Mastering circle geometry doesn’t have to feel like a chore. One of the most effective “secret weapons” for the SAT math section is the Tangent Chord Theorem, a simple rule that can turn a complex-looking problem into a quick win.
In this blog, we’ll break down what this theorem is and how you can use it to boost your SAT score.
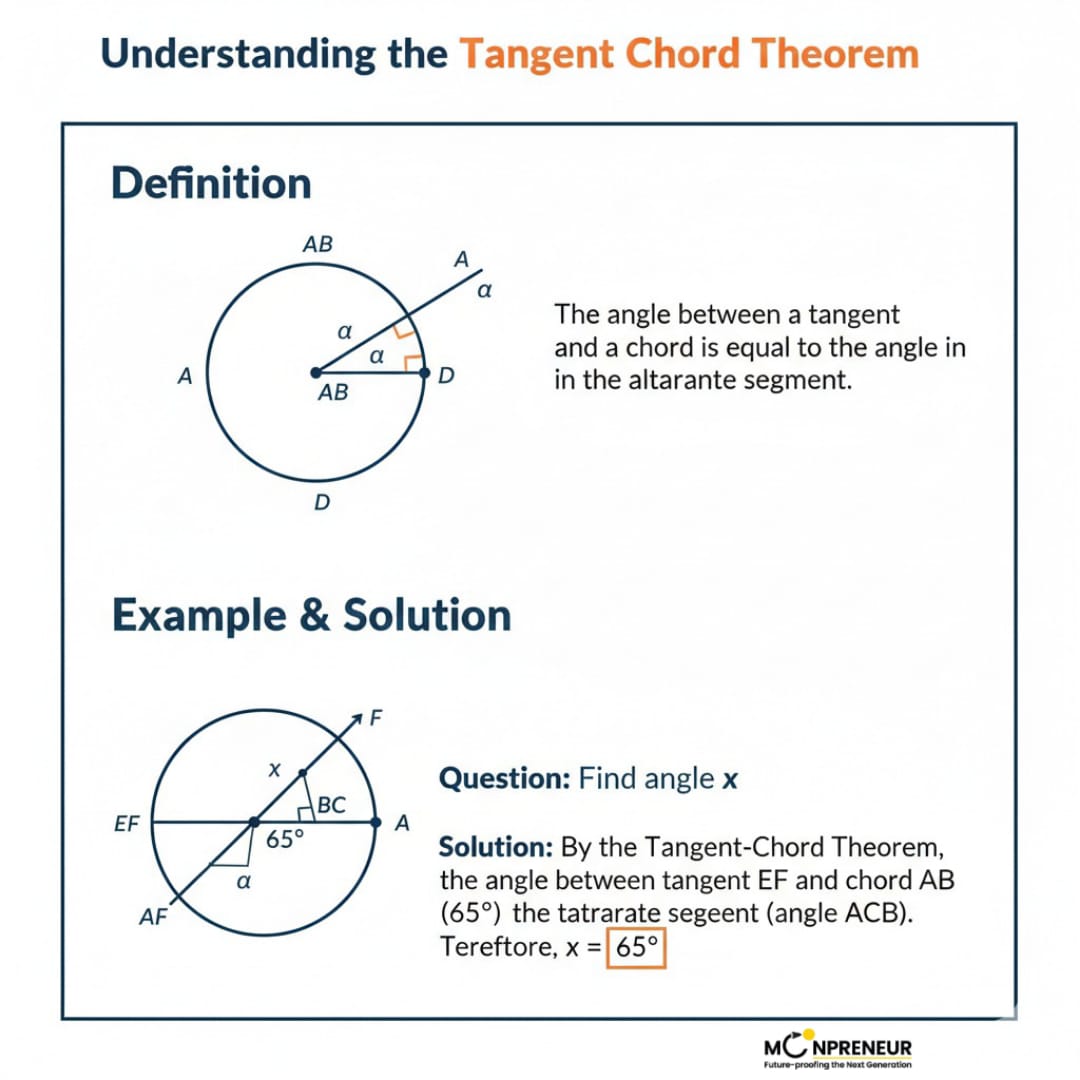
What is the tangent chord theorem?
The theorem states that “For any circle, the angle formed between the tangent and the chord through the point of contact of the tangent is equal to the angle formed by the chord in the alternate segment.” The tangent chord theorem is also known as the alternate segment theorem.
In simpler terms, if you see a triangle drawn inside a circle where one corner touches a tangent line, the angle between the line and the side of the triangle is the same as the angle at the far corner of that triangle.
How to Spot it on the Test
When you’re working through the Math section, look for these “clues”:
- A circle with a line grazing the edge.
- A triangle or inscribed angle where one vertex meets that grazing line.
- Missing angle measurements that seem unrelated to the numbers you are given.
