As of 2022, the International Federation of Robotics (IFR) estimated that approximately 3,903,633 industrial robots were operational worldwide.
An industrial robot is a specialized robotic system employed in manufacturing processes. These robots are automated, programmable, and equipped with the capability to move along three or more axes.
Common tasks performed by industrial robots include welding, painting, assembly, disassembly, pick-and-place operations for printed circuit boards, packaging and labeling, palletizing, product inspection, and testing. They execute these tasks with remarkable endurance, speed, and precision, often aiding in material handling.
This evolution in industrial robotics also underlines the importance of robotics for kids, a field that prepares the next generation for a future where robotics skills will be increasingly essential across various industries.
HISTORY OF INDUSTRIAL ROBOT
The earliest industrial robot fitting the ISO definition was engineered by “Bill” Griffith P. Taylor in 1937 and featured in the March 1938 edition of Meccano Magazine. This crane-like apparatus primarily utilized Meccano components and functioned via a single electric motor.
In 1997, Chris Shute successfully replicated this industrial robot in its entirety.
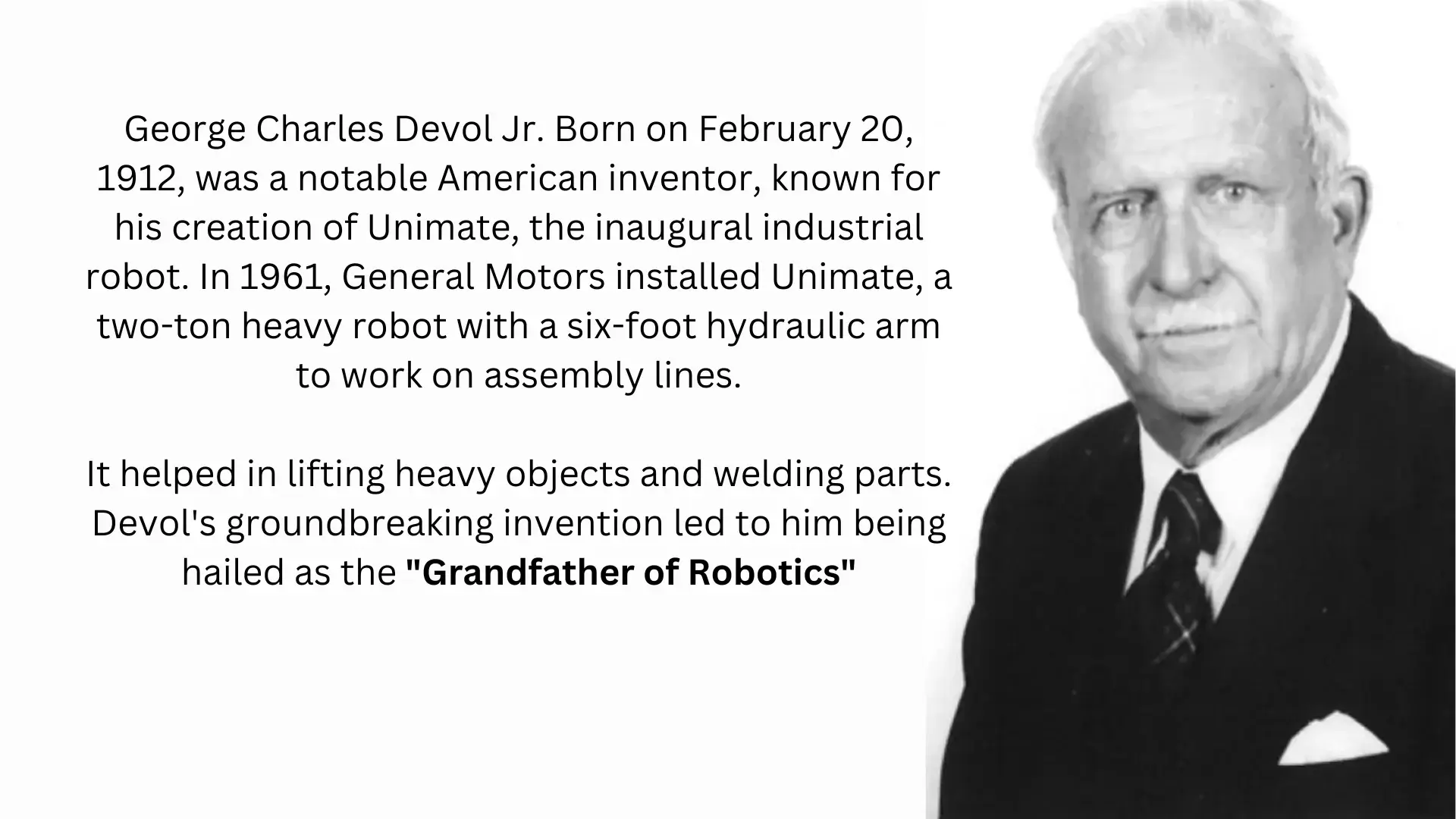
In 1954, George Devol applied for the first patents for robots (approved in 1961). Then, in 1956, Devol and Joseph F. Engelberger started Unimation, the first company to make robots. These industrial robots were also known as programmable transfer machines because they were mainly used to move objects from one place to another, usually within a short distance of less than about twelve feet.
Initially, Cincinnati Milacron Inc. of Ohio posed as Unimation’s major competitor, but the landscape underwent a significant shift in the late 1970s with the emergence of several major Japanese conglomerates manufacturing similar industrial robots.
Similar Blog : TOP ROBOT FOR TRADING FOREX
TYPES OF INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
These are just some of the common types of industrial robots available as of 2024, and the field of robotics continues to evolve with advancements in technology and engineering.
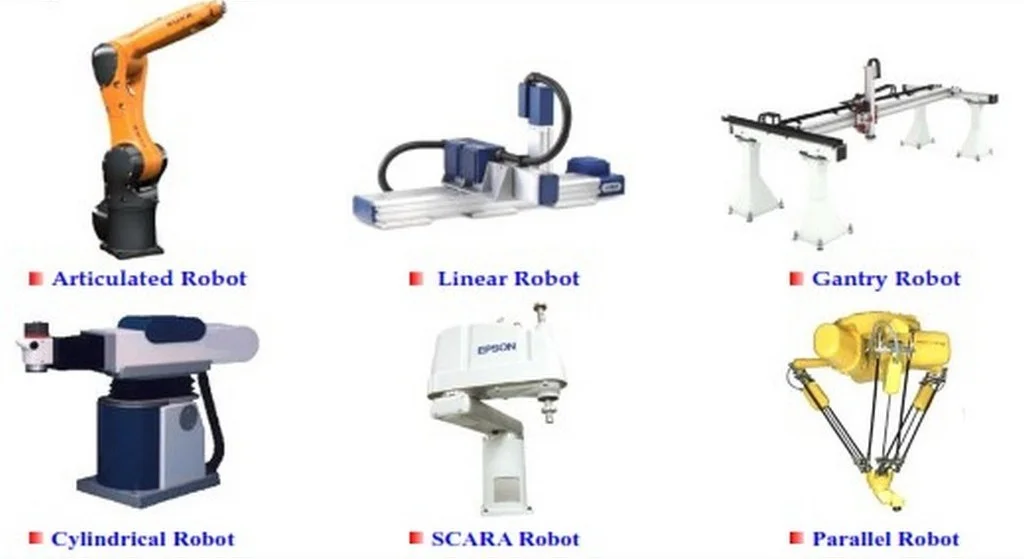
1. Articulated Robots: These robots have rotary joints resembling a human arm, offering flexibility and maneuverability. They are commonly used for wielding, assembly, and material handling.
2. Cartesian (Gantry) Robots: Cartesian robots feature three linear axes of motion, typically moving along orthogonal X, Y, and Z axes. They are well-suited for applications requiring precise, linear movements, such as pick-and-place operations and CNC machining.
3. SCARA Robots: Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm (SCARA) robots have two parallel rotary joints for horizontal motion and one linear joint for vertical motion. They excel in tasks like assembly, packaging, and inspection due to their speed and precision.
4. Delta (Parallel) Robots: Delta robots utilize parallelograms to control the movement of the end effector, offering high-speed operation and accuracy. They are commonly employed in tasks like packaging, sorting, and food processing.
5. Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Collaborative robots are designed to work alongside humans in a shared workspace safely. They feature advanced sensors and programming to enable safe interaction with human workers, facilitating tasks such as assembly, inspection, and machine tending.
6. Cartesian Robots (Linear Robots): Similar to gantry robots, Cartesian robots operate along linear axes but may have fewer degrees of freedom. They are suitable for applications requiring precise linear movement, such as material handling and pick-and-place tasks
7. Mobile Robots: These robots are equipped with mobility capabilities, allowing them to navigate autonomously within a defined workspace. They are often used for tasks like material transport, inventory management, and surveillance in industrial settings.
8. Dual-arm Robots: Dual-arm robots feature two manipulators, enabling them to perform more complex tasks with dexterity and efficiency. They are utilized in applications requiring intricate assembly, manipulation, and handling of objects.
9. Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): AGVs are mobile robots designed for transporting materials or products within a factory or warehouse environment. They navigate using predefined paths or by following markers on the floor, contributing to automated material handling processes.
The role of industrial robots in revolutionizing manufacturing
The role of industrial robots in revolutionizing manufacturing cannot be overstated. Industrial robots play a crucial role in revolutionizing manufacturing by increasing efficiency, improving quality, reducing costs, enhancing flexibility, automating complex tasks, ensuring safety, and enabling data-driven decision-making.
As technology continues to advance, the role of industrial robots in manufacturing will only continue to grow, driving further innovation and efficiency gains in the industry.

These advanced machines have transformed manufacturing processes across various industries in numerous ways:
i. Increased Efficiency: Industrial robots work tirelessly, without breaks or fatigue, leading to increased productivity and efficiency in manufacturing operations. They can perform tasks at a consistent speed and with precision, resulting in higher output levels.
ii. Improved Quality: Robots can execute tasks with a high degree of accuracy, leading to improved product quality and reduced defects. This precision ensures that each product meets stringent quality standards, enhancing customer satisfaction.
iii. Cost Reduction: While the initial investment in industrial robots may be significant, they often lead to long-term cost savings. Robots can replace manual labor in repetitive and hazardous tasks, reducing labor costs, minimizing workplace injuries, and lowering overall manufacturing expenses.
iv. Flexibility and Adaptability: Industrial robots can be reprogrammed and reconfigured to perform a wide range of tasks, providing manufacturers with greater flexibility to adapt to changing production demands and market requirements. This adaptability allows for quicker setup times and smoother transitions between different manufacturing processes.
v. Automation of Complex Tasks: Robots can handle complex tasks that may be difficult or impossible for humans to perform consistently or safely. This includes tasks such as precision welding, intricate assembly, and handling of delicate materials, thereby expanding the capabilities of manufacturing operations.
vi. Enhanced Safety: By taking on hazardous or physically demanding tasks, industrial robots contribute to improved workplace safety. They can operate in environments with high temperatures, toxic fumes, or other dangers, reducing the risk of injury to human workers.
vii. Data Collection and Analysis: Modern industrial robots are equipped with sensors and data collection capabilities, allowing manufacturers to gather real-time information about production processes. This data can be analyzed to identify inefficiencies, optimize workflows, and make data-driven decisions to improve overall manufacturing performance.
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
When contemplating the integration of industrial robots into your production line, it’s essential to weigh both the benefits and drawbacks beforehand. Here, we discuss the advantages and disadvantages of utilizing industrial robots.
Advantages of Industrial robots
a. Increased Efficiency: Robots complete tasks faster and with higher accuracy, automating processes and enhancing production line efficiency.
b. Improved Quality: With precise operations, robots produce higher-quality products, reducing the need for extensive quality control.
c. Enhanced Working Environment: Robots handle dangerous or repetitive tasks, improving workplace safety and conditions for human workers.
d. Increased Profitability: By boosting efficiency, reducing resource usage, and ensuring higher quality, robots contribute to higher profitability.
e. Longer Working Hours: Robots operate continuously, increasing output and productivity compared to human workers with breaks and distractions.
f. Prestige: Operating with robots showcases technological advancement, boosting brand image and market reputation.
Disadvantages of Industrial Robots
Despite their benefits, industrial robots pose some challenges:
a. Capital Cost: Implementing robots requires a significant initial investment, although they typically offer positive returns on investment over time.
b. Expertise Requirement: Setting up and programming robots demands specialized training and expertise, often requiring support from automation companies.
c. Limitations: While robots excel in many tasks, there are limitations to their capabilities. Companies must carefully assess options and integrate surrounding systems for optimal performance.
FINAL THOUGHT
In the future of manufacturing, industrial robots will remain pivotal. Predicted trends include AI and machine learning integration for adaptability. Collaborative robots (cobots) will expand, enhancing productivity. IoT technology will optimize real-time data analysis. Industrial robots promise improved efficiency, productivity, and safety, driving digital transformation. Overall, industrial robots will lead Industry 4.0, revolutionizing manufacturing efficiency.
Want to make your child future-ready with Robotics? Moonpreneur offers a tailor-made program. Reserve a spot in our free 60-minute workshop today and introduce them to the amazing world of robotics and innovations!


























Can you name any industrial robot that can be used in 3D printing?
The cartesian robot is the most commonly used industrial robot for 3D printing.
How many robots are used in manufacturing?
It is estimated that there are approximately 3.4 million industrial robots in use worldwide