We have all been there, staring at a geometry problem on an SAT practice test, wondering how a few lines inside a circle can feel so complicated. Geometry often feels like the “boss level” of the SAT maths section, but here is a secret: most of it comes down to a few elegant rules that work every single time.
Today, we are diving into one of the most useful theorems: The Angle at the Centre and Circumference Theorem
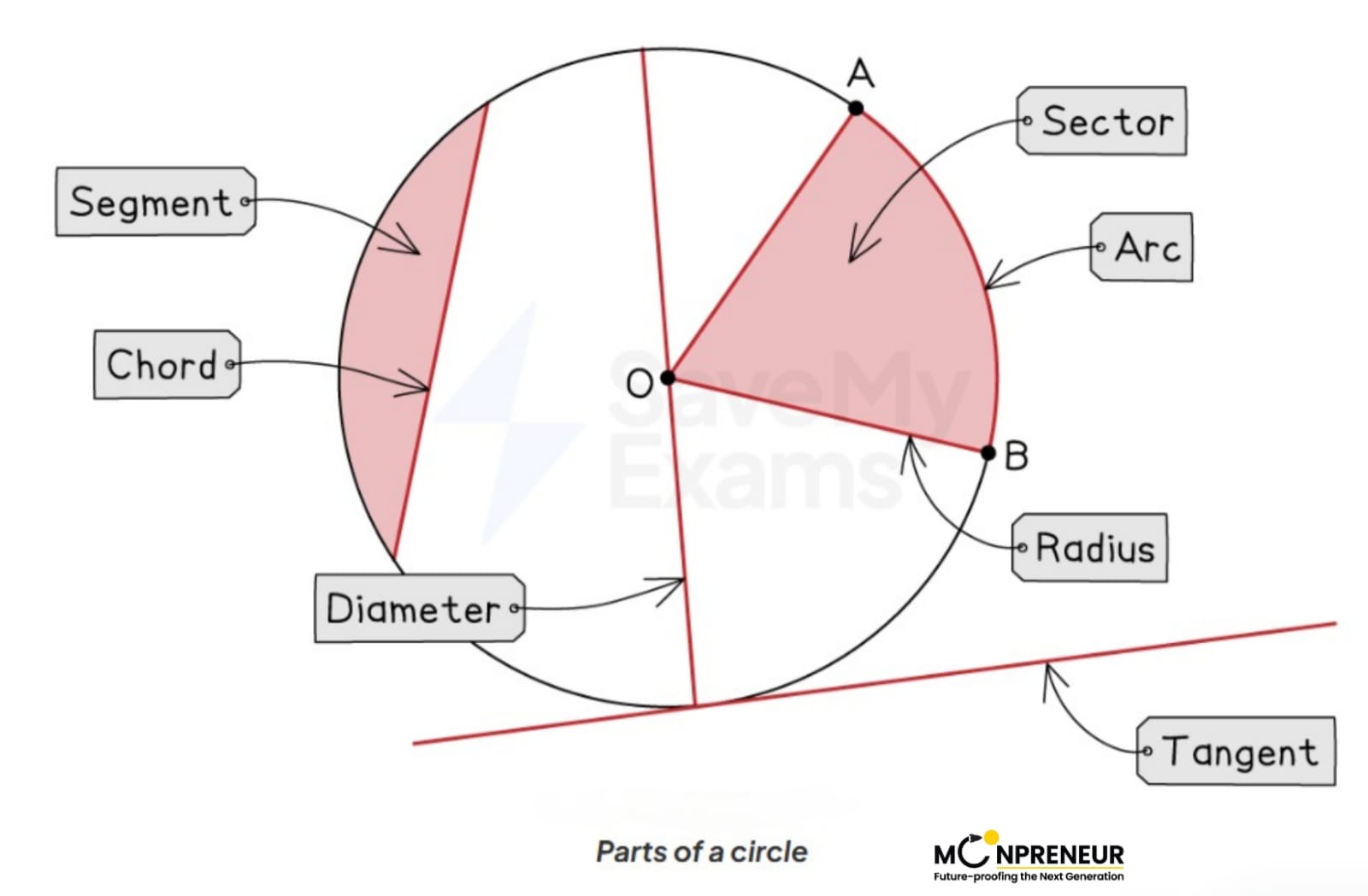
What are circle theorems?
Circle theorems deal with angles that occur when lines are drawn within (and connected to) a circle.