If you see these elements, there is a high probability that the Tangent Chord Theorem is the key to the solution.
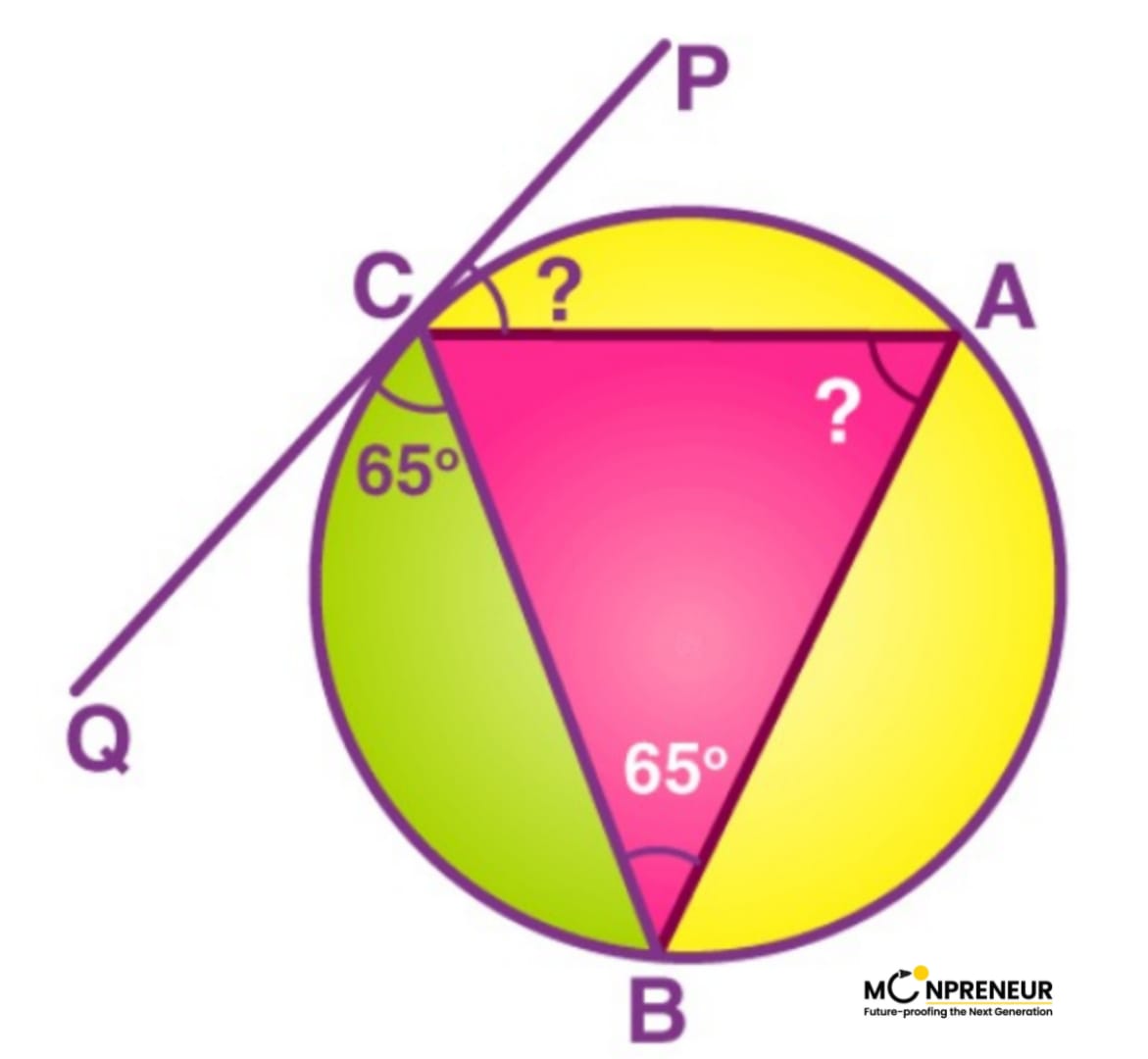
Example Walkthrough (i)
Find the unknown angles in the figure, given that the chord BC makes the angles 65° with the tangent line PQ.
Solution:
Given that ∠QCB = 65º
By using the Tangent chord theorem, we can say that ∠CAB = 65º
Similarly, by using the angles in the alternate segment, ∠PCA = 65º
Therefore, ∠CAB = 65º and ∠PCA = 65º
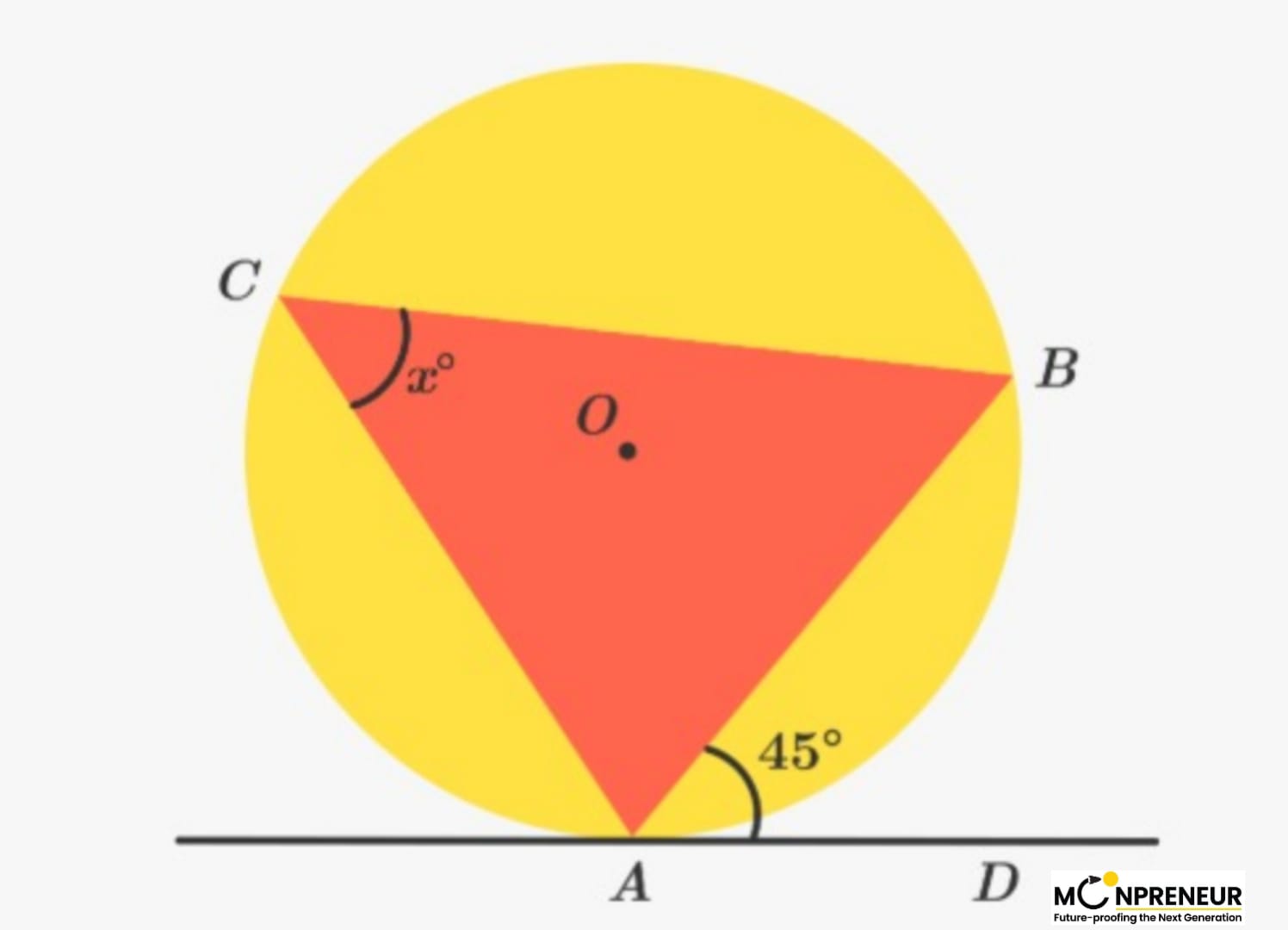
Example (ii)
In the diagram, it is given that ∠BAD = 45°. What is ∠ACB?
Solution:
From the tangent-chord theorem, the angle between a tangent and a chord that meets on a circle is equal to the inscribed angle on the opposite side of the chord. Thus,
∠ACB = ∠BAD = 45º
For a more detailed walkthrough, you can watch this video:
Geometry is all about pattern recognition. Next time you see a circle on your practice test, don’t panic—just look for the tangent and the chord!
Recommended Reading:
- Solving Exponential Equations Using Recursion: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Linear Equation – One Solution, No Solution and Many Solutions
- Interesting Geometry Problem to Solve For Kids
- Application & Proof of the Sherman-Morrison-Woodbury Identity
- The Geometry Problem That Still Defeats ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok
Want to excite your child about math and sharpen their math skills? Moonpreneur’s online math curriculum is unique as it helps children understand math skills through hands-on lessons, assists them in building real-life applications, and excites them to learn math.
You can opt for our Advanced Math or Vedic Math+Mental Math courses. Our Math Quiz for grades 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 6th helps in further exciting and engaging in mathematics with hands-on lessons.