Today, we are going to solve a classic geometry problem that even the Gemini of ChatGPT sometimes fails. The trick to solve it is easy, but needs a little bit of attention. Lets look at the Problem.
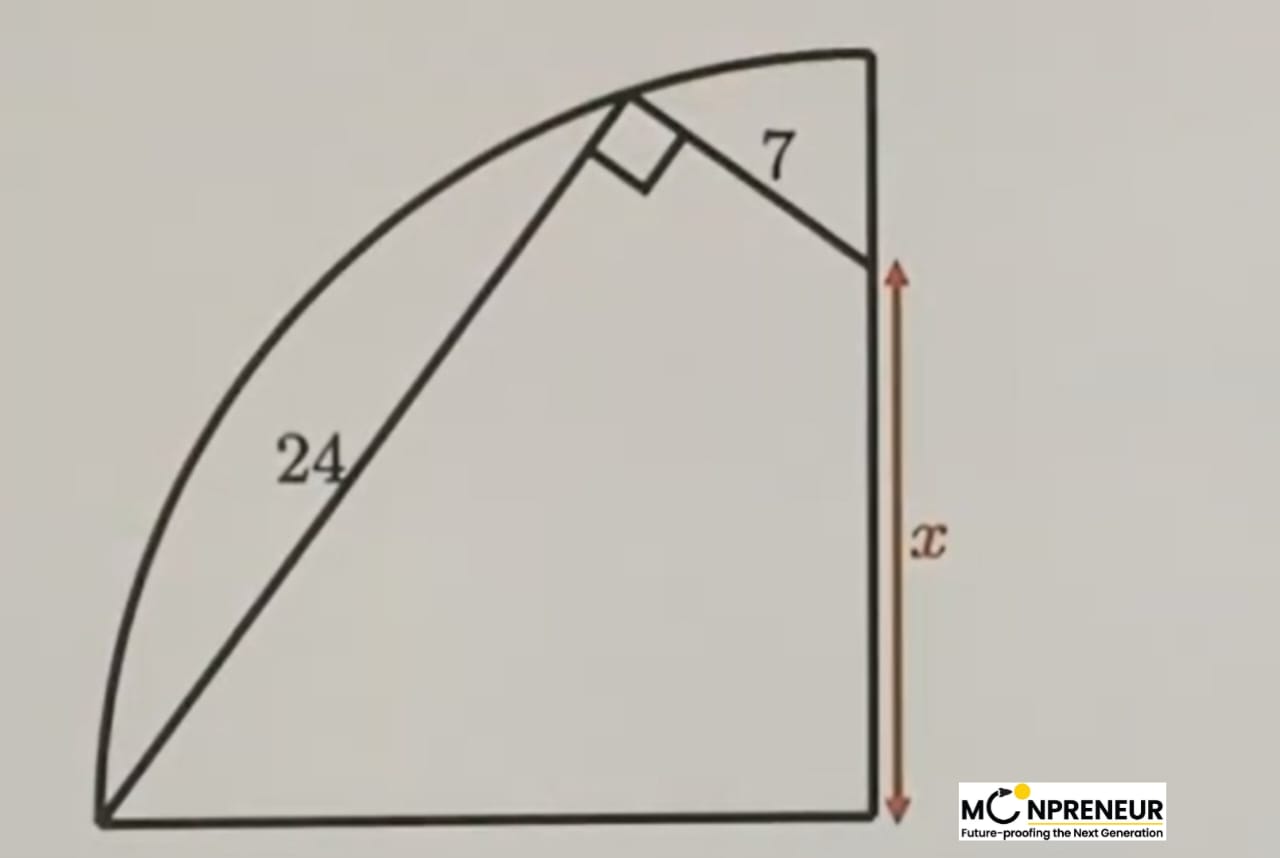
Find the value of x
Step 1: Find the Missing Link
We start with a right-angled triangle with sides of 24 and 7. Your first instinct should always be the Pythagorean theorem!
By calculating \(\displaystyle \sqrt{24^{2} + 7^{2}}\) we get, \(\displaystyle \sqrt{576 + 49}\) which equals \(\displaystyle \sqrt{625}\).
So, our first unknown line is 25.
Recommended Reading: An overview of the SAT Math Test Sections
Step 2: Think Outside the (Semi) Circle
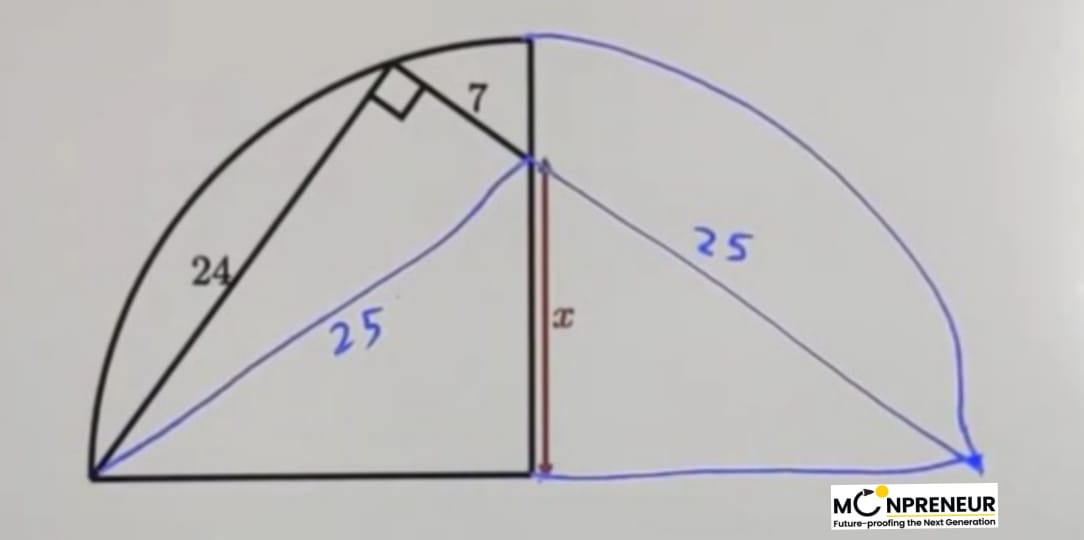
Here is where the “magic” happens. To find x, the trick is to extend the semicircle into a full circle. By doing this and connecting the lines, we create similar triangles that reveal a much larger right-angled triangle.
Recommended eading The Ultimate Guide to Solving SAT Quadratics in Seconds
Step 3: The SAT “Pro-Tip” (The 3-4-5 Trick)
In this new, larger triangle, the height is still 24, but the base is now 7+25, giving us 32. Now, you could spend time squaring 32, or you could use a shortcut. Notice that 24 and 32 are both multiples of 8:
- 8×3=24
- 8×4=32
This is just a massive 3-4-5 triangle! Therefore, the hypotenuse is 8×5, which is 40. Since this 40 represents the diameter of our circle, the radius is 20.
Step 4: The Final Stretch
We are almost there! We now have a final right-angled triangle where the hypotenuse is 25 and one side (the radius) is 20. To find x, we calculate:
\(\displaystyle \sqrt{25^{2} – 20^{2}} = \sqrt{625 – 400} = \sqrt{225}\)The square root of 225 is 15, which is our final answer.
Therefore, the value of x is 15.
Recommended Reading: How to Derive and Use the Quadratic Formula (With Examples)
Let us take another example:
A right triangle with sides 9 and 12. Find x.
Step 1. Find the Hypotenuse: \(\displaystyle \sqrt{9^{2} + 12^{2}} = 15\)
Step 2. Extend the Circle: New base = 9+15=24
Step 3. Find the Diameter: \(\displaystyle \sqrt{12^{2} + 24^{2}} = \sqrt{720}\)
Step 4. Find the Radius: \(\displaystyle \sqrt{\frac{720}{2}} = \sqrt{180}\)
Step 5. Solve for X: \(\displaystyle \sqrt{15^{2} – 180} = \sqrt{225 – 180} = \sqrt{45} = 3\sqrt{5}\)
For a more detailed walkthrough, you can watch this video:
The beauty of these geometry problems is that the figure itself is often enough to explain the solution without needing complex descriptions. While modern AI still struggles to interpret the visual “graph” of such diagrams, your human intuition allows you to spot clever shortcuts like the 3-4-5 triangle ratio. By extending the semicircle and applying the logic of similar triangles, you can confidently arrive at the final answer of 15.
Want to excite your child about math and sharpen their math skills? Moonpreneur’s online math curriculum is unique as it helps children understand math skills through hands-on lessons, assists them in building real-life applications, and excites them to learn math.
You can opt for our Advanced Math or Vedic Math+Mental Math courses. Our Math Quiz for grades 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 6th helps in further exciting and engaging in mathematics with hands-on lessons.