Introduction
In mathematics, interval notation is a systematic way to represent a set of real numbers on a number line. Instead of writing long sets, interval notation provides a compact format that clearly shows whether endpoints are included or excluded. This method is commonly used in algebra, inequalities, and calculus. For example, the set of numbers where \(0 \leq x \leq 5\) can be written as [0, 5], which includes 0, 5, and all values in between.
What is Interval Notation?
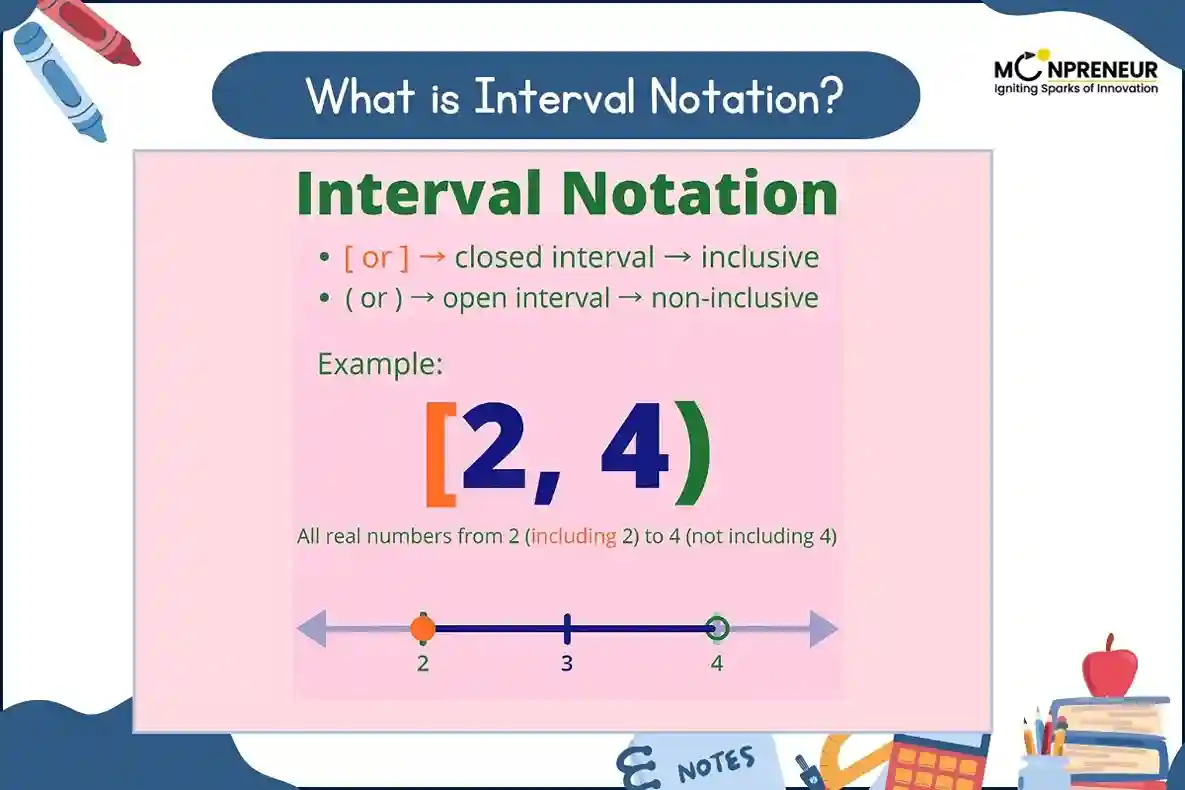
Interval notation expresses a subset of real numbers using two boundary points. These boundaries may or may not be included, depending on the type of interval. It is often used as a quick way to write inequalities.
For example:
– Inequality 1 < x < 5 → Interval notation: (1, 5)
– Inequality x ≥ 2 → Interval notation: [2, ∞)
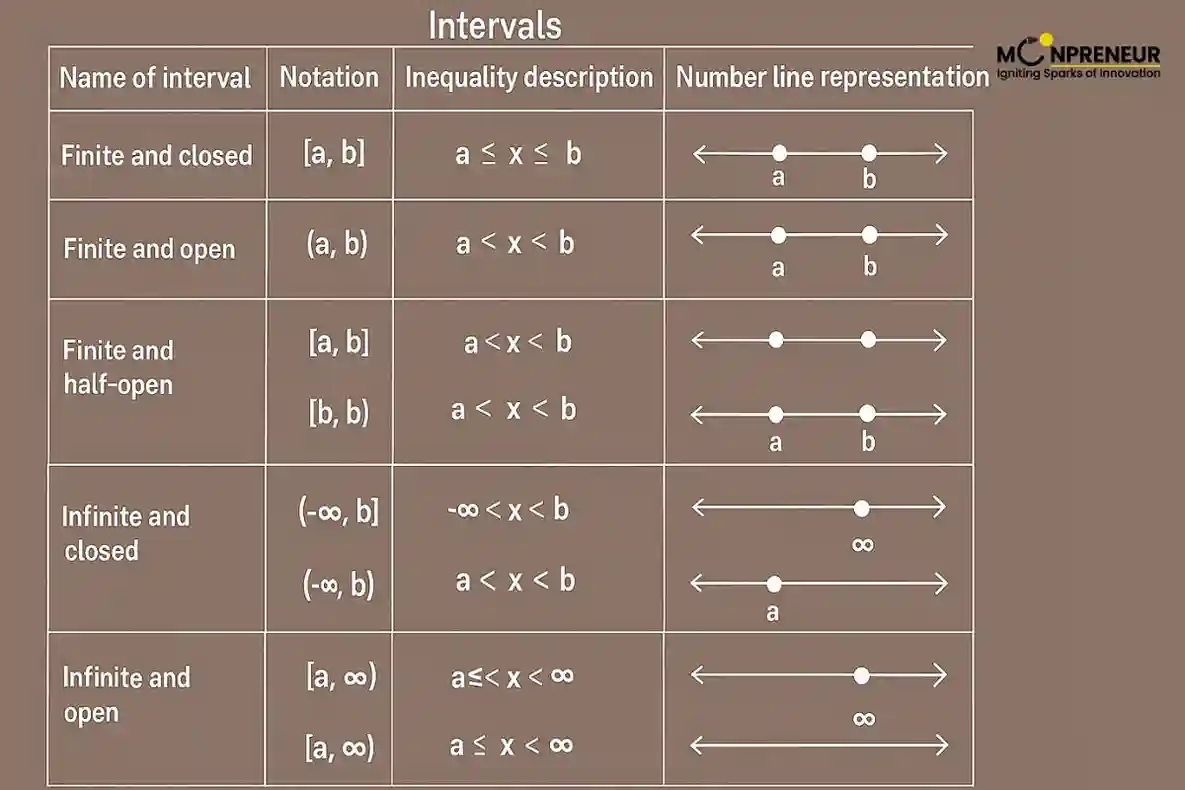
Types of Intervals in Interval Notation
Intervals are classified based on whether their endpoints are included – Expand each type below to learn more:
– Represents numbers strictly between a and b.
– Endpoints are not included.
– Example: x ∈ (−3, 1) → numbers greater than −3 but less than 1.
– Includes all numbers between a and b, including endpoints.
– Example: x ∈ [−3, 1] → includes −3, 1, and everything between.
– One endpoint is included, the other is not.
– Example: x ∈ [−3, 1) → includes −3 but excludes 1.
– Extend infinitely in one direction.
– Example: x > 0 → written as (0, ∞).
Interval Notation Symbols
– [ ] Square brackets → Endpoint included.
– ( ) Parentheses → Endpoint excluded.
– ( ] or [ ) Mixed brackets → Only one endpoint included.
– ∞ or −∞ → Represents unbounded intervals (always written with parentheses).
Converting Inequalities to Interval Notation
Follow these steps:
1. Plot the solution on a number line.
2. Write the left and right boundaries.
3. Use brackets [ ] for ‘≤’ or ‘≥’, and parentheses ( ) for ‘<‘ or ‘>’.
4. Use ∞ or −∞ if the range extends indefinitely.
Examples:
x ≤ 3 → Interval: (−∞, 3]
x > 2 → Interval: (2, ∞)
−5 < x ≤ 3 → Interval: (−5, 3]
Bounded vs. Unbounded Intervals
– Bounded Intervals: Both endpoints are real numbers (e.g., [0, 10]).
– Unbounded Intervals: At least one side extends to infinity (e.g., (−∞, 5)).
Examples of Interval Notation
1. x ≥ 0 → Interval: [0, ∞)
2. −4 < x < 7 → Interval: (−4, 7)
3. All real numbers → Interval: (−∞, ∞)
Applications of Interval Notation
– Algebra: Writing solution sets of inequalities.
– Calculus: Representing domains and ranges of functions.
– Statistics: Defining confidence intervals and probability ranges.
– Real-Life Use: Expressing measurement limits or constraints.
Conclusion
Interval notation is a precise and efficient way to represent sets of real numbers. By using brackets and parentheses, we can indicate whether endpoints are included or excluded. With applications in inequalities, calculus, and real-world problem-solving, mastering interval notation is essential for students and professionals in mathematics.
Want to spark your child’s interest in math and boost their skills? Moonpreneur’s online math curriculum stands out because it engages kids with hands-on lessons, helps them apply math in real-life situations, and makes learning math exciting!
You can opt for our Advanced Math or Vedic Math+Mental Math courses. Our Math Quiz for grades 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 6th helps in further exciting and engaging in mathematics with hands-on lessons.
FAQs
Ans: It represents all numbers between a and b, excluding both endpoints.
Ans: Infinity is not a specific number, so it cannot be included.
Ans: [a, b] includes both endpoints, while (a, b) excludes them.
Related Blogs:
How to Teach Adjacent Angles to Kids | Simple & Fun Guide
What are Congruent Angles?
Understanding Alternate Interior Angles
What is the Area of Trapezoid?
What is the Area of Parallelogram?
Understanding the Geometry Regents: A Comprehensive Guide
How to Prepare for the Geometry Regents: Study Plans & Practice
The Art of Geometry: How to Draw an Equilateral Triangle Inside a Circle












