If you are a student preparing for the SAT, AP Calculus, or competitive exams like the JEE, you know the feeling of dread when you see a trig function raised to a massive power inside an integral. Imagine seeing \(\displaystyle \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \sin^{-7}(x)\,dx\) and thinking you have to use integration by parts or reduction formulas over and over again. It’s exhausting!
But what if I told you there’s a “magic” formula that lets you solve these in seconds? It’s called the Wallis Formula, named after the great mathematician John Wallis. This isn’t just a shortcut; it’s a game-changer for your math toolkit.
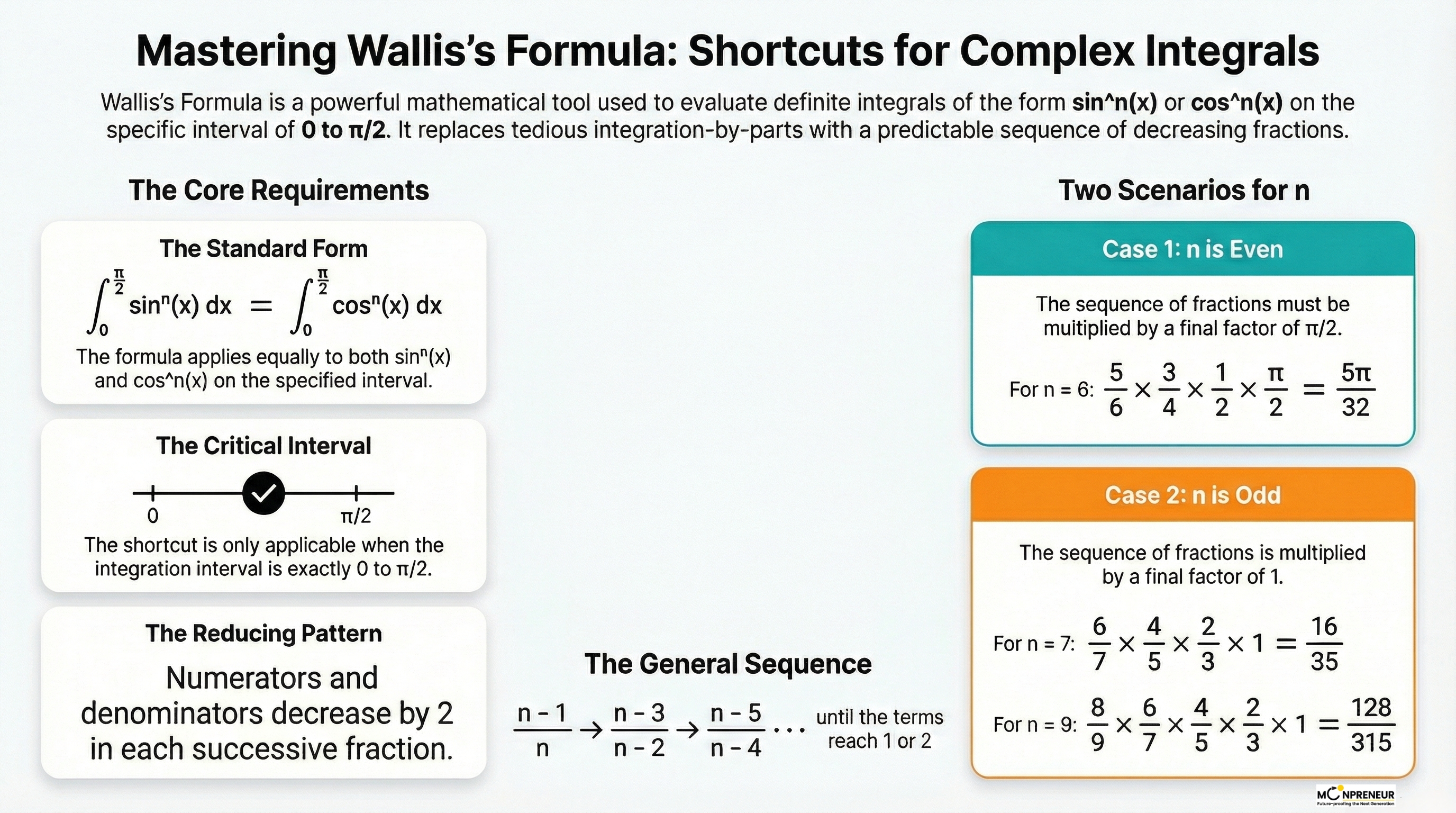
The Golden Rule: Check Your Boundaries
Before we dive into the math, there is one non-negotiable rule. The Wallis Formula only works if your integration interval is from 0 to π/2. If you see those limits and a power of sine or cosine, you’re ready to use the hack.
