A basic term in physics, the electromagnetic spectrum defines the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. It covers the tremendous range of wavelengths and frequencies, from the very long radio frequencies to the extremely short wavelengths of gamma rays. Proved very handy in a lot of spheres, ranging from communication and health services to space search and other ones. In the current blog, the components of electromagnetic spectrum, and the real time application, with some case study and statistics shall be discussed by highlighting its crucial aspects.
An Insight into its Components
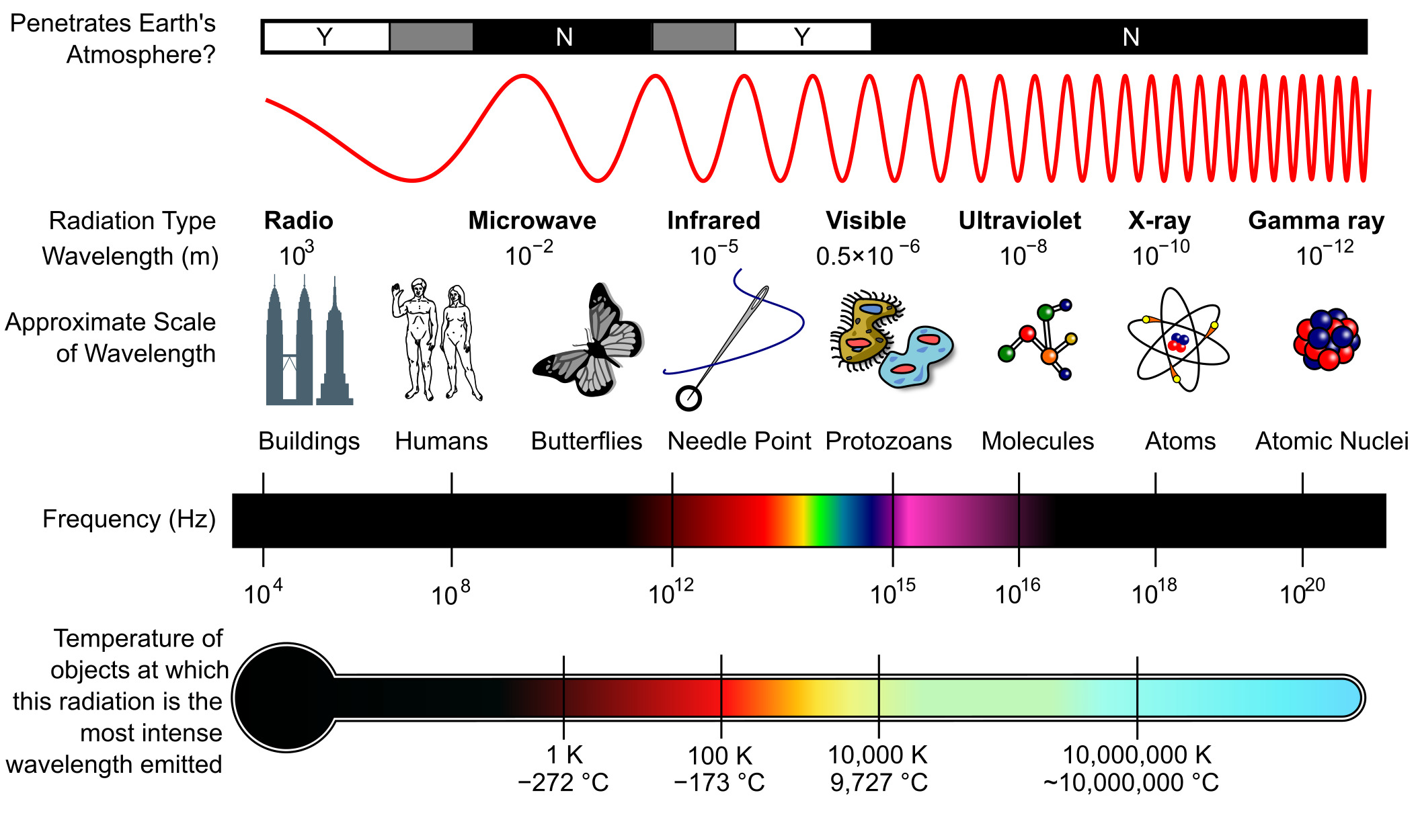
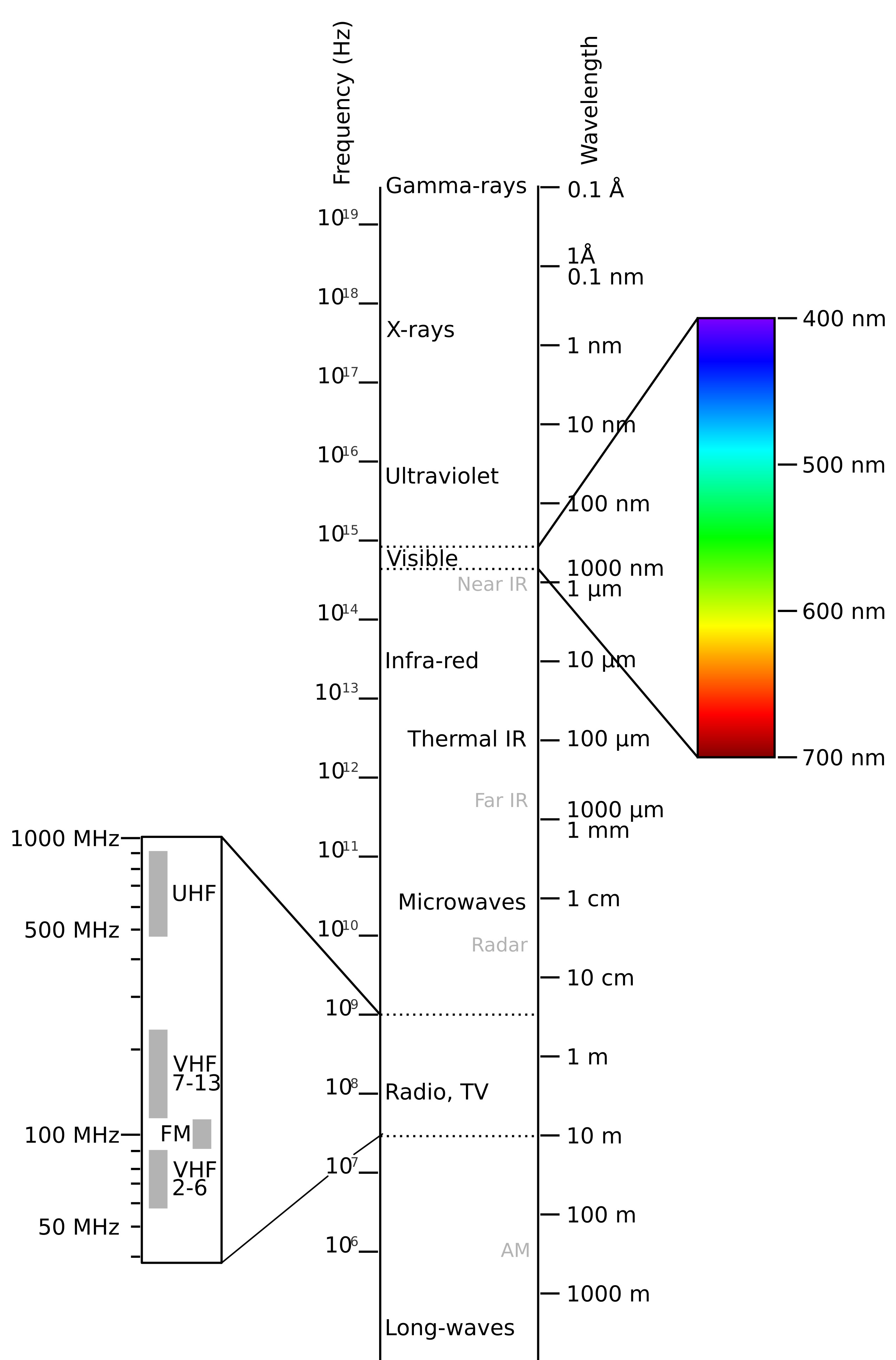
The electromagnetic spectrum has seven major kinds of electromagnetic waves, and each is classified based on its properties and where it applies. These waves have different wavelengths and frequencies; for instance, longer wavelengths correspond to lower frequencies, whereas shorter wavelengths are associated with higher frequencies.
Recommended Reading : Top 50 Science Fair Project Ideas
1. Radio Waves
Radio waves are the ones that have the longest wavelengths within the electromagnetic spectrum. The wavelengths are ranging from a few millimeters to thousands of kilometers. These waves are employed in communication systems like AM and FM radio, television broadcasting, and satellite communications. They are also vital for the technology of GPS.
2. Microwaves
Microwaves are smaller than radio waves and are used in technologies such as microwave ovens, satellite communications, and radar systems. Such waves are utilized in many modes of communication, for example, in Wi-Fi networks, and for detecting objects in weather radars.
3. Infrared Radiation
Infrared waves are a little below visible light in terms of frequency. They have applications in thermal imaging, night vision equipment, and remote controls. Infrared radiation also serves an important heating function. It is also used in different scientific instruments in the measurement of temperature.
4. Visible Light
This encompasses the visible range of electromagnetic waves that human eyes can perceive. These waves are crucial to human vision and have been extensively applied in photography, television, lighting, and many others. Visible light is also fundamental to scientific fields such as optics and astronomy.
5. Ultraviolet Light
UV light is also out of the spectrum of light, barely seen. There are different technologies using UV radiation: from sterilizing processes to tanning beds and blacklight. Even in medicine, UV rays turn out to be useful in the killing of bacteria and viruses harmful to the body.
6. X-rays
X-rays are the higher-frequency electromagnetic waves that have major applications in medical imaging and security screening. These can pass through soft tissues, and so are very essential for non-invasive diagnostics like CT scans and X-ray imaging.
7. Gamma Rays
Gamma rays have the highest energies and the smallest wavelengths of any electromagnetic radiation. They are employed in cancer treatment and in other forms of scientific research. These provide astronomers insight into the cosmos; for example, in a black hole and a supernova context.
Applications in the Real World of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum plays a central role in many technologies that characterise modern life. Let us now consider some important real-world applications:
Telecommunications
It’s greatly important for the telecommunication industry: Radio waves, microwave, millimeter waves form one of the great parts of all mobile networks and Wi-Fi plus satellite communications. The global services market of 5G attained USD 5.53 Billion in the year 2020 and is going to develop through a compound annual growth rate, CAGR of 122.3% from the year 2021 to -2028 according to the expanding desire for much-enhanced robust connections of data.
Health Sector
Electromagnetic waves play a very significant role in medicine, especially in the diagnostic imaging of the body. X-rays and gamma rays enable non-invasive imaging of internal body structures. MRI scans, which rely on magnetic fields and radio waves, are used for over 30 million procedures annually in the U.S. These technologies have increased the speed and accuracy of diagnosis and have improved health care.
Astronomy
Astronomers observe objects within space using the whole electromagnetic spectrum. For instance, the Hubble Space Telescope and Chandra X-ray Observatory collect different wavelengths for the study of phenomena such as cosmic radiation, black holes, and star formation. Our knowledge of the universe would be much weaker without the use of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Defense and Security
The electromagnetic spectrum is used in the defense sector to monitor, communicate, and in electronic warfare. Military forces worldwide have been using radar, infrared sensors, and communication technologies as a strategic edge. Electromagnetic spectrum supremacy is critical in modern defense as the ability to control or interfere with these frequencies can have direct implications on military operations.
Recommended Reading : Science In Kitchen and Art of Eating Well
Case Studies: The Electromagnetic Spectrum in Action
1. Medical Imaging
The most extensive application of electromagnetic waves is medical imaging. MRI and CT scans have transformed the face of diagnostic medicine, with the ability to monitor internal organs and tissues non-invasively. MRI scans are performed over 30 million times annually in the U.S. alone, as this technology plays a vital role in the early detection of diseases.
Recommended Reading : Generative AI in Healthcare
2. Space Exploration
Space agencies like NASA and ESA make use of different frequencies of electromagnetic radiation to study space. For instance, the James Webb Space Telescope detects infrared radiation, which it uses to observe such far-off galaxies, while the Chandra X-ray Observatory gathers information in the X-ray range of the spectrum to gather information about high-energy events, such as the phenomena of black holes and neutron stars.
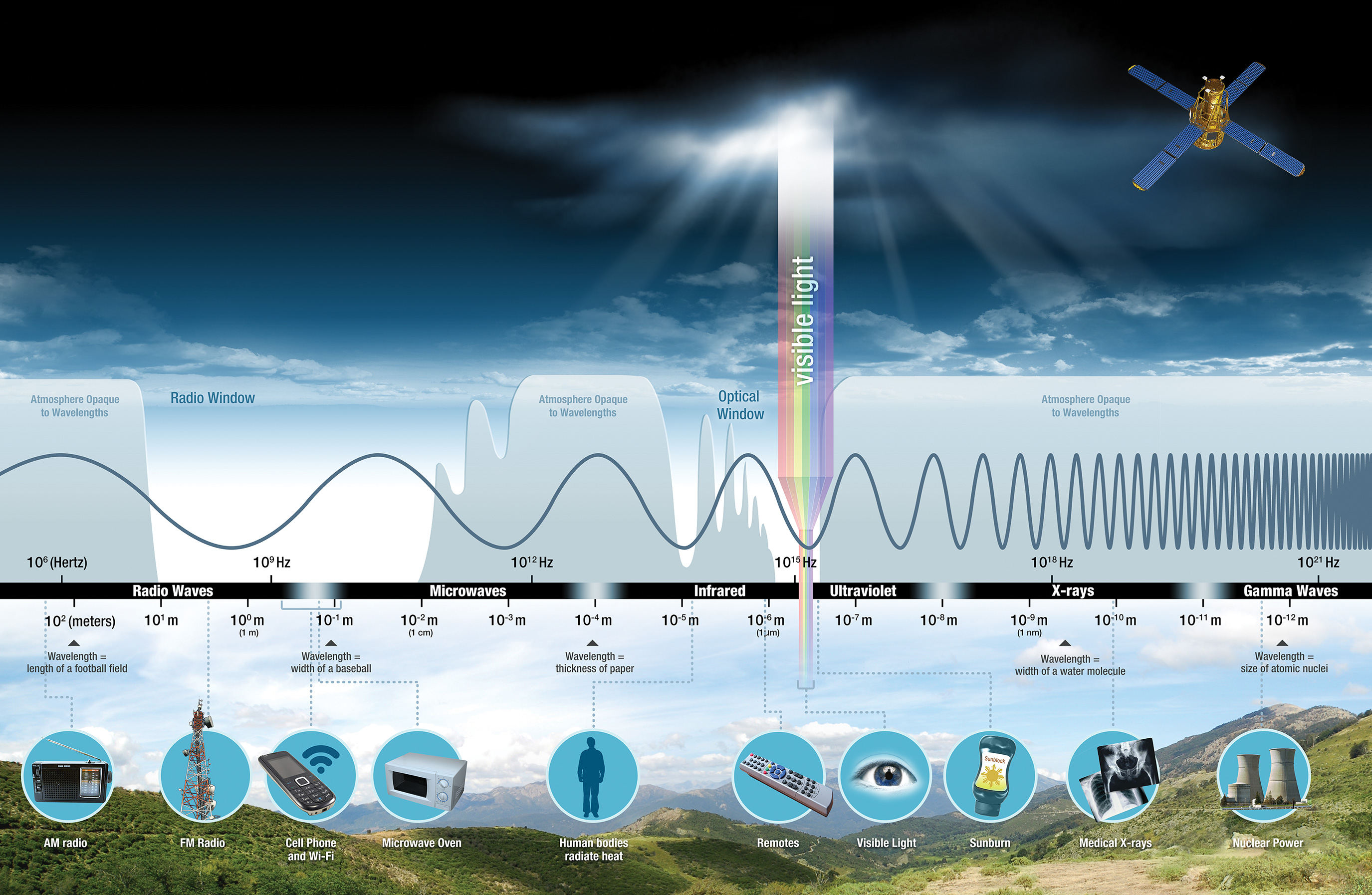
3. Development of Wireless Communication
The transition from 3G to 5G has been highly dependent on the electromagnetic spectrum. The roll-out of 5G networks requires high-frequency radio waves and millimetric waves, which increase data transmission rates and reduce latency. This change will likely spur massive evolution in industries such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and IoT, with the global 5G services market anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 122.3% by 2028.
Recommended Reading : Real-World Applications of Math
Statistical Perspective of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
Market Growth of Spectrum Analyzers
The spectrum analyzer market, which is essential for managing and analyzing electromagnetic waves, was estimated at USD 1.66 billion in 2023. It is expected to grow rapidly, reaching USD 3.17 billion by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.51% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2032.
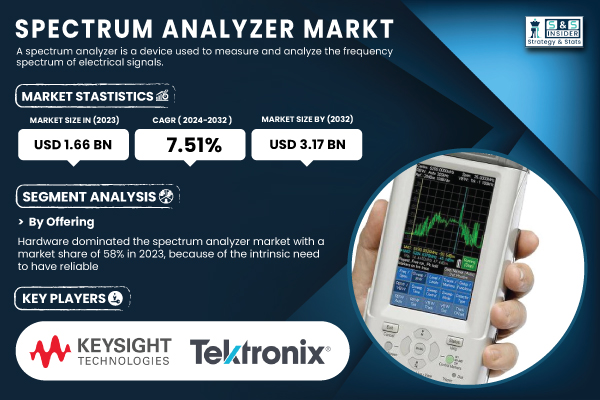
This growth is attributed to the increasing usage of advanced technologies such as 5G networks and IoT. These technologies require significant utilization of the electromagnetic spectrum in a precise and efficient manner. This is the basis for the widespread use of spectrum analyzers in industries such as telecommunication and defense.
Expansion of Telecommunications
The global 5G services market was USD 5.53 billion in 2020, and is likely to expand at a high CAGR of 122.3% from 2021 to 2028, driven by rising demand for mobile communication networks of higher speed. These rely on the radio waves and millimeter waves of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Challenges and Future Outlook
The changing times of today do come with a few challenges to the electromagnetic spectrum. The most pressing of these challenges is spectrum allocation. With devices like smartphones, autonomous vehicles, and IoT, there has been a rise in the demand for available spectrum for bandwidth. Hence, it’s a great challenge for governments and regulatory bodies to effectively manage this resource to prevent overcrowding and interference.
Another concern has been the potential health effects from long-term exposure to electromagnetic fields. Research continues to examine how electromagnetic waves, especially those emitted in wireless communications, affect humans.
The electromagnetic spectrum has a lot of promise for further development. For instance, there could be invented new technologies, such as terahertz imaging applied in the security fields, medical fields, etc. Further, the electromagnetic spectrum carries a lot of potential to develop new innovations.
Want to Ace Mental Math? Check Out these Top Mental Math Tips For Kids
Conclusion
The electromagnetic spectrum is a very essential and diversified portion of our world. Its application can be found in medical diagnostics, communication, space exploration, and defense, and so many other applications vital to modern life. With advancing technologies and an understanding of the spectrum, new opportunities will keep opening up. Undeniably, the role of the electromagnetic spectrum in shaping the future is without doubt, and it has just started to be more than partially explored.
Want to excite your child about math and sharpen their math skills? Moonpreneur’s online math curriculum is unique as it helps children understand math skills through hands-on lessons, assists them in building real-life applications, and excites them to learn math.
You can choose from our Advanced Math or Vedic Math+Mental Math curriculum. Our Math Quiz in grades 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 6th allows further enjoyable and interactive math with on-hand lessons.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
It consists of all forms of electromagnetic radiation, and differs in the amount of wavelength or frequency. Its types are classified from radio waves and microwaves to infrared and visible light through ultraviolet rays, X rays, and even gamma rays. Each kind differs in some distinctive features, making them applied specifically in some forms of communications, medicine, space exploration, among others.
Electromagnetic waves can be classified into several broad categories, arranged from longest to shortest wavelength. These include the following:
- Radio Waves – For communications, radio, television, and satellites.
- Microwaves – Cooking, radar, and telecommunications.
- Infrared Waves – Thermal imaging and night vision.
- Visible Light – That spectrum of electromagnetic radiation visible to the human eye.
- Ultraviolet Rays – Sterilization and tanning.
- X-rays – Medical imaging and security screening.
- Gamma Rays-In the treatment of cancer and investigation of cosmic phenomena.
Electromagnetic waves play a very crucial role in our everyday life. They make possible the use of wireless communication, from Wi-Fi and mobile phones to medical imaging tools like X-rays and MRIs. They are used in household technology in microwave ovens, remote controls, and infrared sensors. In addition, electromagnetic radiation coming from the Sun provides heat and light, both necessary for sustaining life on Earth.
In medicine, many areas of the electromagnetic spectrum are used in diagnosis and treatment. X-rays and gamma rays are used in medical imaging, including CT scans, mammograms, and X-ray images. MRI scans utilize magnetic fields and radio waves to produce highly detailed images of internal body parts. Ultraviolet light is also used in sterilization and for certain diseases, like psoriasis.
The electromagnetic spectrum plays a crucial role in space exploration. Different wavelengths show different aspects of celestial bodies. For example, the Hubble Space Telescope is sensitive to visible light. The Chandra X-ray Observatory can capture high energy wavelengths such as X-rays. These studies are what inform astronomers about cosmic events such as supernovae and black holes. If wavelength did not exist, then astronomers would only know very little about the universe.
5G networks use millimeter waves, in addition to higher frequency electromagnetic waves, to enable data transmission speeds at faster levels and lower latency. The frequency can be used to provide increased bandwidth to support millions of devices in smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and IoT. The market of 5G services is on a rise. As per analysis, in 2020, the value of global 5G services was USD 5.53 billion. For the forecast period, that is from 2021-2028, the value of global 5G services will grow with an estimated CAGR of 122.3%.

















The electromagnetic spectrum is so pervasive in our daily lives, from Wi-Fi signals to imaging at hospitals. I am interested to learn about how new and future technologies such as 6G or space communications will utilize parts of the spectrum in the coming days.
Breaking down real-life applications for each of the categories of waves in the spectrum could potentially make this article even more interesting. Maybe an elementary infographic with examples of some typical devices and their corresponding wavelengths would help one see it better.