Frequency is a key concept in physics, mathematics, and statistics that measures how often a repeating event occurs over a specific period. From the hum of a guitar string to the ticking of a clock, frequency is all around us. Understanding its formula helps in fields like sound engineering, wave mechanics, and even data analysis.
What is Frequency?
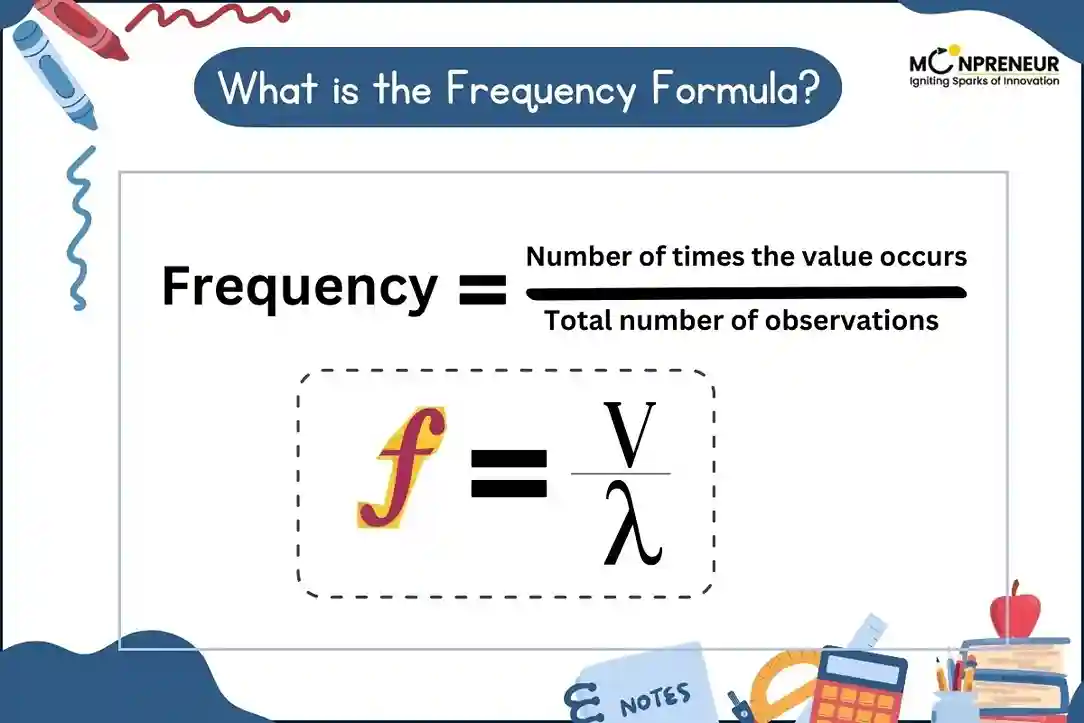
Frequency (f) refers to the number of cycles, oscillations, or repetitions of an event per unit of time. It is commonly measured in Hertz (Hz), where 1 Hz equals one cycle per second.
Fundamental Frequency Formula
The most basic formula for frequency is the reciprocal of the time period (T):
f = 1 / T
Where:
– f = Frequency (in Hertz, Hz)
– T = Time period (seconds), the duration of one complete cycle
Example: If a wave takes 0.1 seconds to complete one cycle:
f = 1 / 0.1 = 10 Hz
This means the wave oscillates 10 times per second.
Alternative Formula Using Number of Cycles
In some cases, frequency is calculated based on the number of cycles in a given total time:
f = N / t
Where:
– N = Number of cycles or events
– t = Total time taken
Example: If a wheel rotates 120 times in 60 seconds:
f = 120 / 60 = 2 Hz
Related Formulas Involving Frequency
1. Wave Speed and Wavelength
f = v / λ
Where:
– v = Wave speed (m/s)
– λ = Wavelength (meters)
Example: If a water wave travels at 4 m/s and has a wavelength of 2 meters:
f = 4 / 2 = 2 Hz
2. Angular Frequency
f = ω / 2π
Where:
– ω = Angular frequency (radians/second)
– π ≈ 3.1416
Example: If angular frequency is 31.4 rad/s:
f = 31.4 / 2π ≈ 5 Hz
Frequency in Statistics
In statistics, frequency shows how many times a specific value appears in a dataset. For example, if “score 8” appears 7 times in test results, the frequency of score 8 is 7.
Units of Frequency
Hertz (Hz) – Cycles per second (SI unit)
Revolutions per minute (RPM) – For rotating machinery
Cycles per minute/second – Common in engineering and wave studies
Real-Life Applications of Frequency
1. Music – Determines pitch of sound waves.
2. Electricity – AC mains supply frequency (50 Hz in India, 60 Hz in the USA).
3. Mechanical Systems – Rotational speed of engines in RPM.
4. Astronomy – Frequency of a planet’s orbit or rotation.
Key Takeaways
Basic formula: f = 1 / T
Frequency tells how often an event happens per second.
Related formulas connect frequency with wavelength, wave speed, and angular motion.
Measured in Hertz (Hz), RPM, or other cycle-based units.
Conclusion
Frequency is a core concept that helps us understand how often events occur, whether it’s sound waves, machinery cycles, or statistical data patterns. Using the basic formula f=1Tf = \frac{1}{T}f=T1 and related equations, we can measure and analyze cycles in various fields. From physics to everyday life, understanding frequency is essential for learning, research, and innovation.
Want to spark your child’s interest in math and boost their skills? Moonpreneur’s online math curriculum stands out because it engages kids with hands-on lessons, helps them apply math in real-life situations, and makes learning math exciting!
You can opt for our Advanced Math or Vedic Math+Mental Math courses. Our Math Quiz for grades 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 6th helps in further exciting and engaging in mathematics with hands-on lessons.
Related Blogs:
How to Teach Adjacent Angles to Kids | Simple & Fun Guide
What are Congruent Angles?
Understanding Alternate Interior Angles
What is the Area of Trapezoid?
What is the Area of Parallelogram?
Understanding the Geometry Regents: A Comprehensive Guide
How to Prepare for the Geometry Regents: Study Plans & Practice
The Art of Geometry: How to Draw an Equilateral Triangle Inside a Circle
