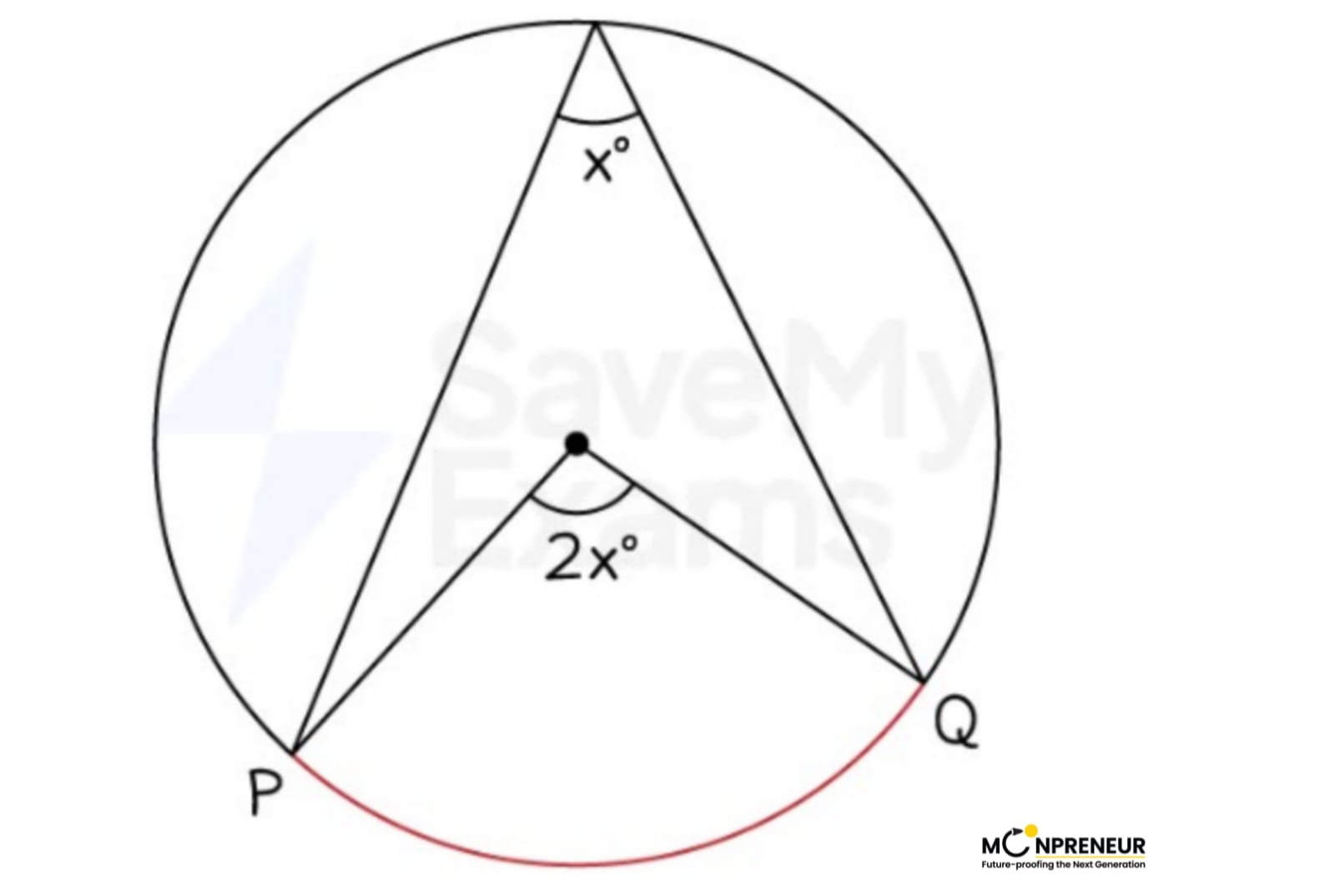
Angle at the centre and circumference theorem
“The angle at the centre is always exactly twice the size of the angle at the circumference.”
In this theorem, the chords (radii) to the centre and the chords to the circumference are both drawn from (subtended by) the ends of the same arc.
To spot this circle theorem on a diagram
- Find any two radii in the circle and follow them to the circumference
- See if there are lines from those points going to any other point on the circumference
- It may look like the shape of an arrowhead
When explaining this theorem in an exam, you must use the keywords:
- The angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference
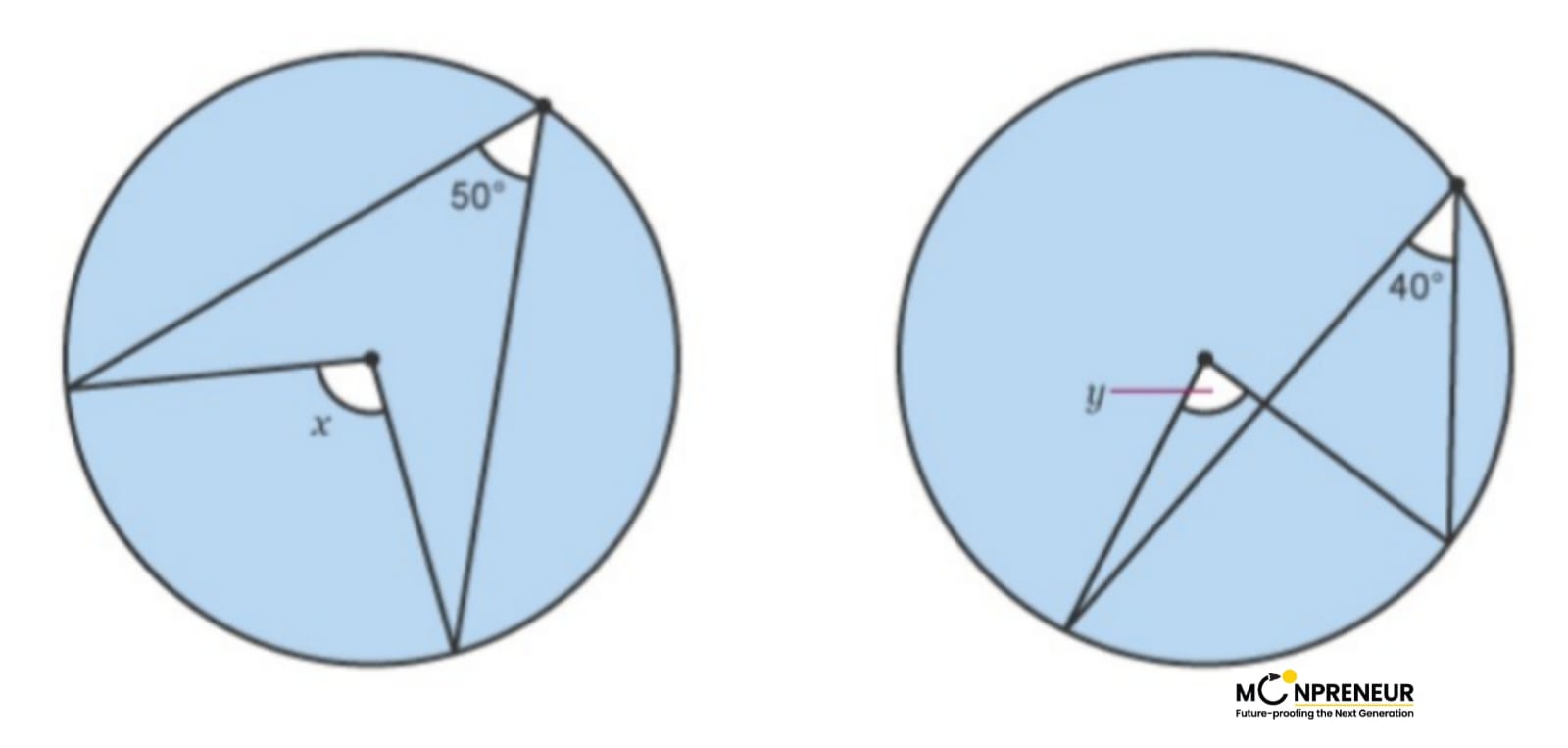
Example (i)
Calculate the missing angles x and y.
Solution:
x = 50 × 2 = 100º
y = 40 × 2 = 80º
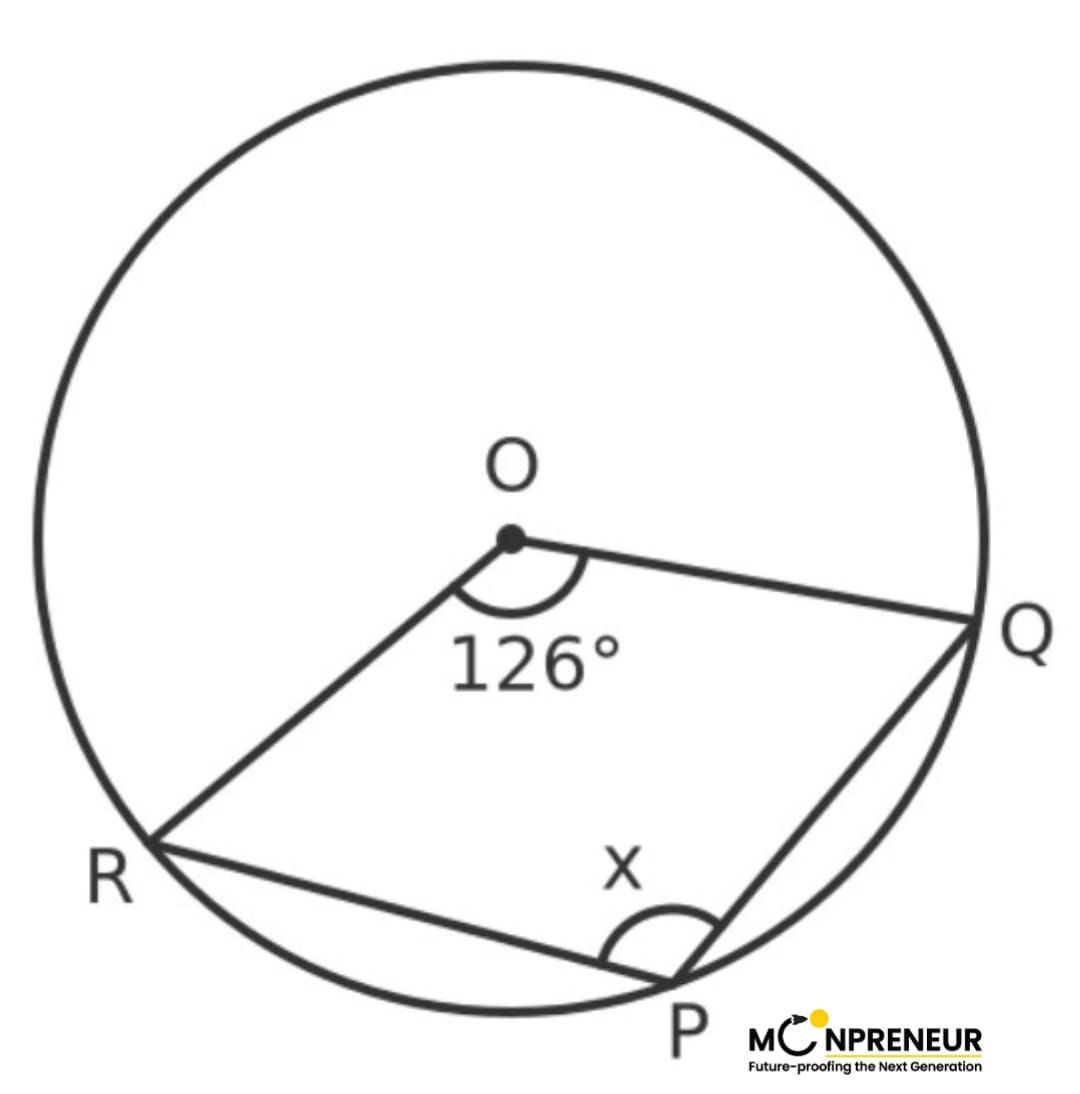
Example (ii)
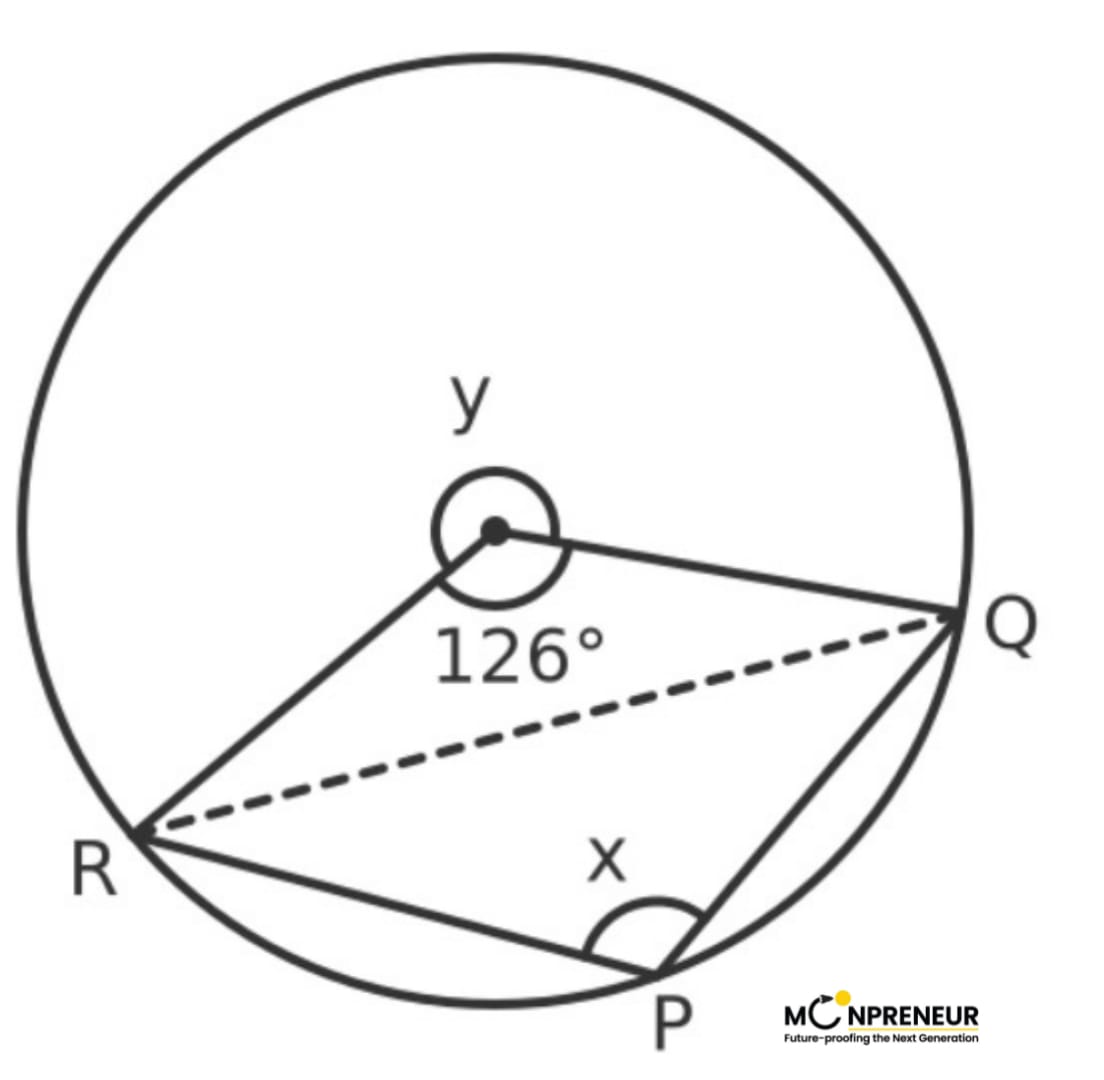
The diagram shows three points, P, Q, and R, on the circumference of a circle with center O. Angle ROQ has a value of 126°.
What is the value of the angle x?
Solution:
Angle x is the angle that the chord QR makes at the circumference of the circle. The angle that the chord makes at the centre is marked as y (we must take the angle in the opposite sector, which is the reflex angle in this case):
Since y and 126° together make up a full turn, they must add up to 360°. So y must be 234°. The angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference. This means that:
2x = 234º
So x = 117º
For a more detailed walkthrough, you can watch this video:
More Than Just Circles
Whether it is mastering circle theorems or learning how to multiply large numbers in seconds, the goal is always the same: speed and confidence. On test day, every second counts. It’s about working smarter, not harder.
Pro-Tip for Your Study Session
Next time you see a circle problem, look for that “arrowhead” or “v-shape” rooted at the same two points on the circumference. If one point of the “v” is at the centre and the other is at the edge, you’ve just found your shortcut.
Geometry doesn’t have to be a headache. With quick visual cues like this, you can turn a “skip” into a “score.” Keep practicing, stay curious, and remember: the centre is always twice as “loud” as the edge!
Want to excite your child about math and sharpen their math skills? Moonpreneur’s online math curriculum is unique as it helps children understand math skills through hands-on lessons, assists them in building real-life applications, and excites them to learn math.
You can opt for our Advanced Math or Vedic Math+Mental Math courses. Our Math Quiz for grades 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 6th helps in further exciting and engaging in mathematics with hands-on lessons.
Recommended Reading:
- Solving Exponential Equations Using Recursion: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Linear Equation – One Solution, No Solution and Many Solutions
- Interesting Geometry Problem to Solve For Kids
- Application & Proof of the Sherman-Morrison-Woodbury Identity
- The Geometry Problem That Still Defeats ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok