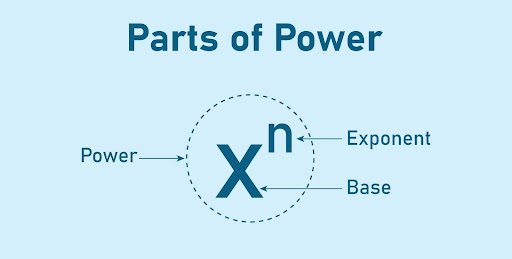
Rules of exponents, or laws of exponents, are basic mathematical rules that are applied to simplify expressions with exponents. The rules play a significant role in carrying out arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division more effectively when powers are taken. They also assist in working with complex numbers involving fractions, decimals, and roots.
We will discuss various exponent rules and their uses in this guide.
Recommended Reading: Enhancing Mathematical Thinking: Conceptual Understanding & Habits of Mind
What are Exponent Rules?
Exponent rules or the ‘laws of exponents’ are mathematical principles applied to make calculations with powers easier. They are useful in simplifying expressions with decimal, fractional, irrational, or negative numbers as exponents.
For example, if you need to solve 3^4 × 3^2, you can apply the exponent rule a^m × a^n = a^(m+n). This simplifies the expression to 3^(4+2) = 3^6. Similarly, using exponent rules reduces complex calculations to simple steps.
Recommended Reading: SAT Device Requirements and Device Lending
List of Exponent Rules:
Following are the general exponent rules used in mathematics widely:
- Zero Exponent Rule: Any non-zero base raised to the power of zero is always 1.
- Formula: a^0 = 1
- Identity Exponent Rule: Any base raised to the power of one is the base itself.
- Formula: a^1 = a
- Product Rule: When multiplying two powers with the same base, add the exponents.
- Formula: a^m × a^n = a^(m+n)
- Quotient Rule: When dividing two powers with the same base, subtract the exponents.
- Formula: a^m ÷ a^n = a^(m-n)
- Negative Exponent Rule: A negative exponent indicates the reciprocal of the base raised to the positive exponent.
- Formula: a^-m = 1/a^m
- Power of a Power Rule: When raising a power to another power, multiply the exponents.
- Formula: (a^m)^n = a^(m×n)
- Power of a Product Rule: When raising a product to a power, distribute the exponent to each base.
- Formula: (ab)^m = a^m × b^m
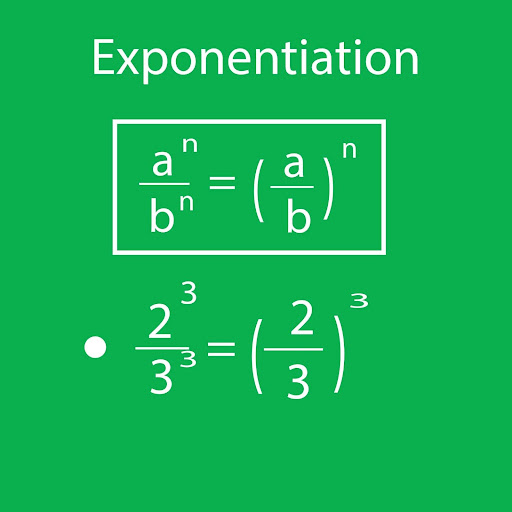
- Power of a Quotient Rule: When raising a quotient to a power, distribute the exponent to both the numerator and denominator.
- Formula: (a/b)^m = a^m/b^m
- Fractional Exponents Rule: Fractional exponents represent roots of numbers.
- Formula: a^(1/n) = √[n]{a}
- Radical Exponent Rule: Fractional exponents can also represent higher roots.
Formula: a^(m/n) = √[n]{a^m}
Conclusion
Exponent rules simplify calculations involving powers, making it easier to solve mathematical expressions with large exponents. By understanding and applying these rules, students can approach algebra, geometry, and other advanced mathematical concepts with confidence. Keep practicing these laws, and soon working with exponents will become second nature!
Want to excite your child about math and sharpen their math skills? Moonpreneur’s online math curriculum is unique as it helps children understand math skills through hands-on lessons, assists them in building real-life applications, and excites them to learn math. You can opt for our Advanced Math or Vedic Math+Mental Math courses. Our Math Quiz for grades 3rd, 4th, 5th, and 6th helps in further exciting and engaging in mathematics with hands-on lessons.
