Interestingly, the formula works exactly the same for both \(\displaystyle \sin^{n}(x)\) and \(\displaystyle \cos^{n}(x)\) .\
The Wallis Formula allows for the instant evaluation of definite integrals of \(\displaystyle \sin^{n}(x)\) or \(\displaystyle \cos^{n}(x)\) from 0 to π/2 without standard integration techniques. For a non-negative integer n, the integral is \(\displaystyle \frac{(n – 1)!!}{n!!}\) ⋅ k, where k = π/2 if n is even and k = 1 if n is odd.
The core Formulas
For an integer n ≥ 0, the integral is defined as:
\(\displaystyle I_n = \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \sin^{n}(x)\,dx
= \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \cos^{n}(x)\,dx\)
The result depends entirely on whether n is odd or even:
Even power Case(n is even):
\(\displaystyle
\int_{0}^{\pi/2} \sin^{n}(x)\,dx
= \frac{n-1}{n} \cdot \frac{n-3}{n-2} \cdots \frac{1}{2} \cdot \frac{\pi}{2}
\quad \text{(for even } n\text{)}
\)
Odd Power Case (n is odd):
\(\displaystyle
\int_{0}^{\pi/2} \sin^{n}(x)\,dx
= \frac{n-1}{n} \cdot \frac{n-3}{n-2} \cdots \frac{2}{3} \cdot 1
\quad \text{(for odd } n\text{)}
\)
How It Works: Even vs. Odd Powers
The beauty of this formula is its symmetry. You just need to look at the exponent (n) and decide if it is even or odd.
Case 1: The Exponent is Odd (e.g., n=3,5,7,9…)
The pattern is simple: start with (n−1) in the numerator and n in the denominator. Then, keep subtracting 2 from both until you hit the end of the line.
The Pattern: \(\displaystyle
\frac{n-1}{n} \times \frac{n-3}{n-2} \times \frac{n-5}{n-4}
\) ending at \(\displaystyle \frac{2}{3} \times 1\)
Example: Let’s Solve \(\displaystyle \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \sin^{7}(x)\,dx\)
- Start with n = 7.
- Numerator: 7 − 1 = 6 and Denominator: 7. Fraction = 6/7.
- Subtract 2: 6 − 2 = 4. 7 − 2 = 5. Fraction = 4/5.
- Subtract 2 again: 4 − 2 = 2. 5 − 2 = 3. Fraction = 2/3.
- Multiply them: (6/7) × (4/5) × (2/3) = 16/35
Case 2: The Exponent is Even (e.g., n=2,4,6…)
The pattern is almost the same, but with one “special ingredient” at the end: multiply by π/2.
- The Pattern: \(\displaystyle
\frac{n-1}{n} \times \frac{n-3}{n-2} \cdots \frac{1}{2} \times \frac{\pi}{2}
\)
Example: Let’s Solve \(\displaystyle \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \cos^{6}(x)\,dx\)
- Start with n = 6.
- Follow the pattern: (5/6) × (3/4) × (1/2).
- Add the special ingredient: multiply by π/2.
- Result: (5/6) × (3/4) × (1/2) × (π/2) = 5π/32
Wait, why does this work?
For the curious minds who want to know the “why” behind the magic: this formula is derived using integration by parts. The formula is derived using a reduction formula. By applying integration by parts, you can prove that: \(\displaystyle I_n = \left(\frac{n-1}{n}\right) I_{n-2}\)
The “tail” of the Wallis Formula exists because the recursion eventually hits either I1( which is \(\displaystyle \int_{0}^{\pi/2} \sin(x)\,dx = 1\) ) or I0(which is \(\displaystyle \int_{0}^{\pi/2} 1\,dx = \frac{\pi}{2}\))
Why You Should Care
In high-pressure exams like the SAT or JEE, time is your most valuable resource. Instead of filling a page with calculations and risking a small arithmetic error, you can jump straight to the answer in one shot.
Pro-Tip for Students:
- Odd power? Ends in a whole number/fraction.
- Even power? Always has a π in the final answer.
Next time you see a trig integral with a high power, don’t panic. Just remember John Wallis, check your limits (0 to π/2), and start subtracting two!
Want to excite your child about math and sharpen their math skills? Moonpreneur’s online math curriculum is unique, as it helps children understand math skills through hands-on lessons, assists them in building real-life applications, and excites them to learn math.
You can opt for our Advanced Math or Vedic Math+Mental Math courses. Our Math Quiz for grades 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 6th helps in further exciting and engaging in mathematics with hands-on lessons.
Recommended Reading:
- Solving Exponential Equations Using Recursion: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Linear Equation – One Solution, No Solution and Many Solutions
- Interesting Geometry Problem to Solve For Kids
- Application & Proof of the Sherman-Morrison-Woodbury Identity
- The Geometry Problem That Still Defeats ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok