Mastering geometry for the SAT doesn’t have to feel like an uphill battle. Whether you are tackling the SAT or looking for help with ACT math questions, understanding this formula is a “simple rule” that can help you solve complex triangle problems with confidence. In this blog, we will deep dive into the cosine formula.
What is the cosine formula?
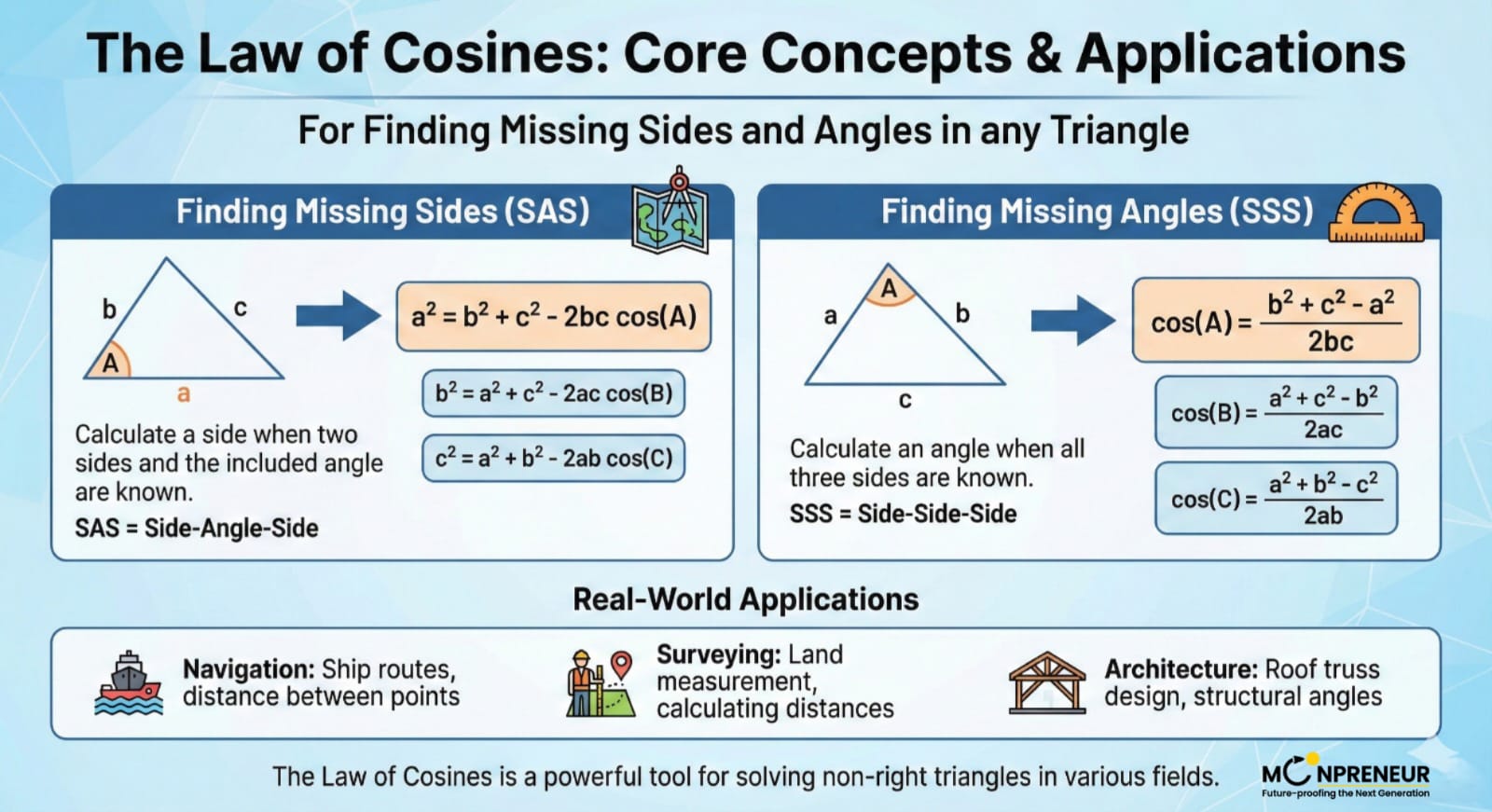
The cosine rule (or the law of cosines) is a formula that can be used to calculate the missing sides of a triangle or to find a missing angle. To do this, we need to know the two arrangements of the formula and what each variable represents.
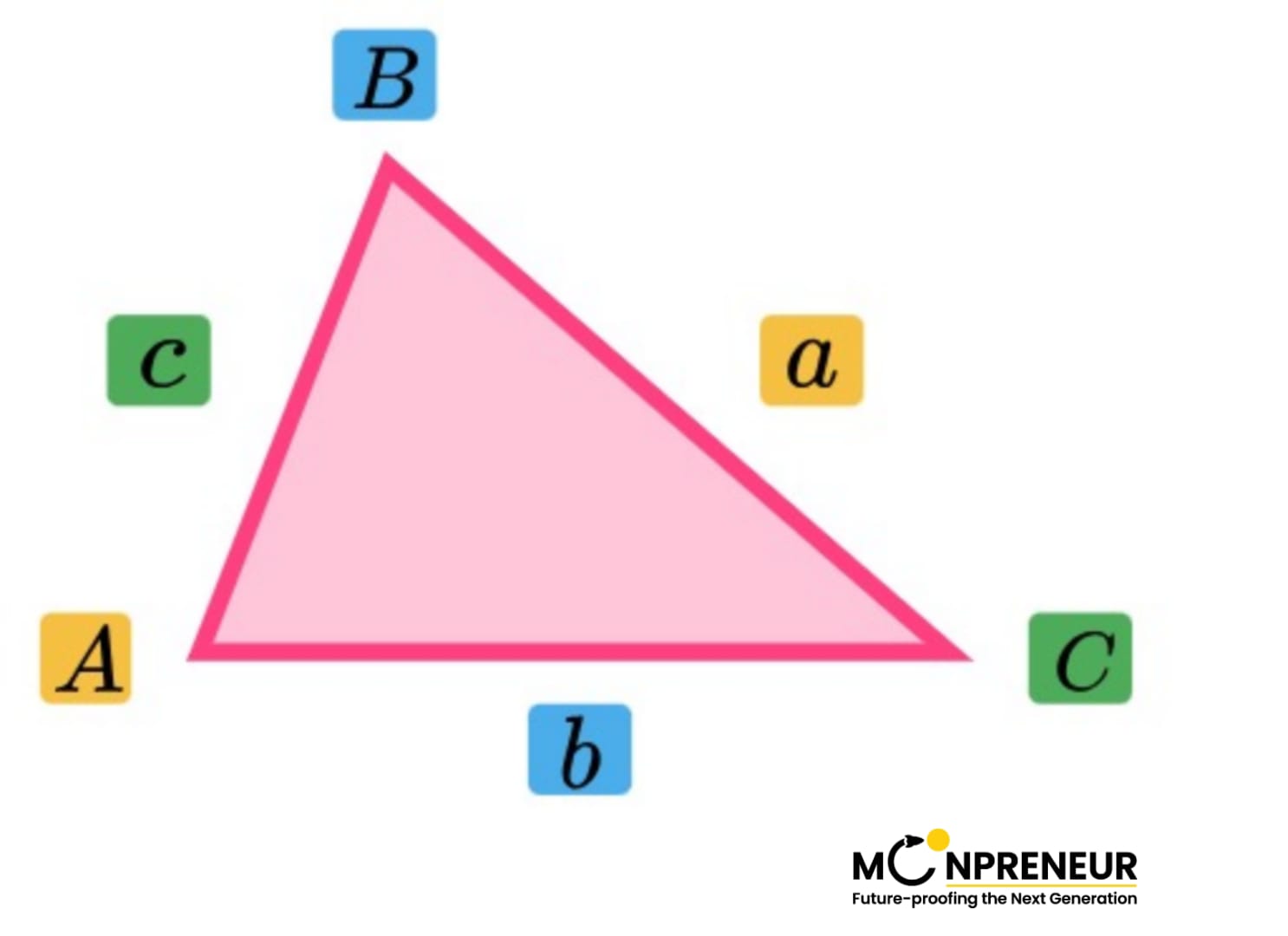
Take a look at the triangle ABC below.
This triangle has exactly the same setup as the sine rule, with the sides represented by lower-case letters and the opposite angles represented by the same capitalized letters, e.g., side b is opposite the angle at B.
This is the cosine rule formula: a²=b²+c²-2bc cos(A)
Rearranged Form: \(\displaystyle \cos(A) = \frac{b^{2} + c^{2} – a^{2}}{2bc}\)
When to Use:
- SAS (Side-Angle-Side): Two sides and the included angle are known.
- SSS (Side-Side-Side): All three sides are known
Finding a Missing Side (SAS)
This is the most common way you’ll see this on the SAT. You should use this formula when you know two sides and the angle between them (Side-Angle-Side).
- Identify the Angle: Identify the angle between two known sides(e.g., angle A between sides b and c)
- Apply Formula: Use the formula a²=b²+c²-2bc cos(A)
- Calculate: Plug in the values and solve for a², then take the square root to find side a.
Example: Find the missing side using the cosine rule
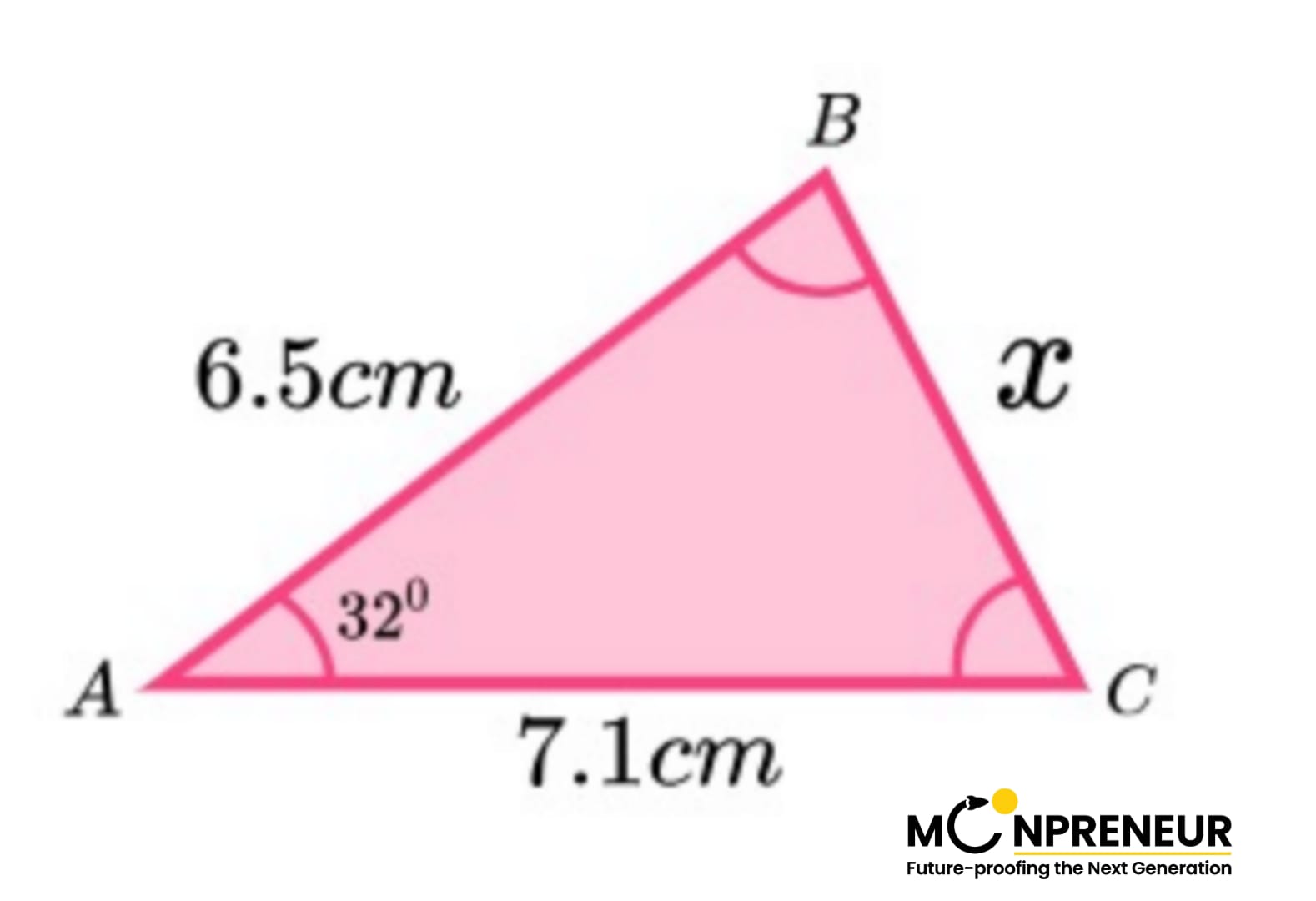
Find the value of x for triangle ABC.
Solution:
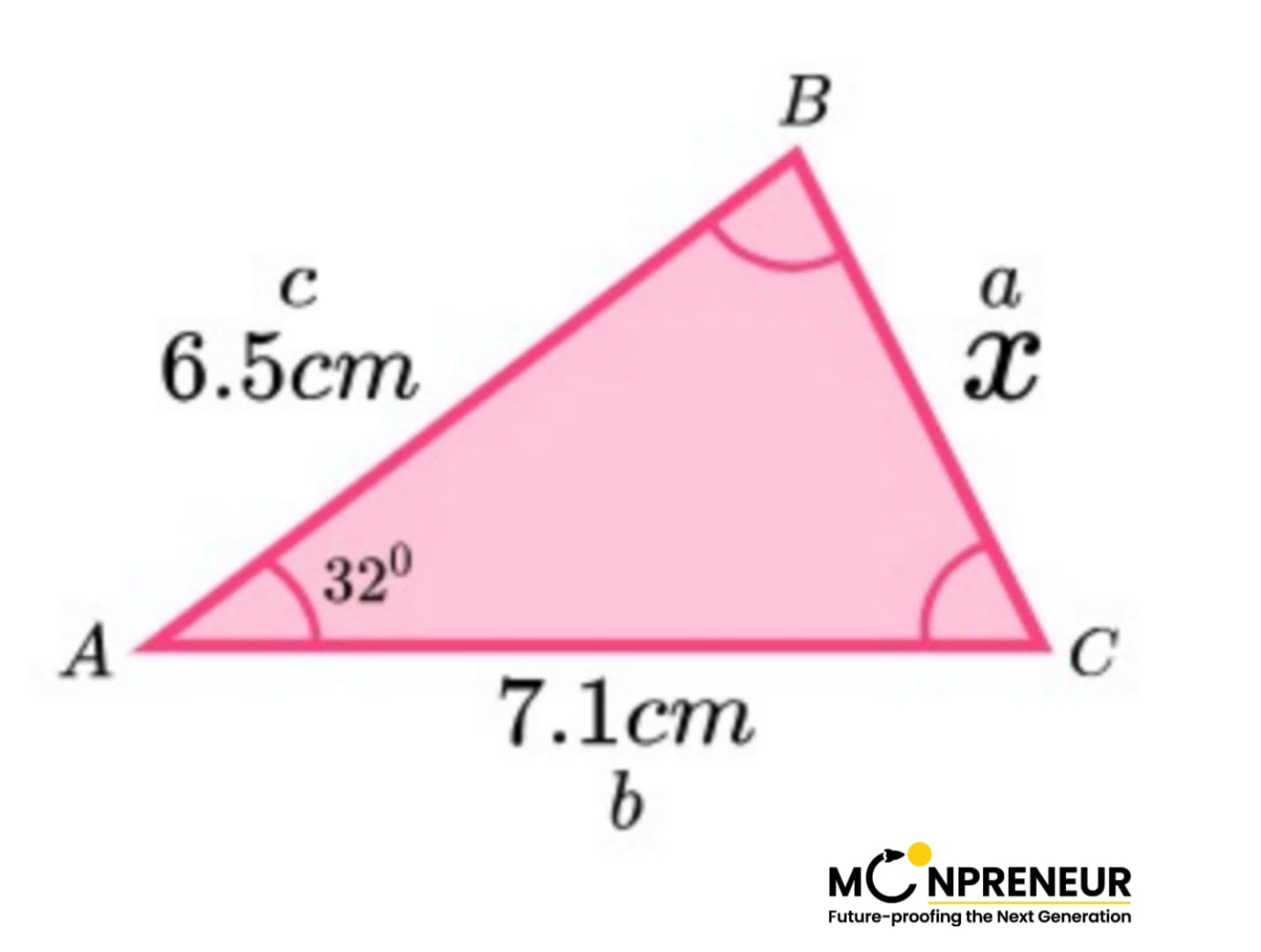
1. Label each angle (A, B, C) and each side (a, b, c) of the triangle.
2. State the cosine rule, then substitute the given values into the formula.
Here, we need to find the missing side a; therefore, we need to state the cosine rule with a² as the subject: a²=b²+c²-2bc cos(A)
x² = 7.1² + 6.5² – 2 × 7.1 × 6.5 × cos(32)
3. Solve the equation.
First, we need to simplify the right-hand side of the equation and then take the square root of the solution to find the value for x.
x² = 50.41 + 42.25 – 92.3 × cos(32)
x² = 92.66 – 78.27483928…
x² = 14.38516072…
x = √14.38516072…
x = 3.79 cm
How to Find a Missing Angle (SSS)
- Identify Sides: Identify all three side lengths (a, b, c).
- Rearrange Formula: Rearrange the cosine rule to solve for the cosine of the angle: \(\displaystyle \cos(A) = \frac{b^{2} + c^{2} – a^{2}}{2bc}\)
- Calculate Angle: Find the value, then use the inverse cosine function (cos⁻¹) to find the angle A.
If the result for cos(A) is negative, the angle is obtuse (an angle greater than 90º).
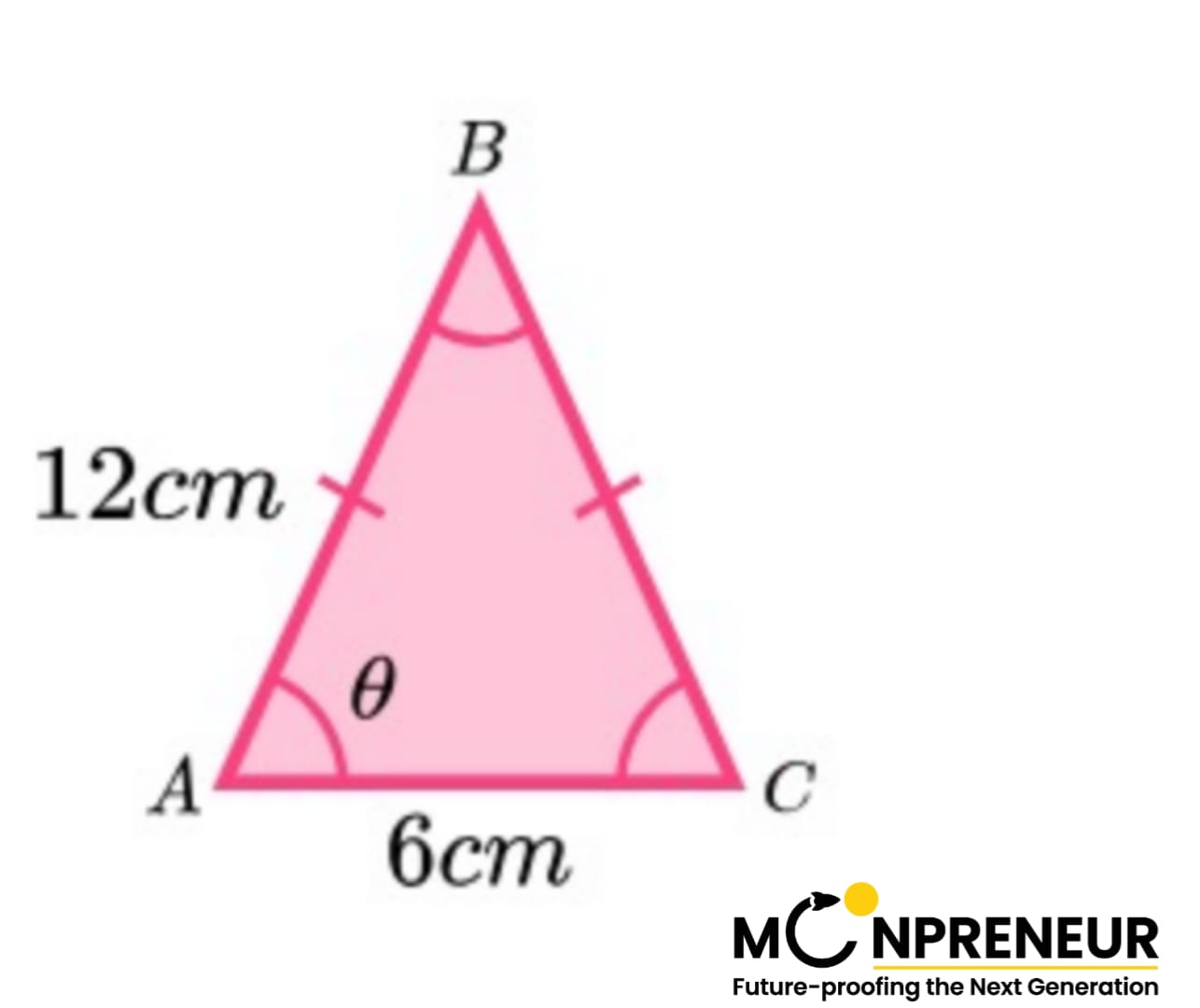
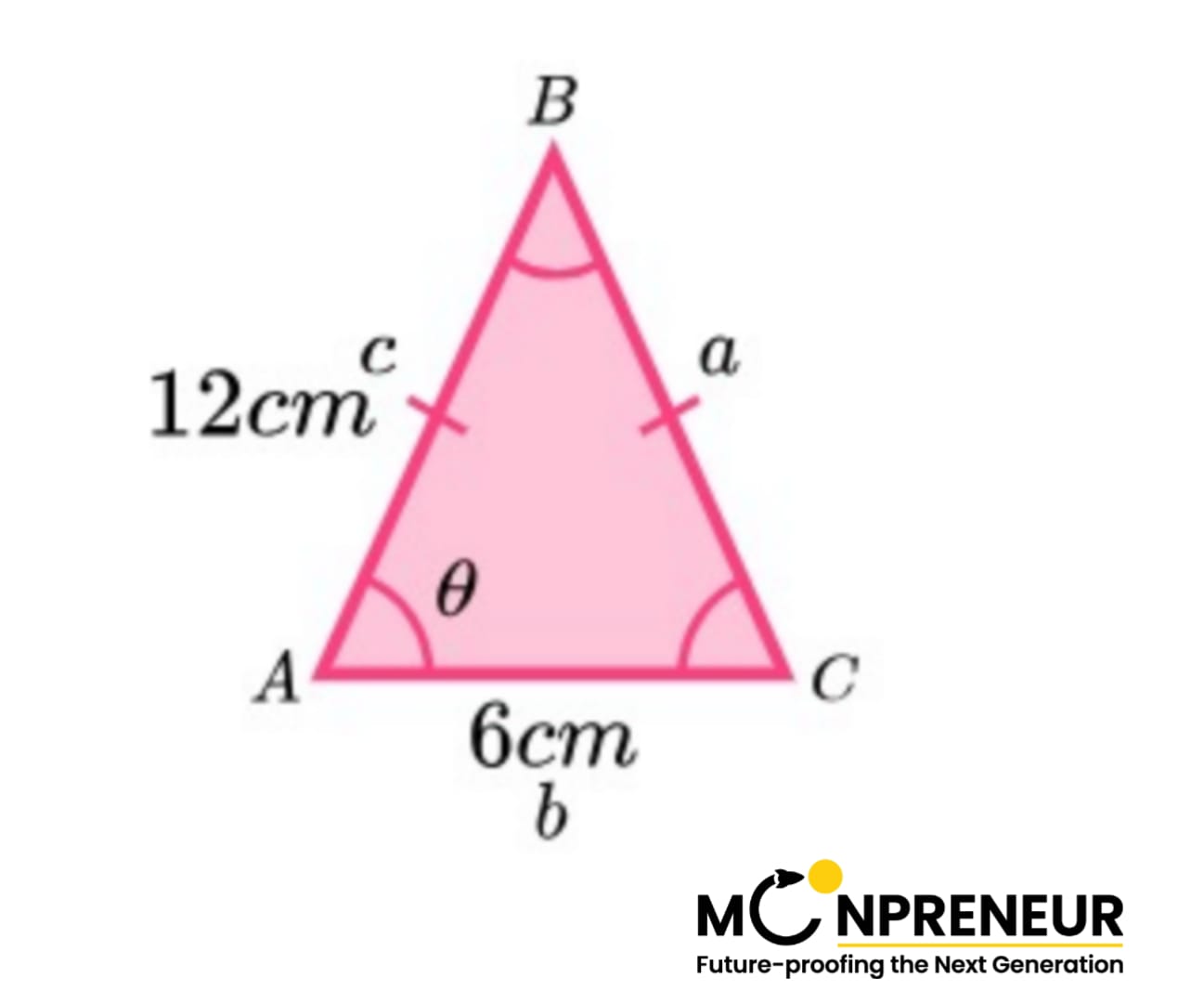
Example: Find angle Θ.
1. Label each angle (A, B, C) and each side (a, b, c) of the triangle.
Here, the vertices are already labelled, and the angle we need to find is already A, so we just need to fill in the opposing sides with a, b, and c.
2. State the cosine rule, then substitute the given values into the formula.
Here, we need to find the missing angle A, we need to state the cosine rule with cos(A) as the subject:
\(\displaystyle \cos(A) = \frac{b^{2} + c^{2} – a^{2}}{2bc}\)\(\displaystyle \cos(\theta) = \frac{6^{2} + 12^{2} – 12^{2}}{2 \times 6 \times 12}\)
3. Solve the equation:
- \(\displaystyle \cos(\theta) = \frac{36 + 144 – 144}{144}\)
- \(\displaystyle \cos(\theta) = \frac{36}{144}\)
- cos(Θ) = 0.25
- Θ = cos⁻¹ (0.25)
- Θ = 76º
For a more detailed walkthrough, you can watch this video:
Why This Matters for SAT Students
The SAT often tests your ability to choose the most efficient path to an answer. Instead of getting stuck trying to force a non-right triangle into a right-triangle method (like SOH CAH TOA), the Cosine Formula gives you a direct path to the result. This saves you precious seconds—and on the SAT, every second counts.
Recommended Reading:
- How to Derive and Use the Quadratic Formula (With Examples)
Application & Proof of the Sherman-Morrison-Woodbury Identity
- Linear Equation – One Solution, No Solution, and Many Solutions
- Solving Exponential Equations Using Recursion: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Condition of Tangency for a Parabola: Formula and Derivation
- How to Prove the Law of Sines: Easy Guide with Diagrams
Want to excite your child about math and sharpen their math skills? Moonpreneur’s online math curriculum is unique as it helps children understand math skills through hands-on lessons, assists them in building real-life applications, and excites them to learn math.
You can opt for our Advanced Math or Vedic Math+Mental Math courses. Our Math Quiz for grades 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 6th helps in further exciting and engaging in mathematics with hands-on lessons.