Whether you are preparing for high-stakes exams or just trying to survive your next math test, there is a specific kind of dread that sets in when you see Modulus (∣x∣) or greatest integer function (⌊x⌋) inside an integral sign. It feels like someone added a puzzle inside your calculus problem.
But here is the secret: these functions aren’t there to stop you—they are just asking you to take a slightly different path. In this blog, let’s break these down into simple, human steps.
The Big Picture: What is an Integral, Anyway?
Before we dive into the “scary” functions, remember what a definite integral actually represents. At its heart, an integral is just the area under a graph.
- If the value is positive, the graph is above the x-axis.
- If the value is negative, it simply means the area is below the x-axis.
When we add modulus or GIF symbols, we aren’t changing the goal; we are just changing the shape of the area we’re measuring.
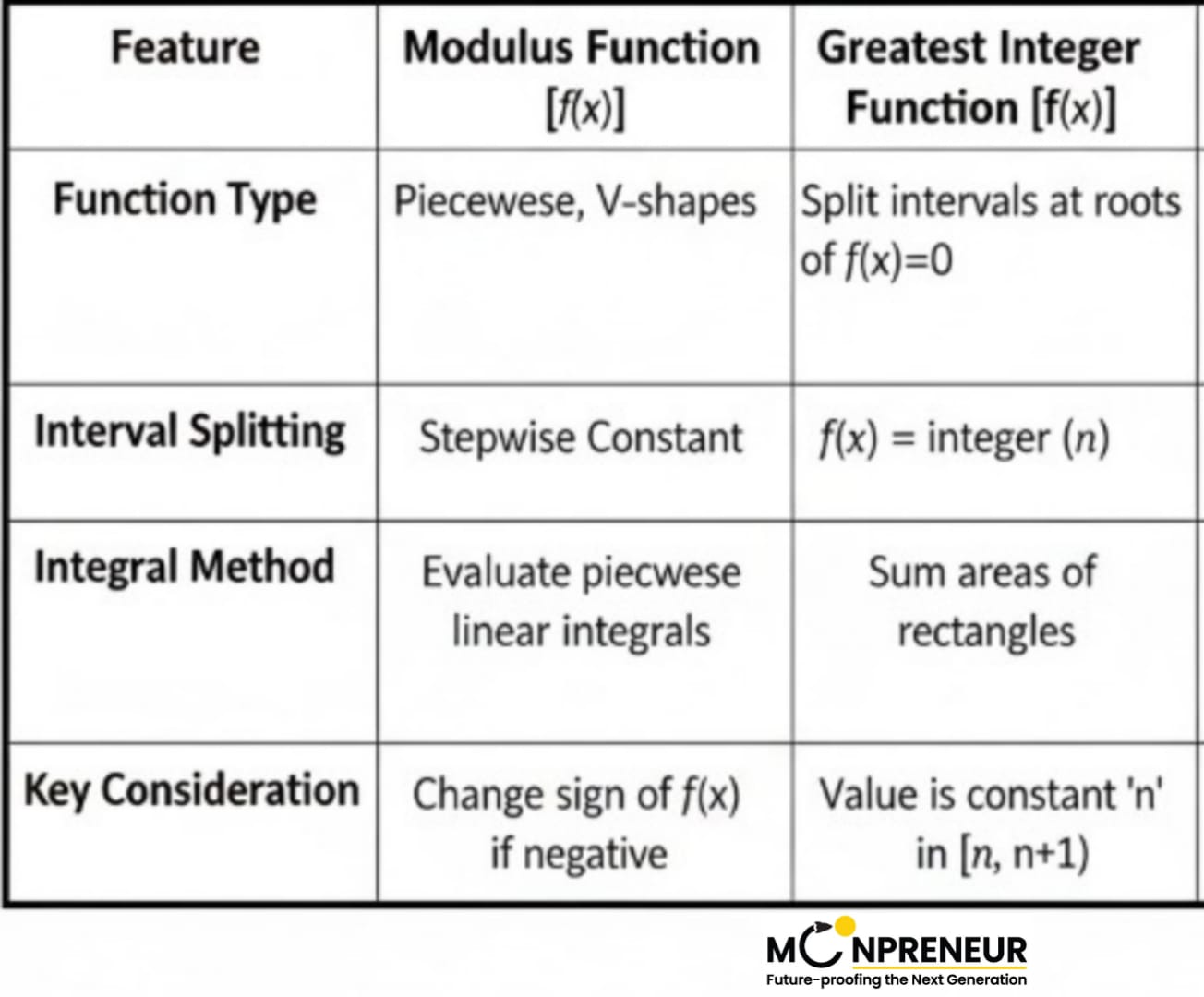
Mastering integrals involving modulus ( | f(x) | ) and greatest integer functions ( [x] ) requires breaking the integral into smaller, manageable intervals based on where the functions change behavior.
Mastering the Modulus ( ∣ f (x) ∣ )
The modulus function is like a “positivity filter”—it flips everything below the x-axis to be above it. To integrate a modulus function, you have to find the critical points where the function inside the bars changes its sign. The goal with modulus integrals is to remove the absolute value bars by determining where the expression inside is positive or negative.
The Strategy:
1. Find the Zeroes: Find where the expression inside the modulus equals zero. For example, in ∫∣ ln(x) ∣, the function ln(x) changes from negative to positive at x = 1.
2. Break the Path: Split your integral at that point.
3. Flip the Sign: If the function is negative in a certain interval, open the modulus with a negative sign (to make it positive). If it’s already positive, just drop the bars
Pro Tip: If you see something like \(\displaystyle \sqrt{1 – \sin(2x)}\) , remember that square roots always result in a modulus: ∣cos(x)−sin(x)∣. You’ll need to break this at 45º (π/4), because that is where Sin and Cos cross each other.
Example:
\(\displaystyle \int_{0}^{3} |x – 2|\,dx\)
Critical point: x – 2 = 0 ⇒ x = 2
Intervals: From [0, 2], (x-2) is negative. From [2, 3], (x – 2) is positive.
Setup: \(\displaystyle \int_{0}^{2} -(x – 2)\,dx + \int_{2}^{3} (x – 2)\,dx\)
Greatest Integer Function ([x])
The Greatest Integer Function (GIF) is often called a “step function” because its graph looks like a staircase. It stays at one constant integer value until it “jumps” to the next. The floor function is a “step function.” It remains constant between integers but jumps at every integer value.
The Strategy:
1. Identify Integer Jumps: Find every value of x (within your limits) that makes the expression inside the floor function an integer.
2. Break into Unit Steps: Split the integral at every one of those values.
3. Substitute the Constant: Within each sub-interval, replace ⌊f(x)⌋ with the specific integer value it takes.
Example:
\(\displaystyle \int_{0}^{2} \lfloor x^{2} \rfloor\,dx\)
Critical points: When does x² hit an integer between x = 0 and x = 2?
- x² = 1 ⇒ x = 1
- x² = 2 ⇒ x = √2
- x² = 3 ⇒ x = √3
The Breakdown:
- On [0,1), ⌊x²⌋ = 0
- On [1,√2), ⌊x²⌋ = 1
- On [√2,√3), ⌊x²⌋ = 2
- On [√3,2), ⌊x²⌋ = 3
Integral: (0 ⋅ 1) + (1 ⋅ (√2 – 1)) + (2 ⋅ (√3 – √ 2)) + (3 ⋅ (2 – √3))
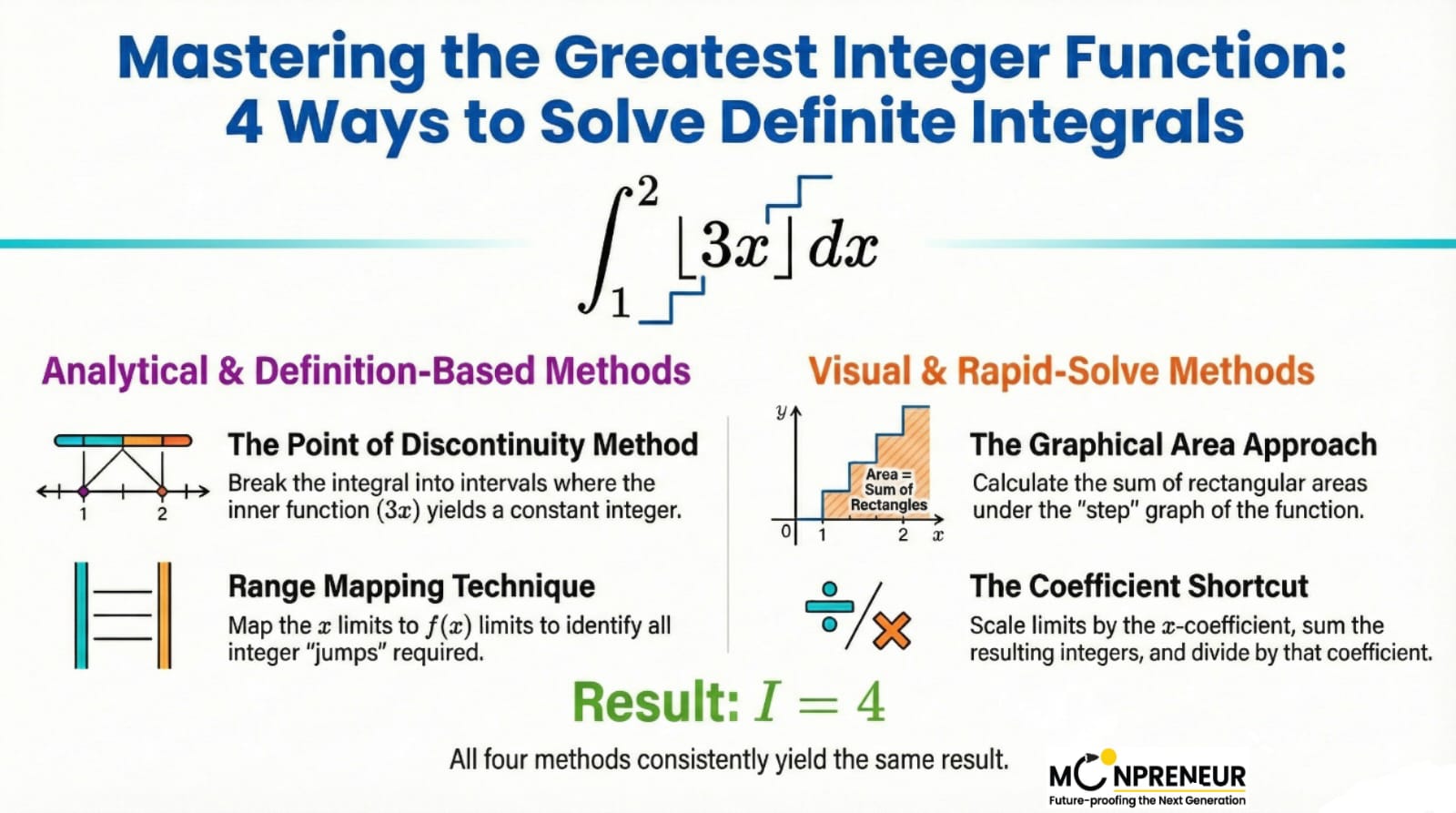
A Shortcut for the SAT/JEE Level:
If you have an integral like \(\displaystyle \int_{1}^{2} [3x]\,dx\), you can use a quick numerical trick:
- Multiply your limits by the coefficient inside (so 1 becomes 3, and 2 becomes 6).
- List the integers in that range: 3, 4, 5
- Sum them up and divide by that same coefficient: (3 + 4 + 5) / 3 = 4
Mastering these advanced integration techniques is less about memorising complex formulas and more about developing a winner’s attitude. Whether you are facing a Modulus or a Greatest Integer Function, the goal is to break the problem down into manageable parts, much like how you should approach your overall exam preparation.
Want to excite your child about math and sharpen their math skills? Moonpreneur’s online math curriculum is unique as it helps children understand math skills through hands-on lessons, assists them in building real-life applications, and excites them to learn math.
You can opt for our Advanced Math or Vedic Math+Mental Math courses. Our Math Quiz for grades 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 6th helps in further exciting and engaging in mathematics with hands-on lessons.
Recommended Reading:
- Solving Exponential Equations Using Recursion: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Linear Equation – One Solution, No Solution and Many Solutions
- Interesting Geometry Problem to Solve For Kids
- Application & Proof of the Sherman-Morrison-Woodbury Identity
- The Geometry Problem That Still Defeats ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok