everything, it is very essential to learn soft skills. New courses that teach STEM skills such as leadership, communication, and collaboration will enable individuals to excel in an A.I.- and technology-driven world. These are skills that you can’t rely on the machines to do, so humans must learn them to keep up with industry demands.
Want to future-proof your child with Robotics? Moonpreneur has a customized program for you. Book a seat in our free 60-minute workshop today and acquaint them with the wonderful world of robotics and innovations!
























Does the integration of arts in STEAM truly enhance innovation more than the traditional STEM approach?
The integration of arts in STEAM fosters diverse perspectives and creativity, enriching problem-solving and innovation beyond what traditional STEM education alone can achieve.
In terms of long-term career success and adaptability, do STEAM graduates have an edge over STEM graduates?
STEAM graduates often possess versatile skills, blending creativity with technical expertise, offering an edge in adapting to diverse career demands and fostering innovative solutions.