In recent years, technological advances have revolutionized the disaster response landscape. One of the key players in this transformation is robotics, which plays a critical role in improving emergency response efficiency, safety, and effectiveness. In this blog post, we will explore the changing landscape of robotic technology in disaster management and its applications, as well as how it impacts real-world situations.
The Role of Robots in Disaster Relief
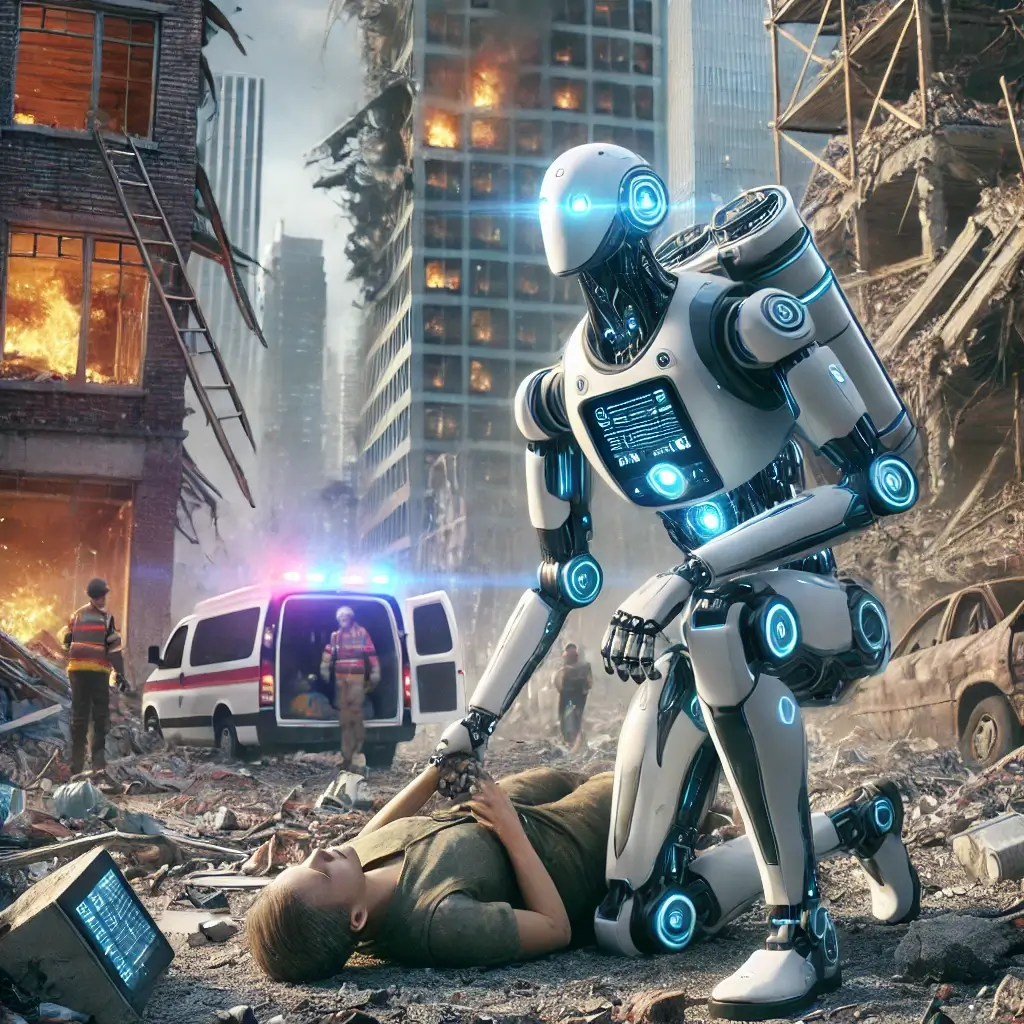
Disaster response is one of the most difficult and dangerous jobs in the world. The growing use of robots in disaster response is due to their versatility and ability to significantly reduce the risk of injury to human responders. Innovative robotic solutions are being developed for various disaster response applications.
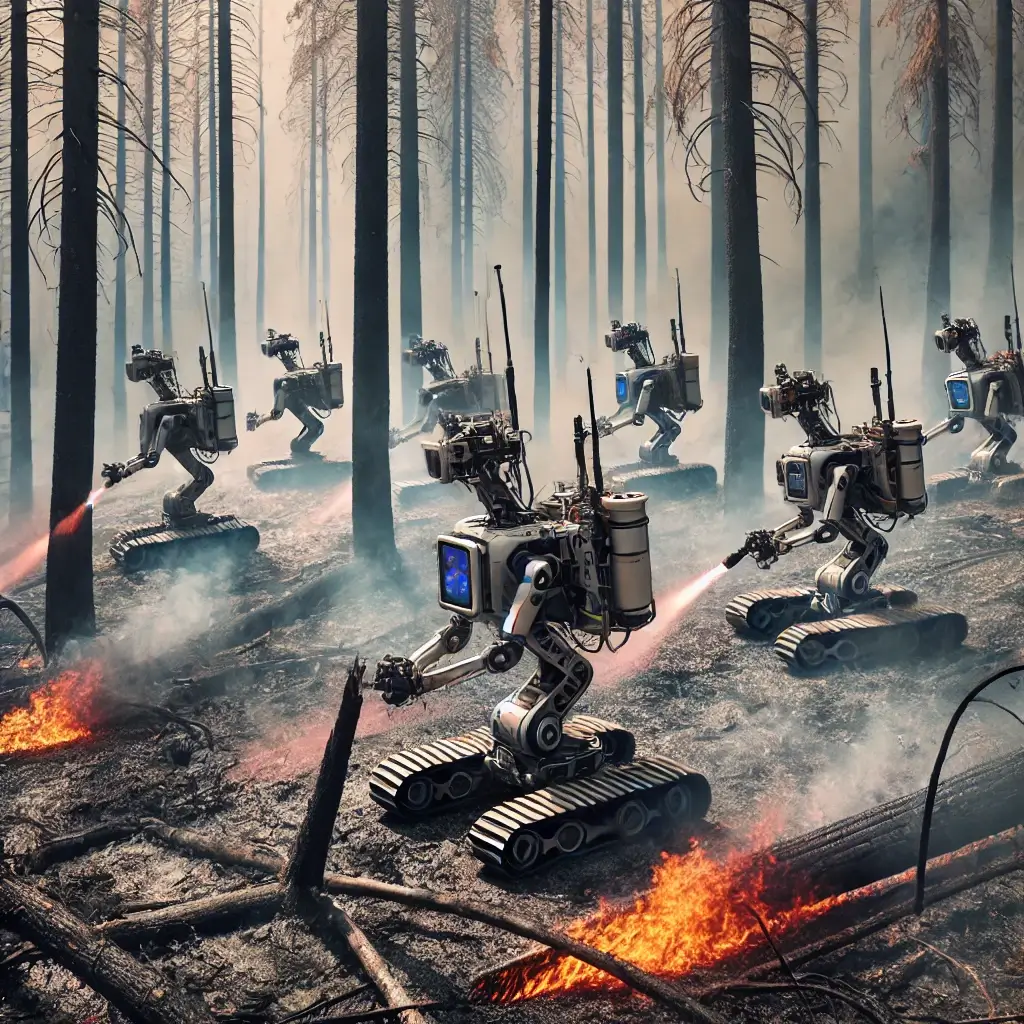

1. Operational Search and Rescue:
One crucial aspect where robots shine is in search and rescue operations. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) equipped with advanced cameras and sensors swiftly survey disaster-affected areas, providing real-time information. Drones enable emergency responders to locate survivors and assess damage across vast regions, enhancing operational efficiency.
2. Ground Robots for Hazardous Environments:
In hazardous conditions where human interaction is unsafe, ground robots come to the forefront. Tailored for maneuvering through perilous environments, these robots leverage cameras, sensors, and even robotic arms to find and recover survivors while minimizing risks to human rescue crews.
3.Communication and Data Collection:
Robotic systems with communication devices establish and maintain connections in disaster-affected areas, crucial where traditional networks may be compromised. These robots not only gather vital information such as environmental conditions and structural integrity but also ensure rescuers can make informed decisions.
4. Medical Assistance:
Robots are increasingly contributing to providing medical help in catastrophic situations. Telepresence robots, equipped with cameras and displays, enable remote communication between doctors and patients. This facilitates initial treatment and advice until on-site medical aid becomes available, proving invaluable in scenarios where quick access to medical staff is limited.
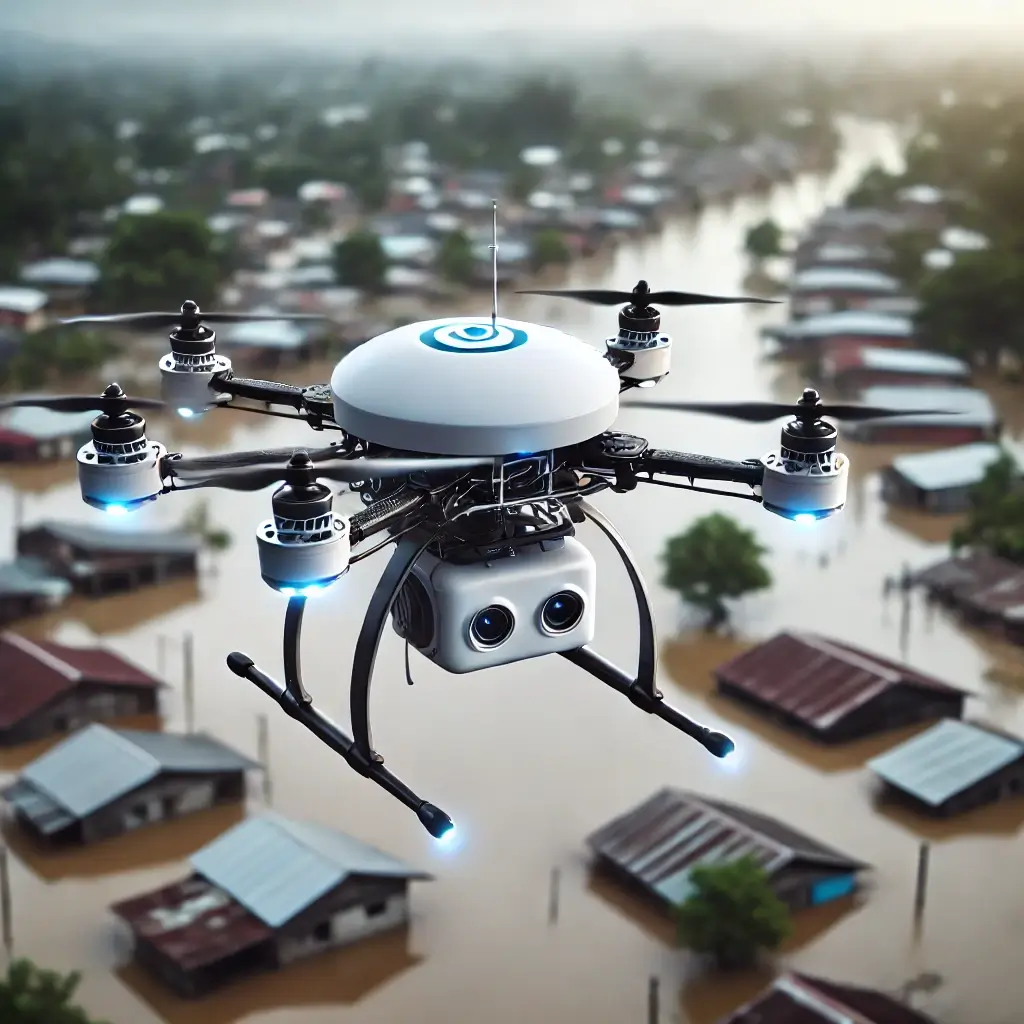

5. Logistics and Supply Delivery:
Ensuring swift delivery of essential supplies to impacted areas is vital for disaster relief. Drones and ground robots transport medical supplies, food, and other necessities to hazardous or hard-to-reach locations, overcoming accessibility challenges for human rescuers.
6. Instruction Simulations:
Robotic catastrophe simulations play a crucial role in training emergency responders. These simulations provide a controlled environment for responders to hone their skills, enhancing their decision-making abilities and familiarizing them with the technologies used in real-world disaster response operations.
Recommended reading: Things To Look For In Coding Classes For Kids In Toronto- A Comprehensive Guide
Benefits of Robotics in Disaster Response
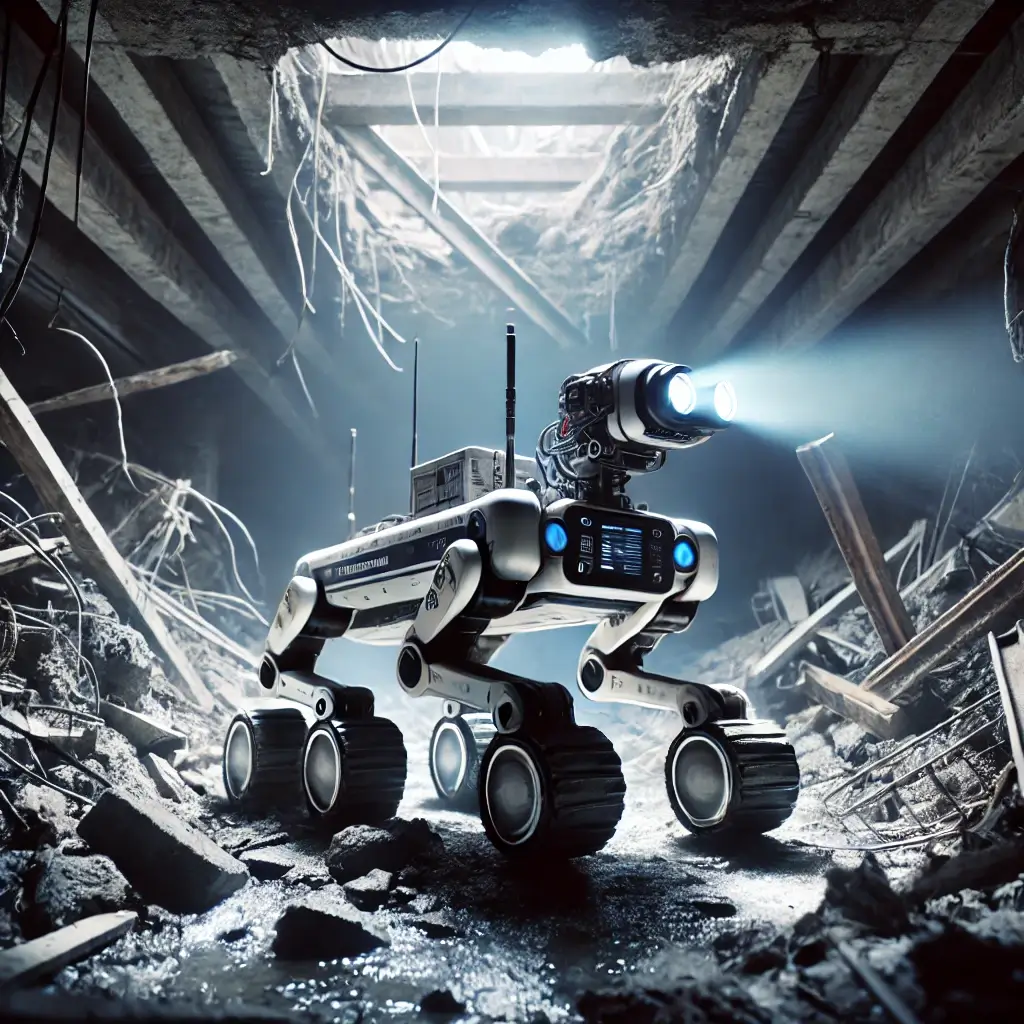

Robots bring several advantages to disaster relief efforts:
- Enhanced Safety: Robots perform tasks in hazardous situations, reducing the risk to human responders.
- Enhanced Capabilities: Equipped with various sensors and instruments, robots can tackle challenges that may be difficult or impossible for humans.
- Enhanced Productivity: Robots work persistently and efficiently, accelerating relief efforts and potentially saving more lives.
Recommended reading: The Rise of Soft Robotics: Revolutionizing Automation for the Future.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While the benefits of using robots in disaster response are evident, challenges persist. Creating durable and reliable robots for dangerous situations and ensuring their safe and effective use by first responders are ongoing concerns. Nevertheless, the field of robotics in disaster response is rapidly advancing, with ongoing improvements making robots more sophisticated and affordable.
Examples of Robot Success Stories
Several recent tragedies underscore the utility of robots in disaster response:
- Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident (2011): Robots were deployed to examine damage within the damaged reactors and collect hazardous material samples.
- Mexico City Earthquake (2017): Robots were instrumental in locating survivors by investigating damaged structures.
- COVID-19 Epidemic (2020): Robots played a crucial role in cleaning public areas and delivering food and supplies to hospitalized patients.
These examples demonstrate the invaluable contribution of robots in responding to disasters. As technology continues to advance, robots are poised to play an increasingly vital role in preserving property and saving lives in the aftermath of disasters.
Conclusion: Robots are becoming increasingly popular in disaster relief, and it’s easy to see why. Compared to humans, robots are more efficient, safe, and capable. But there are still challenges to overcome, like how to make robots reliable in dangerous situations and make sure they’re used safely. Robots are already playing an important role in disaster response around the world, and as technology advances, they’ll become even more important.
Moonpreneur is on a mission to disrupt traditional education and future-proof the next generation with holistic learning solutions. Its Innovator Program is building tomorrow’s workforce by training students in AI/ML, Robotics, Coding, IoT, and Apps, enabling entrepreneurship through experiential learning.

























You missed to add the psychological impact of robots in disaster response. Social robots provide emotional support, reassurance, and guidance, complementing human responders. Integrating robots with mental health professionals can enhance psychological support services, promoting community resilience and recovery.
I witnessed firsthand the impact of robots in disaster response during the COVID-19 pandemic. My sister, who is a nurse, has worked in a hospital that deployed robots to disinfect patient rooms and deliver supplies. These robots significantly reduced exposure risks for healthcare workers and improved efficiency.